|
DSM5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). In the United States, the DSM serves as the principal authority for psychiatric diagnoses. Treatment recommendations, as well as payment by health care providers, are often determined by DSM classifications, so the appearance of a new version has practical importance. The DSM-5 is the only DSM to use an Arabic numeral instead of a Roman numeral in its title, as well as the only living document version of a DSM. The DSM-5 is not a major revision of the DSM-IV-TR but there are significant differences. Changes in the DSM-5 include the reconceptualization of Asperger syndrome from a distinct disorder to an autism spectrum disorder; the elimination of subtypes of schizophrenia; the deletion of the "bereavement exclusion" f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender Dysphoria
Gender dysphoria (GD) is the distress a person experiences due to a mismatch between their gender identitytheir personal sense of their own genderand their sex assigned at birth. The diagnostic label gender identity disorder (GID) was used until 2013 with the release of the diagnostic manual DSM-5. The condition was renamed to remove the stigma associated with the term ''disorder''. People with gender dysphoria commonly identify as transgender. Gender nonconformity is not the same thing as gender dysphoria and does not always lead to dysphoria or distress. The causes of gender incongruence are unknown but a gender identity likely reflects genetic, biological, environmental, and cultural factors. Treatment for gender dysphoria may include supporting the individual's gender expression or their desire for hormone therapy or surgery. Treatment may also include counseling or psychotherapy. Some researchers and transgender people support declassification of the condition because t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
A pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (Including atypical autism) (PDD-NOS) is one of four disorders which were collapsed into the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5 and also was one of the five disorders classified as a pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) in the DSM-IV. According to the DSM-4, PDD-NOS is a diagnosis that is used for "severe or pervasive impairment in the development of reciprocal social interaction and/or verbal and nonverbal communication skills, or when stereotyped behavior, interests, and/or activities are present, but the criteria are not met for a specific PDD" or for several other disorders. PDD-NOS includes atypical autism, because the criteria for autistic disorder are not met, for instance because of late age of onset, atypical symptomatology, or subthreshold symptomatology, or all of these. Even though PDD-NOS is considered milder than typical autism, this is not always true. While some characteristics may be mild ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphilia
Paraphilia (previously known as sexual perversion and sexual deviation) is the experience of intense sexual arousal to atypical objects, situations, fantasies, behaviors, or individuals. It has also been defined as sexual interest in anything other than a consenting human partner. There is no scientific consensus for any precise border between unusual sexual interests and paraphilic ones. There is debate over which, if any, of the paraphilias should be listed in diagnostic manuals, such as the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). The number and taxonomy of paraphilia is under debate; one source lists as many as 549 types of paraphilia. The DSM-5 has specific listings for eight paraphilic disorders. Several sub-classifications of the paraphilias have been proposed, and some argue that a fully dimensional, spectrum or complaint-oriented approach would better reflect the evidence. Terminology Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder (BED) is an eating disorder characterized by frequent and recurrent binge eating episodes with associated negative psychological and social problems, but without the compensatory behaviors common to bulimia nervosa, OSFED, or the binge-purge subtype of anorexia nervosa. BED is a recently described condition, which was required to distinguish binge eating similar to that seen in bulimia nervosa but without characteristic purging. Individuals who are diagnosed with bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorder exhibit similar patterns of compulsive overeating, neurobiological features of dysfunctional cognitive control and food addiction, and biological and environmental risk factors. Some professionals consider BED to be a milder form of bulimia with the two conditions on the same spectrum. Binge eating is one of the most prevalent eating disorders among adults, though there tends to be less media coverage and research about the disorder in comparison to anorexia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
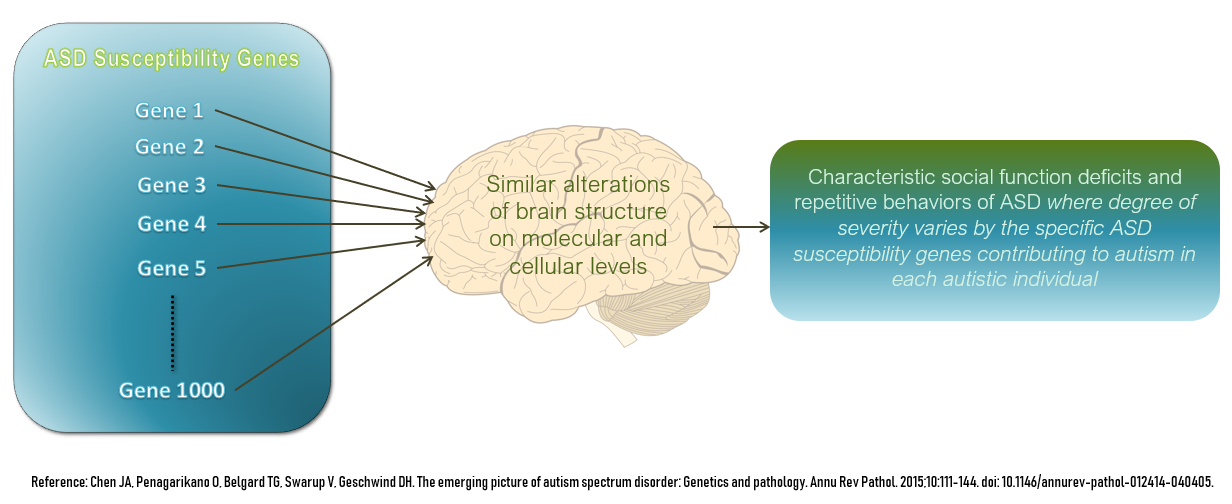
Autism Spectrum
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism Spectrum Disorder
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder, neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in Social relation, social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to Multisensory integration, sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonverbal autism, nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social (pragmatic) Communication Disorder
Social (pragmatic) communication disorder (SPCD) - previously called semantic-pragmatic disorder (SPD) or pragmatic language impairment (PLI) - is a disorder in understanding pragmatic aspects of language. People with SPCD have special challenges with the semantic aspect of language (the meaning of what is being said) and the pragmatics of language (using language appropriately in social situations). Individuals have difficulties with verbal and nonverbal social communication. Relates to Pragmatic Language Impairment and Autism Spectrum Disorder. It has only been since 2013 that SPCD has become its own category in the DSM-5. In creating this new category it allowed individuals to be considered with a form of communication disorder ''distinct'' from PLI and ASD. As well, SPCD lacks behaviors associated with restrictions and repetition which are seen in ASD. Presentation # Issues with communication for social purposes # Unable to adapt communication to context # Struggles to follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttering
Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder in which the flow of speech is disrupted by involuntary repetitions and prolongations of sounds, syllables, words, or phrases as well as involuntary silent pauses or blocks in which the person who stutters is unable to produce sounds. The term ''stuttering'' is most commonly associated with involuntary sound repetition, but it also encompasses the abnormal hesitation or pausing before speech, referred to by people who stutter as ''blocks'', and the prolongation of certain sounds, usually vowels or semivowels. According to Watkins et al., stuttering is a disorder of "selection, initiation, and execution of motor sequences necessary for fluent speech production". arlson, N. (2013). Human Communication. In Physiology of behavior (11th ed., pp. 497–500). Boston: Allyn and Bacon./ref> For many people who stutter, repetition is the main concern. The term "stuttering" covers a wide range of severity, from barely perceptible imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonological Disorder
Speech disorders or speech impairments are a type of communication disorder in which normal speech is disrupted. This can mean stuttering, lisps, etc. Someone who is unable to speak due to a speech disorder is considered mute. Speech skills are vital to social relationships and learning, and delays or disorders that relate to developing these skills can impact individuals function. For many children and adolescents, this can present as issues with academics. Speech disorders affect roughly 11.5% of the US population, and 5% of the primary school population. Speech is a complex process that requires precise timing, nerve and muscle control, and as a result is susceptible to impairments. A person who has a stroke, an accident or birth defect may have speech and language problems. Classification Classifying speech into normal and disordered is more problematic than it first seems. By strict classification, only 5% to 10% of the population has a completely normal manner of spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Sound Disorder
A speech sound disorder (SSD) is a speech disorder in which some sounds (phonemes) are not produced or used correctly. The term "protracted phonological development" is sometimes preferred when describing children's speech, to emphasize the continuing development while acknowledging the delay. Classification Speech sound disorders may be subdivided into two primary types, articulation disorders (also called phonetic disorders) and phonemic disorders (also called phonological disorders). However, some may have a mixed disorder in which both articulation and phonological problems exist. Though speech sound disorders are associated with childhood, some ''residual'' errors may persist into adulthood. Articulation disorders Articulation disorders (also called phonetic disorders, or simply "artic disorders" for short) are based on difficulty learning to physically produce the intended phonemes. Articulation disorders have to do with the main articulators which are the lips, teeth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ under 70, in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living. Intellectual functions are defined under DSM-V as reasoning, problem‑solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning from instruction and experience, and practical understanding confirmed by both clinical assessment and standardized tests. Adaptive behavior is defined in terms of conceptual, social, and practical skills involving tasks performed by people in their everyday lives. Intellectual disability is subdivided into syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits associated with other medical and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)