|
DR Class 99.23-24
The engines of DR Class 99.23 are metre gauge tank locomotives, that were procured by the Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR) in East Germany from 1954 to 1956. When they entered service they had operating numbers 99 231–99 247. Today they are numbered 99 7231–99 7247. History A total of 17 locomotives were bought by the DR between 1954 and 1956 for the railways of the Harzquerbahn and Brockenbahn, and for the line from Eisfeld to Schönbrunn to replace much of the outdated fleet. Four locomotives were built for the USSR in 1956, but their ultimate fate is unknown. The first seven units (99 231 to 99 237) were originally equipped with two Krauss-Helmholtz bogies. Due to problems with curve running, the engines in the second series were given Beugniot levers between the first and second coupled axles in addition to the Krauss-Helmholtz bogies (according to other sources also a Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt II bogieEK-Themen 18, Brockenlok 99.22, Eisenbahn-K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
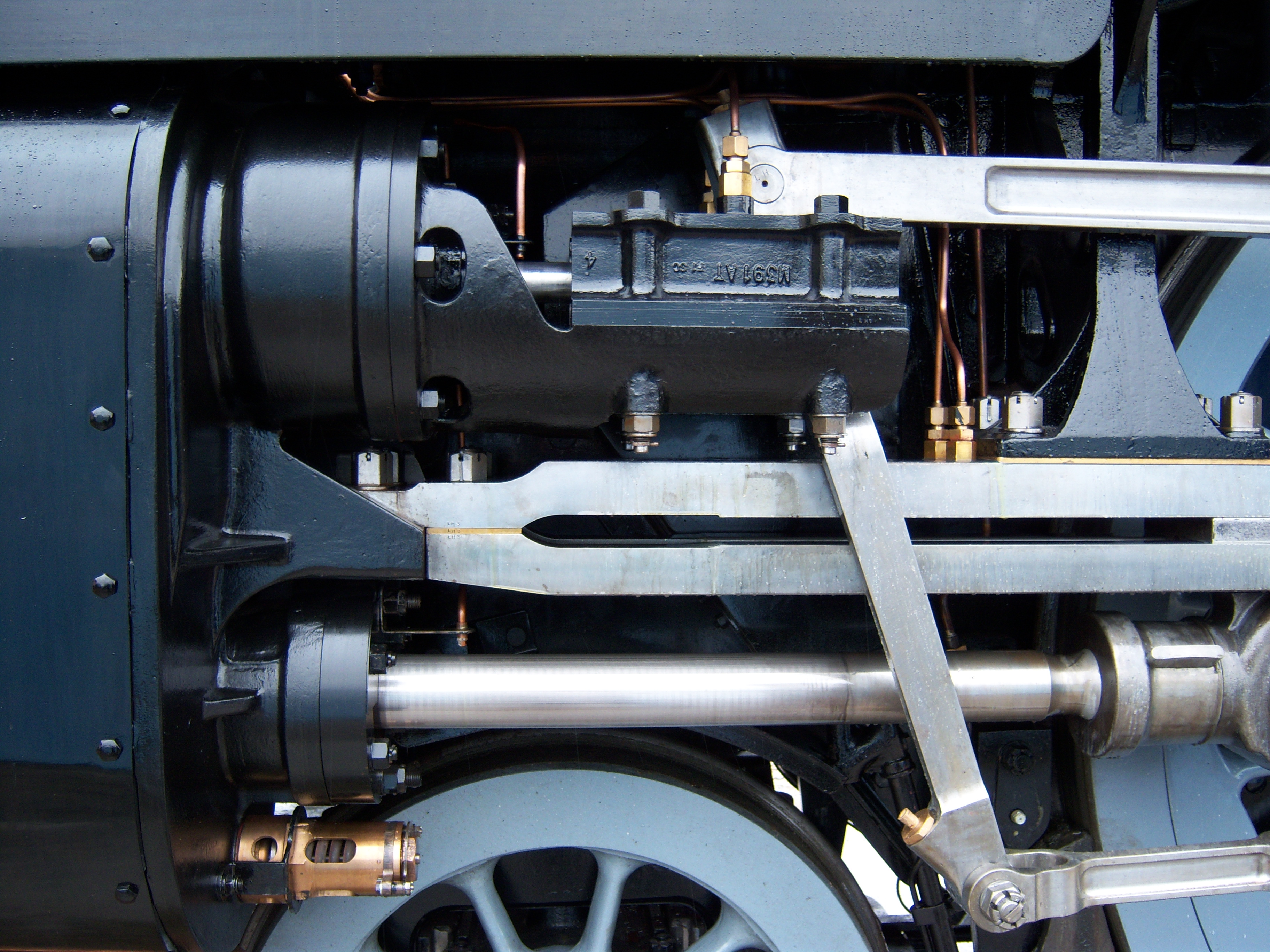
Heusinger Valve Gear
The Walschaerts valve gear is a type of valve gear used to regulate the flow of steam to the pistons in steam locomotives, invented by Belgian railway engineer Egide Walschaerts in 1844. The gear is sometimes named without the final "s", since it was incorrectly patented under that name. It was extensively used in steam locomotives from the late 19th century until the end of the steam era. History The Walschaerts valve gear was slow to gain popularity. The Stephenson valve gear remained the most commonly used valve gear on 19th-century locomotives. However, the Walschaerts valve gear had the advantage that it could be mounted entirely on the outside of the locomotives, leaving the space between the frames clear and allowing easy access for service and adjustment, which resulted in it being adopted in some articulated locomotives. The first locomotive fitted with the Walschaerts valve gear was built at the Belgian Tubize workshops, and was awarded a gold medal at the 1873 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt II Bogie
A Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt II bogie (Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt-II-Lenkgestell or Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt-Gestell) is a mechanical device to improve the curve running of steam locomotives. The Schwartzkopff-Eckhardt II bogie is a further refinement of the Krauss-Helmholtz bogie, whereby two coupled axles and the carrying axle are combined within the bogie. The carrying axle steers the second coupled axle via a long shaft and this also moves the first coupled axle via a Beugniot lever. This bogie is used on the DRG Class 84. Whether DR Class 99.23-24 locomotives were also fitted with this arrangement is not entirely clear. It was named after the L. Schwartzkopff locomotive factory and its chief engineer, Friedrich Wilhelm Eckhardt. See also * DRG Class 84 * DR Class 99.23-24 References *Friedrich Wilhelm Eckhardt: ''Das Fahrgestell der Dampflokomotiven'', Transpress, Berlin 1960 *Friedrich Wilhelm Eckhardt: ''Lokomotivkunde. H. 5. Das Fahrgestell der Dampflokomotiven'', Fachbuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of East German Deutsche Reichsbahn Locomotives And Railbuses
This article contains a list of locomotives and railbuses of the Deutsche Reichsbahn (East Germany) (DR) according to the numbering system introduced by the DR on 1 July 1970. Following the October 1990 reunification of Germany, the DR's locomotives and railbuses were incorporated (and renumbered) on 1 January 1992 into the classification system of the West German ''Deutsche Bundesbahn'' (DB), originally issued on 1 January 1968, in preparation for the merger of the two German national railways that took place on 1 January 1994. This renumbering was also described as the 'locomotive classification of the Deutsche Bahn' as a number of changes and additions to the DB's 1968 system were needed. Classification before 1970: see also DRG classification system. Steam locomotives In the DR numbering plan the following additional practices were common: *xx.6xxx locomotives, that originated from former private railways. From 1970 the following sub-classes for all steam locomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR Locomotive Classification
The DR locomotive classification scheme in East Germany in the initial post-war period used the DRG system, consisting of a class number (''Baureihennummer'') followed by a serial number (''Ordnungsnummer''). With the introduction of computerised ( EDP) numbers in 1970 as part of the UIC framework, the system was fundamentally changed for the first time. In the allocation of operating numbers up to 1970 the Deutsche Bundesbahn and the Deutsche Reichsbahn in East Germany took care, for the most part, to ensure that they did not overlap with one another. To 1970 Steam locomotives On 1 January 1950 almost all the public railways that did not belong to the Reichsbahn were nationalised. In order integrate the many, different locomotives into the existing numbering system, it was essential to adopt the renumbering plan of 12 December 1949 that built on the previous system. The locomotives were grouped together into classes of the same or similar design. Locomotives were given the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harzer Schmalspurbahnen
The Harz Narrow Gauge Railways (German: ''Harzer Schmalspurbahnen'' or HSB) is a railway company that operates a network in the Harz mountains, in central Germany (formerly East Germany). The company was formed after the Second World War as a merger of two earlier companies. It owns about 140 kilometres (86 miles) of track, connecting the principal towns of Wernigerode, Nordhausen and Quedlinburg and several smaller settlements in the area. Much of the network is steeply graded and picturesque, but its most popular destination is the Brocken, the highest mountain in the region. The company runs a significant number of its trains with steam haulage, mostly employing 1950s vintage 2-10-2 tank locomotives, hauling traditional open-platform bogie carriages. The company is mainly owned by the various local authorities whose territories it serves. Forerunners The present-day narrow gauge operator emerged as a result of the merger of two different railway companies that operated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wernigerode
Wernigerode () is a town in the district of Harz, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until 2007, it was the capital of the district of Wernigerode. Its population was 35,041 in 2012. Wernigerode is located southwest of Halberstadt, and is picturesquely situated on the Holtemme river, on the northern slopes of the Harz Mountains. Wernigerode is located on the German Timber-Frame Road. Geography Location The town lies at about 250 metres above sea level (NN) on the northeastern flank of the Harz Mountains in central Germany, at the foot of their highest peak, the Brocken, on the B 6 and B 244 federal highways and on the railway line from Halberstadt to Vienenburg that links the cities of Halle (Saale) and Hanover. The River Holtemme flows through the town and, not far from its western gate, it is joined by the Zillierbach stream, which is also known as the Flutrenne near its mouth. North of the town the Barrenbach flows through several ponds and empties into the Holtemme in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brocken
The Brocken, also sometimes referred to as the Blocksberg, is the highest peak in the Harz mountain range and also the highest peak in Northern Germany; it is near Schierke in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt between the rivers Weser and Elbe. Although its elevation of is below alpine dimensions, its microclimate resembles that of mountains of about . The peak above the tree line tends to have a snow cover from September to May, and mists and fogs shroud it up to 300 days of the year. The mean annual temperature is only . It is the easternmost mountain in northern Germany; travelling east in a straight line, the next prominent elevation would be in the Ural Mountains in Russia. The Brocken has always played a role in legends and has been connected with witches and devils; Johann Wolfgang von Goethe took up the legends in his play ''Faust''. The Brocken spectre is a common phenomenon on this misty mountain, where a climber's shadow cast upon fog creates eerie optical effects. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in iron and later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of the early Rocket locomotive) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope with. This assessment was known as "e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Frame
Plate may refer to: Cooking * Plate (dishware), a broad, mainly flat vessel commonly used to serve food * Plates, tableware, dishes or dishware used for setting a table, serving food and dining * Plate, the content of such a plate (for example: rice plate) * Plate, to present food, on a plate * Plate, a forequarter cut of beef Places * Plate, Germany, a municipality in Parchim, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany * River Plate (other) * Tourelle de la Plate, a lighthouse in France Science and technology Biology and medicine * Plate (anatomy), several meanings * Dental plate, also known as dentures * Dynamic compression plate, a metallic plate used in orthopedics to fix bone * Microtiter plate (or microplate or microwell plate), a flat plate with multiple "wells" used as small test tubes * Petri dish or Petri plate, a shallow dish on which biological cultures may be grown and/or viewed Geology * Tectonic plate, are pieces of Earth's crust and uppermost mantle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preheater
An air preheater is any device designed to heat air before another process (for example, combustion in a boiler With the primary objective of increasing the thermal efficiency of the process. They may be used alone or to replace a recuperative heat system or to replace a steam coil. In particular, this article describes the combustion air preheaters used in large boilers found in thermal power stations producing electric power from e.g. fossil fuels, biomass or waste. (See Chapter 8 by Z.H. Lin) For instance, as the Ljungström air preheater has been attributed worldwide fuel savings estimated to 4,960,000,000 tons of oil, "few inventions have been as successful in saving fuel as the Ljungström Air Preheater", marked as the 44th International Historic Mechanical Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The purpose of the air preheater is to recover the heat from the boiler flue gas which increases the thermal efficiency of the boiler by reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 99
Class 99 is the classification of German narrow gauge locomotives used by the Deutsche Reichsbahn or her successor administrations. It is therefore divided into numerous sub-classes that are listed in this table. Bibliography * Weisbrod, Manfred, Hans Müller and Wolfgang Petznik (1995). ''Dampflokomotiven deutscher Eisenbahnen. Band 4: Baureihe 99''. Berlin: Transpress. See also {{Commons category, DRG Class 99 * Deutsche Reichsbahn * Deutsche Bundesbahn * Deutsche Reichsbahn (GDR) * List of DRG locomotives and railcars * Einheitsdampflokomotive The Einheitsdampflokomotiven ("standard steam locomotives"), sometimes shortened to ''Einheitslokomotiven'' or ''Einheitsloks'', were the standardized steam locomotives built in Germany after 1925 under the direction of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gese ... Narrow gauge locomotives 99 99 99 99 German railway-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einheitsloks
The Einheitsdampflokomotiven ("standard steam locomotives"), sometimes shortened to ''Einheitslokomotiven'' or ''Einheitsloks'', were the standardized steam locomotives built in Germany after 1925 under the direction of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft. Their manufacture made extensive use of standard design features and components. 300px, Einheitslok of the DRG_Class_01.html" ;"title="Historic Railway, Frankfurt DRG Class 01">Historic Railway, Frankfurt DRG Class 01 in 2007 Development Following the merger of the state railways (''Länderbahnen'') in Germany into the Reich railway in 1920 and into the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft in 1924, the locomotive fleet of the new national railway administration still had 210 different types and classes of steam engine. This considerably hindered the flexible employment of locomotives within the railway network, and servicing and maintenance was very costly as a result of the large number of different spare parts that had to be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |