|
DPEphos
Bis[(2-diphenylphosphino)phenyl] ether, also known as DPEphos, is a wide bite angle diphosphines, diphosphine ligand used in Inorganic chemistry, inorganic and organometallic chemistry. The name DPEphos is derived from diphenyl ether (DPE) which makes up the ligand's backbone. It is similar to Xantphos, another diphosphine ligand, but is more flexible and has a smaller bite angle (104 vs 108°). It is synthesized from chlorodiphenylphosphine and DPE. References {{reflist Diphosphines Phenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bite Angle
In coordination chemistry the bite angle is the ligand–metal–ligand bond angle of coordination complex containing a bidentate ligand. This geometric parameter is used to classify chelation, chelating ligands, including those in organometallic complexes. It is most often discussed in terms of catalysis, as changes in bite angle can affect not just the activity and selectivity of a catalytic reaction but even allow alternative reaction pathways to become accessible. Although the parameter can be applied generally to any chelating ligand, it is commonly applied to describe diphosphine ligands, as they can adopt a wide range of bite angles. Diamines Diamines form a wide range of coordination complexes. They typically form 5- and 6-membered chelate rings. Examples of the former include ethylenediamine and 2,2'-bipyridine, 2,2′-bipyridine. Six-membered chelate rings are formed by 1,3-diaminopropane. The bite angle in such complexes is usually near 90°. Longer chain diamines, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
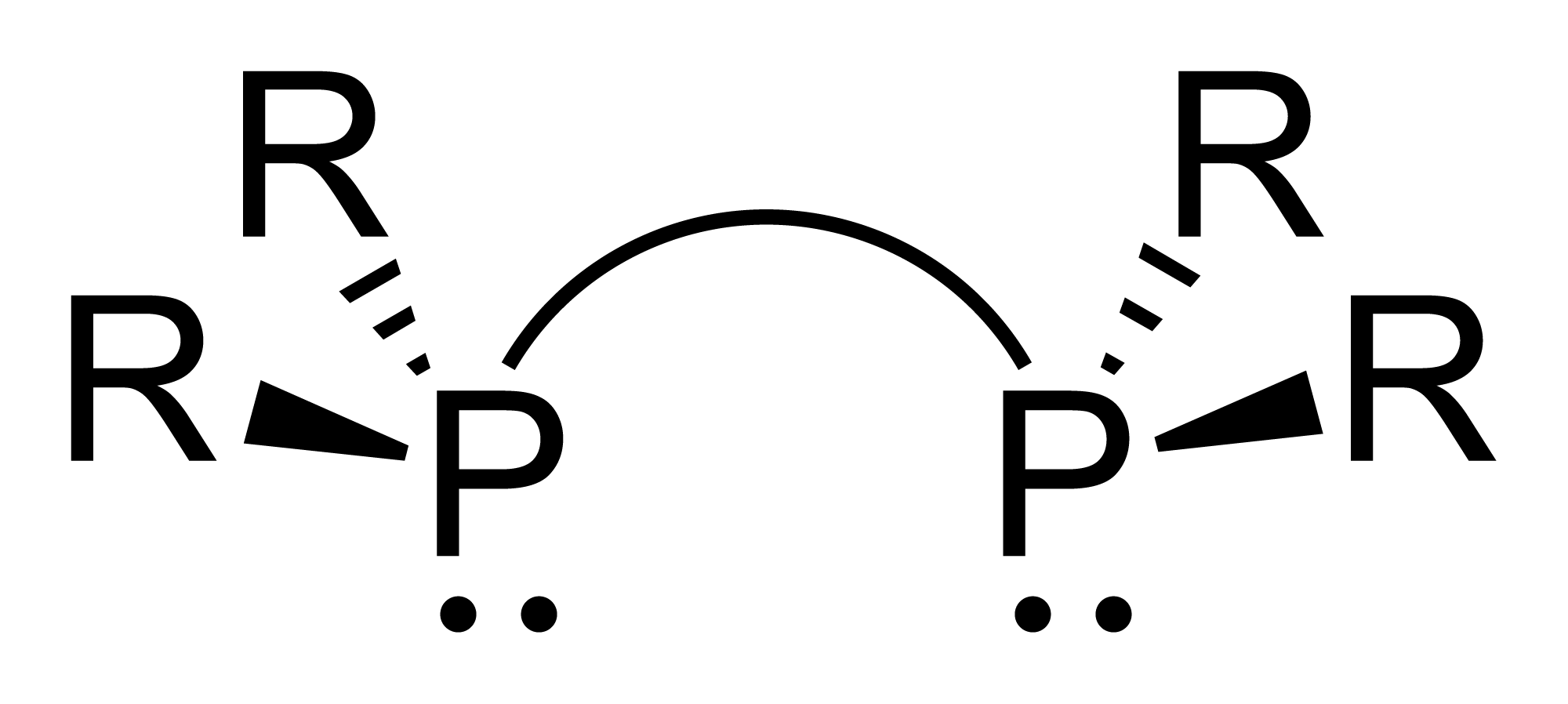
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture. Key concepts Many inorganic compounds are ionic compounds, consisting of cations and anions joined by ionic bonding. Examples of salts (which are ionic compounds) are magnesium chloride MgCl2, which consists of magnesium cations Mg2+ and chloride anions Cl−; or sodium oxide Na2O, which consists of sodium cations Na+ and oxide anions O2−. In any salt, the proportions of the ions are such that the electric charges cancel out, so that the bulk compound is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenyl Ether
Diphenyl ether is the organic compound with the formula ( C6 H5)2 O. It is a colorless solid. This, the simplest diaryl ether, has a variety of niche applications. Synthesis and reactions Diphenyl ether and many of its properties were first reported as early as 1901. It is synthesized by a modification of the Williamson ether synthesis, here the reaction of phenol and bromobenzene in the presence of base and a catalytic amount of copper: :PhONa + PhBr → PhOPh + NaBr Involving similar reactions, diphenyl ether is a significant side product in the high-pressure hydrolysis of chlorobenzene in the production of phenol. Related compounds are prepared by Ullmann reactions. The compound undergoes reactions typical of other phenyl rings, including hydroxylation, nitration, halogenation, sulfonation, and Friedel–Crafts alkylation or acylation. Uses The main application of diphenyl ether is as a eutectic mixture with biphenyl, used as a heat transfer fluid. Such a mixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xantphos
Xantphos is an organophosphorus compound derived from the heterocycle xanthene. It is used as a bidentate diphosphine ligand and is noteworthy for having a particularly wide bite angle (108°). Such ligands are useful in the hydroformylation of alkenes. Illustrative of its wide bite angle, it forms both cis and trans adducts of platinum(II) chloride. In the latter context, xantphos is classified as a trans-spanning ligand. A related bidentate ligand with a greater bite angle is spanphos. The ligand is prepared by double directed lithiation of 9,9-dimethylxanthene with sec-butyllithium followed by treatment with chlorodiphenylphosphine.{{cite journal , author = Mirko Kranenburg, Yuri E. M. van der Burgt, Paul C. J. Kamer, Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen, Kees Goubitz, and Jan Fraanje , title = New Diphosphine Ligands Based on Heterocyclic Aromatics Inducing Very High Regioselectivity in Rhodium-Catalyzed Hydroformylation: Effect of the Bite Angle , year = 1995 , journal = Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorodiphenylphosphine
Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is useful reagent for introducing the Ph2P group into molecules, which includes many ligands.Quin, L. D. ''A Guide to Organophosphorus Chemistry''; Wiley IEEE: New York, 2000; pp 44-69. Like other halophosphines, Ph2PCl is reactive with many nucleophiles such as water and easily oxidized even by air. Synthesis and reactions Chlorodiphenylphosphine is produced on a commercial scale from benzene and phosphorus trichloride (PCl3). Benzene reacts with phosphorus trichloride at extreme temperatures around 600 °C to give dichlorophenylphosphine (PhPCl2) and HCl. Redistribution of PhPCl2 in the gas phase at high temperatures results in chlorodiphenylphosphine. :2PhPCl2 → Ph2PCl + PCl3 Alternatively such compounds are prepared by redistribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-3D-balls.png)