|
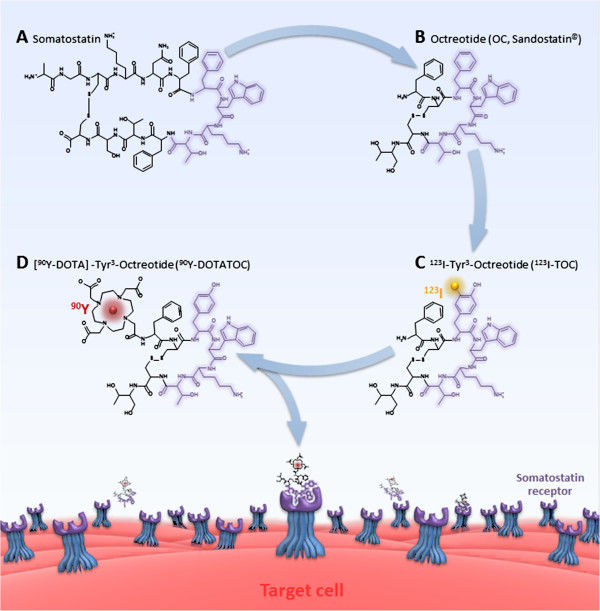
DOTATATE
DOTA-TATE (DOTATATE, DOTA-octreotate, oxodotreotide, DOTA-(Tyr3)-octreotate, and DOTA-0-Tyr3-Octreotate) is an eight amino acid long peptide, with a covalently bonded DOTA bifunctional chelator. DOTA-TATE can be reacted with the radionuclides gallium-68 (T1/2 = 68 min), lutetium-177 (T1/2 = 6.65 d) and copper-64 (T1/2 = 12.7 h) to form radiopharmaceuticals for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging or radionuclide therapy. 177Lu DOTA-TATE therapy is a form of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) which targets somatostatin receptors (SSR). In that form of application it is a form of targeted drug delivery. Chemistry and mechanism of action DOTA-TATE is a compound containing tyrosine3-octreotate, an SSR agonist, and the bifunctional chelator DOTA (tetraxetan). SSRs are found with high density in numerous malignancies, including CNS, breast, lung, and lymphatics. The role of SSR agonists (i.e. somatostatin and its analogs such as octreotide, somatuline and va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is a type of radionuclide therapy, using a radiopharmaceutical that targets peptide receptors to deliver localised treatment, typically for neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). Mechanism A key advantage of PRRT over other methods of radiotherapy is the ability to target delivery of therapeutic radionuclides directly to the tumour or target site. This works because some tumours have an abundance (overexpression) of peptide receptors, compared to normal tissue. A radioactive substance can be combined with a relevant peptide (or its analogue) so that it preferentially binds to the tumour. With a gamma emitter as the radionuclide, the technique can be used for imaging with a gamma camera or PET scanner to locate tumours. When paired with alpha or beta emitters, therapy can be achieved, as in PRRT. The current generation of PRRT targets somatostatin receptors, with a range of analogue materials such as octreotide and other DOTA compounds. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium-68
Natural gallium (31Ga) consists of a mixture of two stable isotopes: gallium-69 and gallium-71. The most commercially important radioisotopes are gallium-67 and gallium-68. Gallium-67 (half-life 3.3 days) is a gamma-emitting isotope (the gamma ray emitted immediately after electron capture) used in standard nuclear medical imaging, in procedures usually referred to as gallium scans. It is usually used as the free ion, Ga3+. It is the longest-lived radioisotope of gallium. The shorter-lived gallium-68 (half-life 68 minutes) is a positron-emitting isotope generated in very small quantities from germanium-68 in gallium-68 generators or in much greater quantities by proton bombardment of 68Zn in low-energy medical cyclotrons, for use in a small minority of diagnostic PET scans. For this use, it is usually attached as a tracer to a carrier molecule (for example the somatostatin analogue DOTATOC), which gives the resulting radiopharmaceutical a different tissue-uptake specificity from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOTA (chelator)
DOTA (also known as tetraxetan) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2NCH2CO2H)4. The molecule consists of a central 12-membered tetraaza (i.e., containing four nitrogen atoms) ring. DOTA is used as a complexing agent, especially for lanthanide ions. Its complexes have medical applications as contrast agents and cancer treatments. Terminology The acronym DOTA (for dodecane tetraacetic acid) is shorthand for both the tetracarboxylic acid and its various conjugate bases. In the area of coordination chemistry, the tetraacid is called H4DOTA and its fully deprotonated derivative is DOTA4−. Many related ligands are referred to using the DOTA acronym, although these derivatives are generally not ''tetra''carboxylic acids or the conjugate bases. Structure DOTA is derived from the macrocycle known as cyclen. The four secondary amine groups are modified by replacement of the N-H centers with N-CH2CO2H groups. The resulting aminopolycarboxylic acid, upon ionization of the carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumour
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasm A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...s that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. Classification WHO The World Health Organization (WHO) classification scheme places neuroendocrine tumors into three main categories, which emphasize the Grading (tumors), tumor grade rather than the anato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a Hydrophobe, hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code#Codons, codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octreotide
Octreotide, sold under the brand name Sandostatin among others, is an octapeptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologically, though it is a more potent inhibitor of growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin than the natural hormone. It was first synthesized in 1979 by the chemist Wilfried Bauer, and binds predominantly to the somatostatin receptors SSTR2 and SSTR5. It was approved for use in the United States in 1988. Octreotide (Mycapssa) was approved for medical use in the European Union in 2022. , octreotide (Mycapssa) is the first and only oral somatostatin analog (SSA) approved by the FDA. Medical uses Tumors Octreotide is used for the treatment of growth hormone producing tumors ( acromegaly and gigantism), when surgery is contraindicated, pituitary tumors that secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropinomata), diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with carcinoid syndrome, and diarrhea in people with vasoactive intestinal peptide-secreting tumors (VIPomas) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatuline
Lanreotide, sold under the brand name Somatuline among others, is a medication used in the management of acromegaly and symptoms caused by neuroendocrine tumors, most notably carcinoid syndrome. It is a long-acting analogue of somatostatin, like octreotide. Lanreotide (as lanreotide acetate) is manufactured by Ipsen. It is available in several countries, including the United Kingdom, Australia and Canada, and was approved for sale in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on August 30, 2007. Medical uses Lanreotide is used in the treatment of acromegaly, due to both pituitary and non-pituitary growth hormone-secreting tumors, and the management of symptoms caused by neuroendocrine tumors, particularly carcinoid tumors and VIPomas. In the United States and Canada, lanreotide is only indicated for the treatment of acromegaly. In the United Kingdom, it is also indicated in the treatment of thyrotrope, thyrotrophic pituitary adenoma, adenoma, a rare tumor of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapreotide
Vapreotide (Sanvar) is a synthetic somatostatin analog. It is used in the treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhotic liver disease and AIDS-related diarrhea Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi .... It is an 8 residue peptide with sequence H-D-Phe-Cys(1)-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys(1)-Trp-NH2. References Antineoplastic drugs Lactams Peptides Somatostatin receptor agonists {{systemic-hormonal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSR2
Translocon-associated protein subunit beta also known as TRAP-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SSR2'' gene. Function The signal sequence receptor (SSR) is a glycosylated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane receptor associated with protein translocation across the ER membrane. The SSR consists of 2 subunits, a 34-kD glycoprotein (alpha-SSR or SSR1 Translocon-associated protein subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SSR1'' gene. The signal sequence receptor (SSR) is a glycosylated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane receptor associated with protein translocation acros ...) and a 22-kD glycoprotein (beta-SSR or SSR2). The human beta-signal sequence receptor gene (SSR2) maps to chromosome bands 1q21-q23. References Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Receptors
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane. Structure and mechanism Many membrane receptors are transmembrane proteins. There are various kinds, including glycoproteins and lipoproteins. Hundreds of different receptors are known and many more have yet to be studied. Transmembrane receptors are typically classified based on their tertiary (three-dimensional) struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |