|
DOCK10
Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 10 (Dock10), also known as Zizimin3, is a large (~240 kDa) protein involved in intracellular signalling networks that in humans is encoded by the ''DOCK10'' gene. It is a member of the DOCK-D subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors, which function as activators of small G-proteins. Discovery Dock10 was identified via bioinformatic approaches as one of a family of evolutionarily conserved proteins (the DOCK family) that share significant sequence homology. Dock10 is expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes as well as in the brain, spleen, lung and thymus. Structure and function Dock10 shares the same domain arrangement as other members of the DOCK-D/Zizimin subfamily as well as a high level of sequence similarity. It contains a DHR2 domain that is involved in G protein binding and a DHR1 domain, which, in some DOCK family proteins, interacts with membrane phospholipids. Like other DOCK-D subfamily proteins Dock10 co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DHR1 Domain
DHR1 (DOCK homology region 1), also known as CZH1 or Docker1, is a protein domain of approximately 200–250 amino acids that is present in the DOCK family of signalling proteins. This domain binds phospholipids and so may assist in recruitment to cellular membranes. There is evidence that this domain may also mediate protein–protein interaction Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and th ...s. References Further reading * * {{refend Protein domains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Early on, there are typically no symptoms. Later, non-painful lymph node swelling, feeling tired, fever, night sweats, or weight loss for no clear reason may occur. Enlargement of the spleen and low red blood cells (anemia) may also occur. It typically worsens gradually over years. Risk factors include having a family history of the disease, with 10% of those who develop CLL having a family history of the disease. Exposure to Agent Orange, certain insecticides, sun exposure, exposure to hepatitis C virus, and common infections are also considered risk factors. CLL results in the buildup of B cell lymphocytes in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and blood. These cells do not function well and crowd out healthy blood cells. CLL is divided into two main types: those with a mutated IGHV gene and those without. Diagnosis is typically based on blood te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
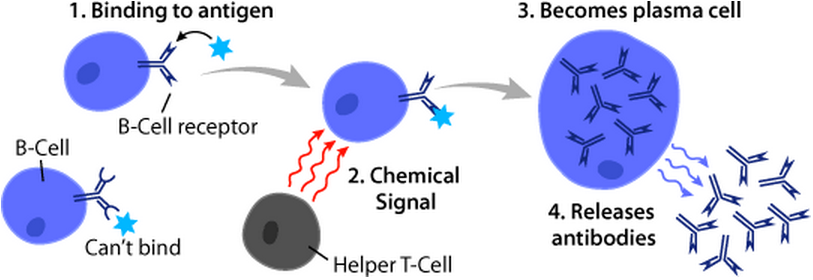
B-lymphocyte
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCL (GTPase)
TCL is a small (~21 kDa) signaling G protein (more specifically a GTPase), and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases.,. TCL (TC10-like) shares 85% and 78% amino acid similarity to TC10 and Cdc42, respectively. TCL mRNA is 2.5 kb long and is mainly expressed in heart. In vitro, TCL shows rapid GDP/GTP exchange and displays higher GTP dissociation and hydrolysis rates than TC10. Like other Rac/Cdc42/RhoUV members, GTP-bound TCL interacts with CRIB domains, such as those found in PAK and WASP. TCL produces large and dynamic F-actin-rich ruffles on the dorsal cell membrane in REF-52 fibroblasts. TCL activity is blocked by dominant negative Rac1 and Cdc42 mutants, suggesting a cross-talk between these three Rho GTPases. TCL is unrelated to TCL1A, a proto-oncogene implicated in the development of T-Cell Leukemias. See also *TCL1A T-cell leukemia/lymphoma protein 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TCL1A'' gene. Interactions TCL1A has been shown to interact with AKT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TC10 Protein
TC10 is a small (~21 kDa) signaling G protein (more specifically a GTPase), and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases. ''Further reading: Rho family of GTPases'' References G proteins {{Protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dock9
Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 9 (Dock9), also known as Zizimin1, is a large (~230 kDa) protein encoded in the human by the ''DOCK9'' gene, involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-D subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors that function as activators of small G-proteins. Dock9 activates the small G protein Cdc42. Discovery Dock9 was discovered using an affinity proteomic approach designed to identify novel activators of the small G protein Cdc42 in fibroblasts. Subsequent northern blot analysis revealed that Dock9 is expressed primarily in the brain, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, placenta and lung. Lower levels were detected in the colon, thymus, liver, small intestine and in leukocytes from peripheral blood. Structure and function Dock9 shares a similar structure of two core domains (known as DHR1 and DHR2), which are shared by all DOCK family members. The C-terminal DHR2 domain functions as an atypical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |