|
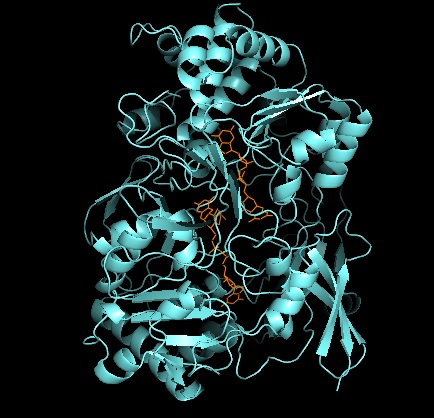
DMSO Reductase
DMSO reductase is a molybdenum-containing enzyme that catalyzes reduction of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to dimethyl sulfide (DMS). This enzyme serves as the terminal reductase under anaerobic conditions in some bacteria, with DMSO being the terminal electron acceptor. During the course of the reaction, the oxygen atom in DMSO is transferred to molybdenum, and then reduced to water. DMSO reductase (DMSOR) and other members of the DMSO reductase family are unique to bacteria and archaea. Enzymes of this family in anaerobic oxidative phosphorylation and inorganic-donor-based lithotrophic respiration. These enzymes have been engineered to degrade oxoanions. DMSOR catalyzes the transfer of two electrons and one oxygen atom in the reaction: The active site of DMSOR contains molybdenum, which is otherwise rare in biology. Tertiary structure and active site As for other members of DMSO reductase family, the tertiary structure of DMSOR is composed of Mo-surrounding domains I-IV, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanesulfonic Acid
Methanesulfonic acid (MsOH) or methanesulphonic acid (in British English) is an organosulfuric, colorless liquid with the chemical formula and structure . It is the simplest of the alkylsulfonic acids (). Salts and esters of methanesulfonic acid are known as mesylates (or methanesulfonates, as in ethyl methanesulfonate). It is hygroscopic in its concentrated form. Methanesulfonic acid can dissolve a wide range of metal salts, many of them in significantly higher concentrations than in hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dig ... (HCl) or sulfuric acid (). Applications Methanesulfonic acid is used as an acid catalyst in organic reactions because it is a non-volatile, strong acid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is convenient for industrial appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Cycle
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. It is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element ( CHNOPS), being a constituent of many proteins and cofactors, and sulfur compounds can be used as oxidants or reductants in microbial respiration. The global sulfur cycle involves the transformations of sulfur species through different oxidation states, which play an important role in both geological and biological processes. Steps of the sulfur cycle are: * Mineralization of organic sulfur into inorganic forms, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), elemental sulfur, as well as sulfide minerals. * Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide, sulfide, and elemental sulfur (S) to sulfate (). * Reduction of sulfate to sulfide. * Incorporation of sulfide into organic compounds (including metal-containing derivatives). These are often termed as follows: :''Assimilative sulfate reduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reporter Gene
In molecular biology, a reporter gene (often simply reporter) is a gene that researchers attach to a regulatory sequence of another gene of interest in bacteria, cell culture, animals or plants. Such genes are called reporters because the characteristics they confer on organisms expressing them are easily identified and measured, or because they are selectable markers. Reporter genes are often used as an indication of whether a certain gene has been taken up by or expressed in the cell or organism population. Common reporter genes To introduce a reporter gene into an organism, scientists place the reporter gene and the gene of interest in the same DNA construct to be inserted into the cell or organism. For bacteria or prokaryotic cells in culture, this is usually in the form of a circular DNA molecule called a plasmid. For viruses, this is known as a viral vector. It is important to use a reporter gene that is not natively expressed in the cell or organism under study, since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMSO Reductase Proposed Mechanism
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO has the unusual property that many individuals perceive a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO makes contact with their skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Dimethyl sulfoxide is produced industrially from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the Kraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials that have unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes and organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford. Theory Origin of an EPR signal Every electron has a magnetic moment and spin quantum number s = \tfrac , with magnetic components m_\mathrm = + \tfrac or m_\mathrm = - \tfrac . In the presence of an external magnetic field with strength B_\mathrm , the electron's magnetic moment aligns itself either antiparallel ( m_\mathrm = - \tfrac ) or parallel ( m_\mathrm = + \tfrac ) to the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is a widely used technique for determining the local geometric and/or electronic structure of matter. The experiment is usually performed at synchrotron radiation facilities, which provide intense and tunable X-ray beams. Samples can be in the gas phase, solutions, or solids. Background XAS data is obtained by tuning the photon energy, using a crystalline monochromator, to a range where core electrons can be excited (0.1-100 keV). The edges are, in part, named by which core electron is excited: the principal quantum numbers n = 1, 2, and 3, correspond to the K-, L-, and M-edges, respectively. For instance, excitation of a 1s electron occurs at the K-edge, while excitation of a 2s or 2p electron occurs at an L-edge (Figure 1). There are three main regions found on a spectrum generated by XAS data which are then thought of as separate spectroscopic techniques (Figure 2): # The ''absorption threshold'' determined by the transition to the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodobacter Sphaeroides
''Rhodobacter sphaeroides'' is a kind of purple bacterium; a group of bacteria that can obtain energy through photosynthesis. Its best growth conditions are anaerobic phototrophy ( photoheterotrophic and photoautotrophic) and aerobic chemoheterotrophy in the absence of light. ''R. sphaeroides'' is also able to fix nitrogen.De Universiteit van Texas over ''Rhodobacter sphaeroides'' It is remarkably metabolically diverse, as it is able to grow ically via fermentation and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |