|
DIRC (detector)
In particle detectors a detection of internally reflected Cherenkov light (DIRC) detector measures the velocity of charged particles and is used for particle identification. It is a design of a ring imaging Cherenkov detector where Cherenkov radiation, Cherenkov light that is contained by total internal reflection inside the solid radiator has its angular information preserved until it reaches the light sensors at the detector perimeter. A charged particle travelling through a material (for instance Fused quartz, fused silica) with a speed greater than c/n (n refractive index, c speed of light, vacuum speed of light) emits Cherenkov radiation. If the light angle on the surface is sufficiently shallow, this radiation is contained inside and transmitted through internal reflections to an expansion volume, coupled to photomultipliers (or other types of photon detectors), to measure the angle. Preserving the angle requires a precise planar and rectangular cross section of the radiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
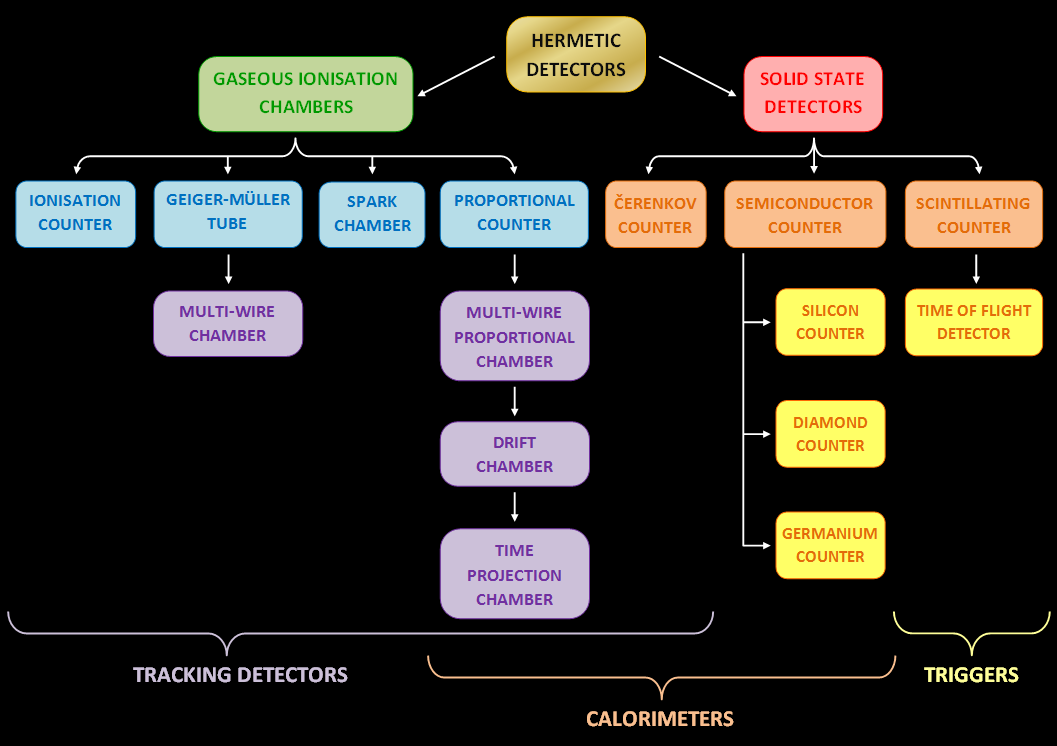
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blair Ratcliff
Blair is a Scots-English-language name of Scottish Gaelic origin. The surname is derived from any of the numerous places in Scotland called ''Blair'', derived from the Scottish Gaelic ''blàr'', meaning "plain", "meadow" or "field", frequently a battlefield. The given name ''Blair'' is unisex and derived from the surname. Blair is generally a masculine name in Scotland and Canada, although it is more popular in the United States, where it is also a feminine name. A variant spelling of the given name is ''Blaire'' and ''Blare''.In 2016, in the United States, Blair was the 521st most popular name for girls born that year, and the 1807th most popular for boys. Scottish clan *Clan Blair People with the surname A–E *Adam Blair (born 1986), New Zealand rugby league player *Andrea Blair, New Zealand geothermal consultant * Andrew M. Blair (1818–???), American politician in Wisconsin *Andy Blair (footballer) (born 1959) Scottish footballer *Andy Blair (ice hockey) (1908–1977), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where is the wavelength of that light in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring-imaging Cherenkov Detector
The ring-imaging Cherenkov, or RICH, detector is a device for identifying the type of an electrically charged subatomic particle of known momentum, that traverses a transparent refractive medium, by measurement of the presence and characteristics of the Cherenkov radiation emitted during that traversal. RICH detectors were first developed in the 1980s and are used in high energy elementary particle-, nuclear- and astro-physics experiments. The RICH detector Origins The ring-imaging detection technique was first proposed by Jacques Séguinot and Tom Ypsilantis, working at CERN in 1977. Their research and development, of high precision single-photon detectors and related optics, lay the foundations for the design development and construction of the first large-scale Particle Physics RICH detectors, at CERN's OMEGA facility and LEP (Large Electron–Positron Collider) DELPHI experiment. Principles A ring-imaging Cherenkov (RICH) detector allows the identification of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlueX
GlueX is a particle physics experiment located at the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (JLab) accelerator in Newport News, Virginia. Its primary purpose is to better understand the nature of confinement in quantum chromodynamics (QCD) by identifying a spectrum of hybrid and exotic mesons generated by the excitation of the gluonic field binding the quarks. Such mesonic states are predicted to exist outside of the well-established quark model, but none have been definitively identified by previous experiments. A broad high-statistics survey of known light mesons up to and including the J/\psi is also underway. Experimental apparatus The experiment uses photoproduction (that is, the scattering of a real photon on a nucleon) to produce mesonic states. Unlike previous similar experiments, it uses linearly polarized photons, which allows the analysis of accumulated events for certain polarization observables that are thought to make identification of exotic states feas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PANDA Experiment
The PANDA experiment is a planned particle physics experiment at the Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research in Darmstadt. PANDA is an acronym of antiProton ANnihilation at DArmstadt. PANDA will use proton–antiproton annihilation to study strong interaction physics at medium energy including hadron spectroscopy, search for exotic hadrons, hadrons in media, nucleon structure and exotic nuclei. A more detailed description of the experiment is availablat the scholarpedia Antiproton Beam A proton beam will be provided by the existing GSI facility and will be further accelerated by FAIR's SIS100 ring accelerator up to 30 GeV. By the beam hitting the antiproton production target, antiprotons with a momentum of around 3 GeV/c will be produced and can be collected and pre-cooled in the Collector Ring (CR). Afterwards the antiprotons will be injected into the High Energy Storage Ring (HESR). This race track shaped storage ring will host the P̄ANDA experiment. The antiprotons can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle II Detector
The BelleII experiment is a particle physics experiment designed to study the properties of B mesons (heavy particles containing a bottom quark) and other particles. BelleII is the successor to the Belle experiment, and commissioned at the SuperKEKB accelerator complex at KEK in Tsukuba, Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. The BelleII detector was "rolled in" (moved into the collision point of SuperKEKB) in April 2017. BelleII started taking data in early 2018. Over its running period, BelleII is expected to collect around 50 times more data than its predecessor, mostly due to a 40-fold increase in an instantaneous luminosity provided by SuperKEKB as compared to the previous KEKB accelerator. Physics program Many interesting analyses of the Belle and BaBar experiments were limited by statistical uncertainties, which was the main motivation to build a new generation of B-factory - Belle II. The target dataset is 50,000 fb−1 at BelleII compared to 988 fb−1 (with 711fb−1 at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a federally funded research and development center in Menlo Park, California, United States. Founded in 1962, the laboratory is now sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administrated by Stanford University. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, accelerator physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. The laboratory is under the programmatic direction of the United States Department of Energy Office of Science. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BaBar Experiment
The BaBar experiment, or simply BaBar, is an international collaboration of more than 500 physicists and engineers studying the subatomic world at energies of approximately ten times the rest mass of a proton (~10 GeV). Its design was motivated by the investigation of charge-parity violation. BaBar is located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy in California. Physics BaBar was set up to understand the disparity between the matter and antimatter content of the universe by measuring Charge Parity violation. CP symmetry is a combination of Charge-conjugation symmetry (C symmetry) and Parity symmetry (P symmetry), each of which are conserved separately except in weak interactions. BaBar focuses on the study of CP violation in the B meson system. The name of the experiment is derived from the nomenclature for the B meson (symbol ) and its antiparticle (symbol , pronounced B bar). The experiment' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via Dr. C.N. BootPHY304 Particle Physics Sheffield University The technique was an improvement over the bubble chamber particle detection method, which used photographic techniques, as it allowed high speed electronics to track the particle path. Description The multi-wire chamber uses an array of wires at a positive dc voltage (anode)s, which run through a chamber with conductive walls held at a lower potential (cathode). The chamber is filled with gas, such as an argon/methane mix, so that any ionizing particle that passes through the tube will ionize surrounding gaseous atoms and produce ion pairs, consisting of positive ions and electrons. These are accelerated by the electric field across the chamber, preventing recombination; the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |