|
DGAT1
Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGAT1 gene. Function This gene encodes a multipass transmembrane protein that functions as a key metabolic enzyme. The encoded protein catalyzes the conversion of diacylglycerol and fatty acyl CoA to triacylglycerol. This enzyme can also transfer acyl CoA to retinol. Activity of this protein may be associated with obesity and other metabolic diseases. This enzyme is essential for lactation in mice, and mutations in this gene affect the composition and volume of milk produced by both cattle and goats. Without this gene activity, infants who have a mutation in this gene are incapable of breaking down fat. This lack of capability to break down fat causes diarrhea and vomiting which eventually causes FTT (Failure to Thrive) and need of TPN (Total Parenteral Nutrition) if not given correct formula. Further this will cause protein losing enteropathy and very low albumin. See also * Diglyceride acyltra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diglyceride Acyltransferase
Diglyceride acyltransferase (or O-acyltransferase), DGAT, catalyzes the formation of triglycerides from diacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA]. The reaction catalyzed by DGAT is considered the terminal and only committed step in triglyceride synthesis. The conversion is essential for intestinal absorption (i.e. DGAT1) and adipose tissue formation (i.e. DGAT2). The protein is homologous to other membrane-bound O-acyltransferases. Isoforms Two DGAT isozymes are encoded by the genes DGAT1 and DGAT2. Although both isozymes catalyze similar reactions, they share no sequence homology.DGAT1is mainly located in absorptive enterocyte cells that line the intestine and duodenum where it reassembles triglycerides that were decomposed through lipolysis in the process of intestinal absorption. DGAT1 reconstitutes triglycerides in a committed step after which they are packaged together with cholesterol and proteins to form chylomicrons.DGAT2is mainly located in fat, liver and skin cells. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
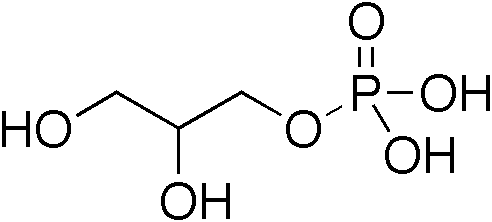
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acyl-CoA Esters
Fatty acyl-CoA esters are fatty acid derivatives formed of one fatty acid, a 3'-phospho-AMP linked to phosphorylated pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) and cysteamine. Long-chain acyl-CoA esters are substrates for a number of important enzymatic reactions and play a central role in the regulation of metabolism as allosteric regulators of several enzymes. To participate in specific metabolic processes, fatty acids must first be activated by being joined in thioester linkage (R-CO-SCoA) to the -SH group of coenzyme A, where R is a fatty carbon chain. The thioester bond is a high energy bond. The activation reaction normally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the outer mitochondrial membrane. This is an ATP-requiring reaction (fatty acyl-CoA synthase), yielding AMP and pyrophosphate (PPi). Different enzymes are specific for fatty acids of different chain length. Then, the acyl CoA esters are transported in mitochondria. They are converted to fatty acyl carnitine by carnitine a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triacylglycerol
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride''). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have ''no'' C=C groups; unsaturated fats feature one or more C=C groups. Unsaturated fats tend to have a lower melting point than saturated analogues; as a result, they are often liquid at room temperature. Chemical structure Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
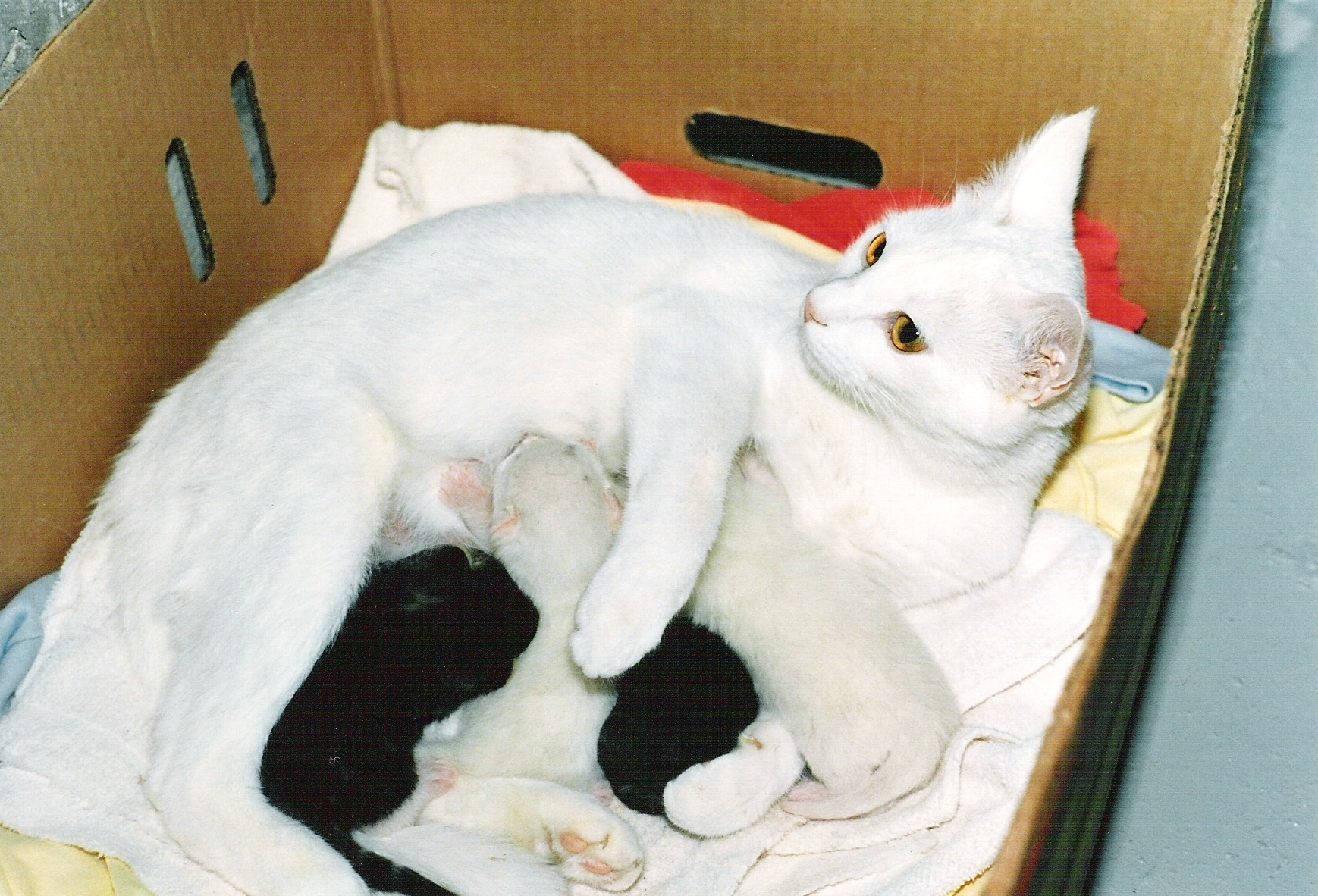
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all animals (including humans) is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has nipples; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only one species of mammal, the Dayak fruit bat from Southeast Asia, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is critical for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |