|
DEC Professional 350
The Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) are PDP-11 compatible microcomputers introduced in 1982 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC. History Like the cosmetically similar Rainbow 100 and DECmate II (also introduced at that time), the PRO series uses the LK201 keyboard and 400KB single-sided quad-density floppy disk drives (known as RX50), and offers a choice of color or monochrome monitors. For DEC, none of the three would be favorably received, and the industry instead standardized on Intel 8088-based IBM PC compatibles which are all binary program compatible with each other. In some ways, the PDP-11 microprocessors are technically superior to the Intel-based chips. While the 8088 is restricted to 1MB of memory because of its 20-bit address bus, DEC microprocessors are capable of accessing 4MB with their 22-bit addressing (although direct addressing of memory is limited in both approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
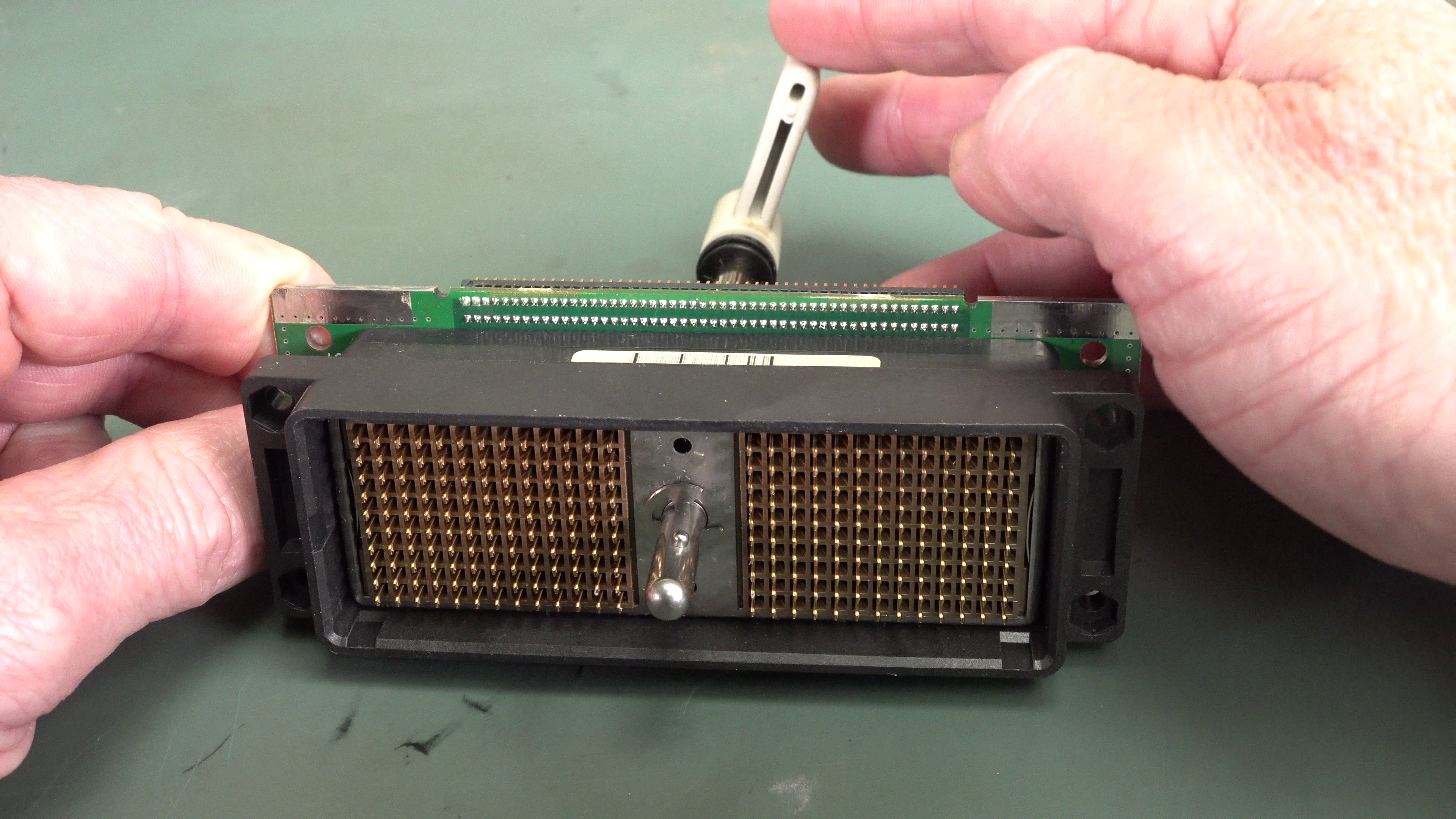
Zero Insertion Force
Zero insertion force (ZIF) is a type of IC socket or electrical connector that requires very little (but not literally zero) force for insertion. With a ZIF socket, before the IC is inserted, a lever or slider on the side of the socket is moved, pushing all the sprung contacts apart so that the IC can be inserted with very little force - generally the weight of the IC itself is sufficient and no external downward force is required. The lever is then moved back, allowing the contacts to close and grip the pins of the IC. ZIF sockets are much more expensive than standard IC sockets and also tend to take up a larger board area due to the space taken up by the lever mechanism. Typically, they are only used when there is a good reason to do so. Design A normal integrated circuit (IC) socket requires the IC to be pushed into sprung contacts which then grip by friction. For an IC with hundreds of pins, the total insertion force can be very large (hundreds of newtons), leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are no ... in one or more integrated circuits known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the Central processing unit, processor, computer memory, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining Computer performance, system performance. Computers In computing, the term ''chipset'' commonly refers to a set of specialized integrated circuit, chips on a computer's motherboard or an expansion card. In personal computers, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KL DEC F11
KL, kL, kl, or kl. may refer to: Businesses and organizations * KLM, a Dutch airline (IATA airline designator KL) * Koninklijke Landmacht, the Royal Netherlands Army * Kvenna Listin ("Women's List"), a political party in Iceland * KL FM, a Malay language radio station Places * Kaiserslautern, Germany (license plate code KL) * Kerala, India (ISO 3166-2:IN subcode KL) * Kirkland Lake, Ontario, Canada * Kowloon, Hong Kong * Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Science, technology, and mathematics * KL engine, version of the Mazda K engine * Klepton (kl.), a type of species in zoology * Kiloliter (kL), a unit of volume * Kullback–Leibler divergence in mathematics * KL (gene), a gene which encodes the klotho enzyme in humans Other uses * Jeep Cherokee (KL) * Kalaallisut language (ISO 639 alpha-2 language code "kl") * Kl (digraph), used in the Zulu language to write /kʟ̥ʼ/ or /kxʼ/ * Konzentrationslager, or concentration camp, abbreviated KZ or KL * ''KL – A History of the Nazi Concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolics
Symbolics was a computer manufacturer Symbolics, Inc., and a privately held company that acquired the assets of the former company and continues to sell and maintain the Open Genera Lisp system and the Macsyma computer algebra system.Symbolics Sales by David Schmidt The symbolics.com domain was originally registered on March 15, 1985, making it the first -domain in the world. In August 2009, it was sold to napkin.com (formerly XF.com) Investments. History Symbolics, Inc. was a |
Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance materials and technologies (PMT), and safety and productivity solutions (SPS). Honeywell is a Fortune 100 company, ranked 94th in 2021. In 2021 the corporation had a global workforce of approximately 99,000 employees, down from 113,000 in 2019. The current chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) is Darius Adamczyk. The corporation's current name, Honeywell International Inc., is a product of the merger of Honeywell Inc. and AlliedSignal in 1999. The corporation headquarters were consolidated with AlliedSignal's headquarters in Morristown, New Jersey; however, the combined company chose the name "Honeywell" because of the considerable brand recognition. Honeywell was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average index from 1999 to 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computervision
Computervision, Inc. (CV) was an early pioneer in Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM). Computervision was founded in 1969 by Marty Allen and Philippe Villers, and headquartered in Bedford, Massachusetts, United States. Its early products were built on a Data General Nova platform. Starting around 1975, Computervision built its own "CGP" (Computervision Graphics Processor) Nova-compatible 16-bit computers with added instructions optimized for graphics applications and using its own operating system known as Computervision Graphic Operating System (CGOS). In the 1980s, Computervision rewrote their code to operate on Unix-based platforms. Computervision was acquired by Prime Computer in 1988 for $434 million. Prime subsequently adopted the Computervision name. On December 12, 1998 Parametric Technology Corporation acquired Computervision. CADDS product history Computervision's first product, CADDS-1, was aimed at the printed circuit board layout and 2-D drafting ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Computer
Prime Computer, Inc. was a Natick, Massachusetts-based producer of minicomputers from 1972 until 1992. With the advent of PCs and the decline of the minicomputer industry, Prime was forced out of the market in the early 1990s, and by the end of 2010 the trademarks for both PRIME and PRIMOS no longer existed The alternative spellings "PR1ME" and "PR1MOS" were used as brand names or logos by the company. Founders The company was started by seven founders, some of whom worked on the Multics project at MIT. * Robert Baron (President) * Sidney Halligan (VP Sales) * James Campbell (Director of Marketing) * Joseph Cashen (VP Hardware Engineering) * Robert Berkowitz (VP Manufacturing) * William Poduska (VP Software Engineering) * John Carter (Director of Human Resources) The company started with the motto ''"Software First"''. Poduska left in 1981, to start Apollo Computer.Alfred Dupont Chandler, Takashi Hikino, Andrew Von Nordenflycht ''Inventing the electronic century: the epic st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Laboratories
Wang Laboratories was a US computer company founded in 1951 by An Wang and G. Y. Chu. The company was successively headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts (1954–1963), Tewksbury, Massachusetts (1963–1976), and finally in Lowell, Massachusetts (1976–1997). At its peak in the 1980s, Wang Laboratories had annual revenues of US$3 billion and employed over 33,000 people. It was one of the leading companies during the time of the Massachusetts Miracle. The company was directed by An Wang, who was described as an "indispensable leader" and played a personal role in setting business and product strategy until his death in 1990. The company went through transitions between different product lines, beginning with typesetters, calculators, and word processors, then adding computers, copiers, and laser printers. Wang Laboratories filed for bankruptcy protection in August 1992. After emerging from bankruptcy, the company changed its name to Wang Global. It was acquired by Getronics of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General
Data General Corporation was one of the first minicomputer firms of the late 1960s. Three of the four founders were former employees of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Their first product, 1969's Data General Nova, was a 16-bit minicomputer intended to both outperform and cost less than the equivalent from DEC, the 12-bit PDP-8. A basic Nova system cost or less than a similar PDP-8 while running faster, offering easy expandability, being significantly smaller, and proving more reliable in the field. Combined with Data General RDOS (DG/RDOS) and programming languages like Data General Business Basic, Novas provided a multi-user platform far ahead of many contemporary systems. A series of updated Nova machines were released through the early 1970s that kept the Nova line at the front of the 16-bit mini world. The Nova was followed by the Eclipse series which offered much larger memory capacity while still being able to run Nova code without modification. The Eclipse launch wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, ''The New York Times'' suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than (), with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end use application. During the two decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 companies formed and only a half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |