|
D'Artagnan (fictional Character)
Charles de Batz de Castelmore (), also known as d'Artagnan and later Count d'Artagnan ( 1611 – 25 June 1673), was a French Musketeer who served Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV as captain of the Musketeers of the Guard. He died at the Siege of Maastricht (1673), siege of Maastricht in the Franco-Dutch War. A fictionalised account of his life by Gatien de Courtilz de Sandras formed the basis for the d'Artagnan Romances of Alexandre Dumas, Alexandre Dumas ''père'', most famously including ''The Three Musketeers'' (1844). The heavily fictionalised version of d'Artagnan featured in Dumas' works and their The Three Musketeers (film), subsequent screen adaptations is now far more widely known than the real historical figure. Early life D'Artagnan was born at the Château de Castelmore near Lupiac in south-western France. His father, Bertrand de Batz lord of Castelmore, was the son of a newly ennobled merchant, Arnaud de Batz, who purchased the Château de Castelmore. Charles de Batz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
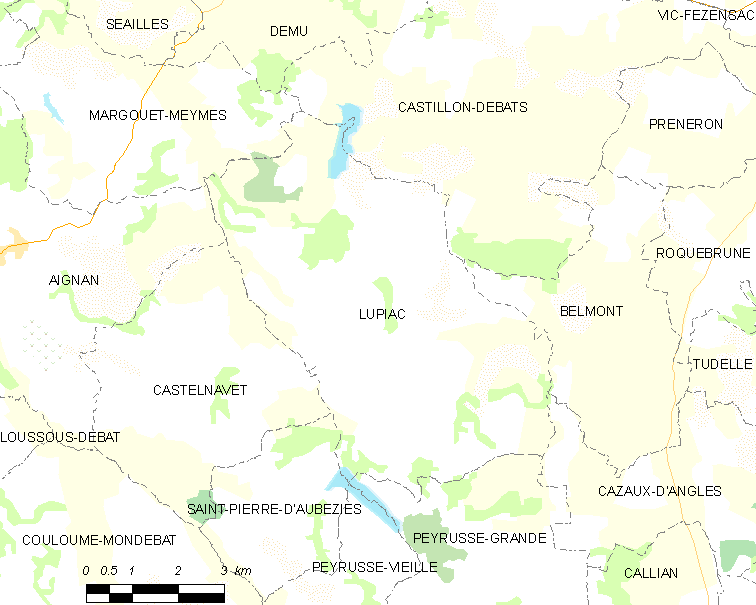
Lupiac
Lupiac () is a Communes of France, commune in the Gers Departments of France, department in southwestern France. Geography The Auzoue forms most of the commune's southeastern border. The Douze forms the commune's western border. Population Literature Charles de Batz de Castelmore d'Artagnan ( 1611 – 25 June 1673), a captain of the Musketeers of the Guard, was born here. A fictionalized version of his life is central to ''The Three Musketeers'' by Alexandre Dumas, père. Lupiac has a museum dedicated to him. See also * Communes of the Gers department References Communes of Gers {{Gers-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Three Musketeers
''The Three Musketeers'' () is a French historical adventure novel written and published in 1844 by French author Alexandre Dumas. It is the first of the author's three d'Artagnan Romances. As with some of his other works, he wrote it in collaboration with ghostwriter Auguste Maquet. It is in the swashbuckler genre, which has heroic, chivalrous swordsmen who fight for justice. Set between 1625 and 1628, it recounts the adventures of a young man named d'Artagnan (a character based on Charles de Batz de Castelmore d'Artagnan, Charles de Batz-Castelmore d'Artagnan) after he leaves home to travel to Paris, hoping to join the Musketeers of the Guard. Although d'Artagnan is not able to join this elite corps immediately, he is befriended by three of the most formidable musketeers of the age – Athos (character), Athos, Porthos and Aramis, "the three musketeers" or "the three inseparables" – and becomes involved in affairs of state and at court. ''The Three Musketeers'' is primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Fouquet
Nicolas Fouquet, marquis de Belle-Île, vicomte de Melun et Vaux (; 27 January 1615 – 23 March 1680) was the Superintendent of Finances in France from 1653 until 1661 under King Louis XIV. He had a glittering career, and acquired enormous wealth. He fell out of favor, accused of peculation (maladministration of the state's funds) and ''lèse-majesté'' (disrespect to the monarch). The king had him imprisoned from 1661 until his death in 1680. Early life Nicolas Fouquet was born in Paris to an influential family of the ''noblesse de robe'' (members of the nobility under the Ancien Régime who had high positions in government, especially in law and finance). He was the second child of François IV Fouquet (who held numerous high positions in government) and of Marie de Maupeou (who came from a family of the ''noblesse de robe'' and who was famous for her piety and charitable works).:18–23, Contrary to the pretensions of the family, the Fouquets did not come from a lineage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services and police forces. The rank in armies and air forces is often subdivided into subcategories of seniority. In Comparative navy officer ranks of Anglophone countries, English-speaking navies, lieutenants are often equivalent to the army rank of Captain (armed forces), captain; in other navies, the lieutenants are usually equal to their army counterparts. ''Lieutenant'' may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command", and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organisation using both ranks. Political uses include lieu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering, as a subfield of the intelligence field, is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence). A person who commits espionage on a mission-specific contract is called an ''espionage agent'' or ''spy''. A person who commits espionage as a fully employed officer of a government is called an intelligence officer. Any individual or spy ring (a cooperating group of spies), in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law. Espionage is often part of an institutional effort by a government or commercial concern. However, the term tends to be associated with state spying on potential or actual enemies for military purposes. Spying involving corporations is known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue DArtagnan
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size. A sculpture that represents persons or animals in full figure, but that is small enough to lift and carry is a ''statuette'' or figurine, whilst those that are more than twice life-size are regarded as ''colossal statues''. Statues have been produced in many cultures from prehistory to the present; the oldest-known statue dating to about 30,000 years ago. Statues represent many different people and animals, real and mythical. Many statues are placed in public places as public art. The world's tallest statue, ''Statue of Unity'', is tall and is located near the Narmada dam in Gujarat, India. Colors Ancient statues often show the bare surface of the material of which they are made. For example, many people associate Greek classical art with white marb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Mazarin
Jules Mazarin (born Giulio Raimondo Mazzarino or Mazarini; 14 July 1602 – 9 March 1661), from 1641 known as Cardinal Mazarin, was an Italian Catholic prelate, diplomat and politician who served as the chief minister to the Kings of France Louis XIII and Louis XIV from 1642 to his death. He was made a cardinal in 1641. After serving as a papal diplomat for Pope Urban VIII, Mazarin offered his diplomatic services to Cardinal Richelieu and moved to Paris in 1640. After the death of Richelieu in 1642, Mazarin took his place as first minister of Louis XIII, and then of Louis XIV, when he succeeded to the throne in 1643. Mazarin acted as the head of the government for Anne of Austria, the regent for the young Louis XIV, and was also responsible for the king's education until he came of age. The first years of Mazarin in office were marked by military victories in the Thirty Years' War, which he used to make France the main European power and establish the Peace of Westphalia (1646� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Perpignan (1642)
The siege of Perpignan was a siege during the Reapers' War, Catalan Revolt. History Already in June 1641, the cities of Perpignan, Fort de Salses, Salses, Port-Vendres and Collioure were the last strongholds of the Spanish in Roussillon. A French army of 14,000 men conquered the rest of the province and left Perpignan isolated. The siege of the city was then postponed, as the bulk of the French army marched south to participate in the Battle of Tarragona (August 1641), Siege of Tarragona in August. In the meantime, the blockade of Perpignan was maintained by the remaining French troops, which led to famine in the city. The Spanish suucceed in breaking the siege between 4-8 January 1642, when the Marquis of Mortara and Girolamo Maria Caracciolo, Marquis of Torrecusa, managed to conquer Argelès-sur-Mer, opening the way for a convoy with grain from Collioure to enter Perpignan. On 25 January, a new French army of 25,000 infantry and 4,000 cavalry under command of Charles de La Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comte De Troisville
Jean-Armand du Peyrer, Comte de Troisville (or Tresville) (1598 – 8 May 1672) was a French officer. He was fictionalized under the name Monsieur de Tréville in Alexandre Dumas's 1844 novel ''The Three Musketeers''. Biography Origins Du Peyrer was born at Oloron-Sainte-Marie. He was not from aristocratic stock, but of recent nobility. It was his father, Jean du Peyrer, who introduced the name de Trois-villes or Tréville into the family. In 1607 he bought the region of Trois-Villes which effectively brought him nobility, according to the customs of the Basque Country at the time. This purchase also allowed the elder Du Peyrer the right to be considered a gentleman and to sit upon the council of gentlemen in the viscountcy of Soule Soule (; Basque language, Basque: Zuberoa; Zuberoan/ Soule Basque: Xiberoa or Xiberua; ) is a former viscounty and France, French Provinces of France, province and part of the present-day Pyrénées-Atlantiques ''département in France, dé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montesquiou Family
The de Montesquiou family is a French noble family stemming from Montesquiou in Gascony whose documented filiation traces back to circa 1190. In the 18th century, the family was recognized as coming in the 11th century from the Counts of Fezensac (extinct in the 12th century). The Montesquiou family split into several branches, of which only the d'Artagnan branch now remains. Origins The first ancestor of proven genealogy is Raimond-Aimeri de Montesquiou, who died in 1090, grand-father of the Raymond III, baron of Montesquiou, who took part in the Third Crusade with king Philippe Auguste and died around 1190. In the proceedings of the cartulary of Auch (copies from the 13th century), Raymond-Aimeri, first baron of Montesquiou is described around 1096 as the younger brother of Guillaume Astanove Count of Fezensac. The barons of Montesquiou were vassals of their cousins, the counts of Armagnac, who rose to become the most powerful feudal family in medieval France and pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |