|
Cử Nhân
The Confucian court examination system in Vietnam (Chữ Nôm: 制度科舉越南, Vietnamese : ''Chế độ khoa cử Việt Nam'') was a system for entry into the civil service modeled on the Imperial examination in China, based on knowledge of the classics and literary style from 1075 to 1919. __TOC__ History The exams entered Vietnam during the long era of Chinese occupation and adopted by subsequent independent dynasties as a way of filling the civil service. They were instituted at court level by the Lý dynasty's Emperor Lý Nhân Tông in 1075 and continued some 1000 years later toward the final years of the Nguyễn dynasty's Emperor Khải Định. The examinations were suspended by the French in 1913 with the very last local exams occurring from 1915 to 1919, thus making Vietnam the last country to hold Confucian civil service examinations. The royal court exams were typically held every three years, though the award of first prizes was far less frequent. File:To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a way of life, Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher Confucius (551–479 BCE). Confucius considered himself a transmitter of cultural values inherited from the Xia dynasty, Xia (c. 2070–1600 BCE), Shang dynasty, Shang (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and Western Zhou, Western Zhou dynasties (c. 1046–771 BCE). Confucianism was suppressed during the Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist and autocratic Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE), but survived. During the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), Confucian approaches edged out the "proto-Taoist" Huang–Lao as the official ideology, while the emperors mixed both with the real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Doumer
Joseph Athanase Doumer, commonly known as Paul Doumer (; 22 March 18577 May 1932), was the President of France from 13 June 1931 until his assassination on 7 May 1932. Biography Joseph Athanase Doumer was born in Aurillac, in the Cantal ''département'', in France on 22 March 1857, into a family of modest means. Alumnus of the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers, he became a professor of mathematics at Mende in 1877. In 1878 Doumer married Blanche Richel, whom he had met at college. They had eight children, four of whom were killed in the First World War (including the French air ace René Doumer). From 1879 until 1883 Doumer was professor at Remiremont, before leaving on health grounds. He then became chief editor of ''Courrier de l'Aisne'', a French regional newspaper. Initiated into Freemasonry in 1879, at "L'Union Fraternelle" lodge, he became Grand Secretary of Grand Orient de France in 1892. He made his debut in politics in 1885 as ''chef de cabinet'' to Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lê Ý Tông
Lê Ý Tông (黎懿宗 29 March 1719 – 10 August 1759) was the third-last emperor of the Vietnamese Lê dynasty, reigning only nominally under the power of Trịnh Giang of the Trịnh lords The Trịnh lords ( vi, Chúa Trịnh; Chữ Nôm: 主鄭; 1545–1787), formal title Trịnh Viceroy (; ), also known as Trịnh clan (鄭氏, ''Trịnh thị'') or the House of Trịnh, were a noble feudal clan who de facto ruled Northern Viet .... He reigned from 1735 to 1740 and was succeeded by Lê Hiển Tông. References * * Lê dynasty emperors Vietnamese retired emperors 1719 births 1759 deaths 18th-century Vietnamese monarchs Vietnamese monarchs {{Asia-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mạc Thái Tông
Mạc Thái Tông (, 1500 – 25 January 1540), known also by his given name Mạc Đăng Doanh (), was the second emperor of the Mạc dynasty of Vietnam from 1530 to 1540. His father, Mạc Thái Tổ, was still alive during the first year of his reign and also reigning as “senior emperor” (''Thái thượng hoàng'').Bruce M. Lockhart, William J. Duiker ''The A to Z of Vietnam'', p. 229 His posthumous name is Văn hoàng đế (), and his era name is Đại Chính. __TOC__ History Mạc Đăng Doanh was born in Cao Đôi village, Bình Hà district (present-day Nam Tan, Nam Sách District, Hải Dương Province). His father was Mac Dang Dung, and his mother was Nguyễn Thị Ngọc Toàn. He was the oldest son of Mac Dang Dung. After Mac Dang Dung seized the throne from Emperor Lê Chiêu Tông and established the Mạc dynasty in 1527, he made his oldest son crown prince. Mac Dang Doanh died on 25 January 1540 after reigning for 10 years. His full posthumous name is ''Th� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Bỉnh Khiêm
Nguyễn Bỉnh Khiêm ( Hán tự: 阮 秉 謙; 1491–1585) was a Vietnamese administrator, confucianist, poet, prophet and later a saint of the Cao Dai religion and of the new religious movement known as School of Teaching Goodness. Biography Born on the coast in Cổ Am village (which is now part of Hai Phong). As an adult, he studied knowledge from the second-rank doctor Lương Đắc Bằng and passed the official government examination at the fairly late age of 44 in the exams of 1535. However, he passed the exam, ranking number one in the country. This was a period of great instability in Vietnam which may explain why he took the exam at such a late age. He served in the Mạc dynasty court for just seven years until 1542 when he resigned after his official complaints of government corruptions were ignored. He then returned to his native village and opened a school. Among his students were Phùng Khắc Khoan (diplomat), Lương Hữu Khánh, Nguyễn Dữ (author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trần Anh Tông
Trần Anh Tông ( vi-hantu, 陳英宗, 17 September 1276 – 12 December 1320), personal name Trần Thuyên (陳烇), courtesy name Nhật Sủy (日煃) or Nhật Sáng (日㷃/日𤊞), was the fourth emperor of the Trần dynasty, reigning over Dai Viet from 1293 to 1314. After ceding the throne to his son Trần Minh Tông, Anh Tông held the title Retired Emperor for six years. As the first Trần emperor who ruled in total peace with respect to foreign affairs, Anh Tông was known for his successful reign of Đại Việt, which brought a long period of peace and prosperity over the country. He also had several military victories over the kingdoms of Champa and Laos. Early years Anh Tông was born in 1276 as Trần Thuyên, the first son of the then-emperor Trần Nhân Tông and Empress Khâm Từ Bảo Thánh. In 1292 he was invested as crown prince by Nhân Tông and ultimately was ceded the throne in 1293 while his father still reigned as Retired Emperor () for 16 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mạc Đĩnh Chi
Mạc Đĩnh Chi (; 1272–1346) was a renowned Vietnamese Confucian scholar who was the highest-scoring graduate in the palace examinations at the age of only twenty-four. He served three Trần dynasty emperors—first Trần Anh Tông until 1314, then his son Trần Minh Tông from 1314 to 1319, and finally the grandson Trần Hiến Tông after 1329. Mạc Đĩnh Chi was sent twice as envoy to the Chinese court. Among the Trân dynasty court scholars he was almost unique in that his academic degree was recognized by the Chinese.Anh Thư Hà, Hò̂ng Đức Trà̂n ''A brief chronology of Vietnam's history'' 2000 "The Trân Dynasty had to its credit one first degree Doctoral Laureate, Mạc Đĩnh Chi, whose academic degree was accepted by China" He himself is also the ancestor of the emperors of the Mạc dynasty The Mạc dynasty ( vi, Nhà Mạc / ''Mạc triều''; Hán Nôm: 茹莫 / 莫 朝) (1527-1627), as known as House of Mạc ruled the whole of Đại Việt bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuangyuan
''Zhuangyuan'', or ''trạng nguyên'' in Vietnamese, variously translated into English as principal graduate, primus, or optimus, was the title given to the scholar who achieved the highest score on highest level of the Imperial examination, (in the Tang dynasty) and (in the Song dynasty) in ancient China and Vietnam. In China, Fu Shanxiang is known as the first (and last) female zhuangyuan ''(nü zhuangyuan'') in Chinese history, but under the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, not the regular imperial exams. After the Taipings captured the city of Nanjing, they offered an exam for women in January 1853 in which Fu attained the highest score. In Vietnam, the first trạng nguyên in history was Lê Văn Thịnh, who lived in the Lý dynasty era and was the one who persuaded the Song to give back 6 districts of Quảng Nguyên (today Hà Giang province) to Vietnam. The first female trạng nguyên ''(nữ trạng nguyên'') is Nguyễn Thị Duệ who later become a consort of the M� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trần Thái Tông
Trần Thái Tông (17 July 1218 – 5 May 1277), personal name Trần Cảnh or Trần Nhật Cảnh, temple name Thái Tông, was the first emperor of the Trần dynasty, reigned Đại Việt for 33 years (1226–58), being Retired Emperor for 19 years. He reigned during the first Mongol invasion of Vietnam before eventually abdicating in favor of his son Trần Hoảng (Trần Thánh Tông) in 1258. Early life The ancestors of the Trần clan originated from the province of Fujian before they migrated under Trần Kính (陳京, Chén Jīng) to Đại Việt. According to a Chinese writer, Zhou Mi (1232–1298), Trần Nhật Cảnh's real name was Hsieh Sheng-ch'ing, "a man from Qinglo district in Fujian". Trần Cảnh ( 陳 煚) was born in 1218 in modern-day Nam Định province during the last years of the Lý. Trần Thủ Độ, his uncle, prepared the way for his marriage to Empress Lý Chiêu Hoàng, the last empress of the House of Lý, who later abdicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
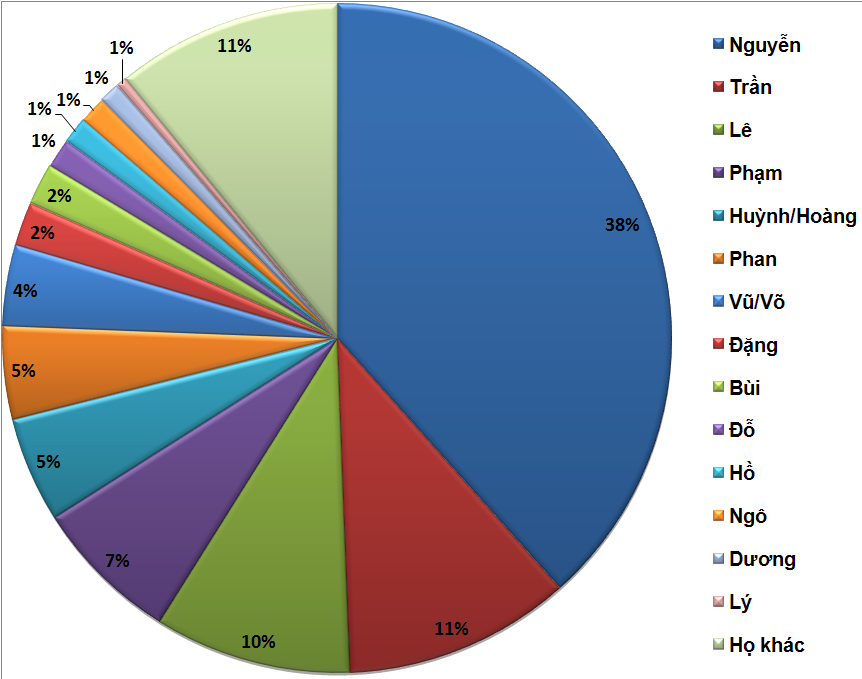
Nguyễn Hiền
Nguyễn () is the most common Vietnamese surname. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as Nguyen. Nguyên (元)is a different word and surname. By some estimates 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.Lê Trung Hoa, ''Họ và tên người Việt Nam'', NXB Khoa học - Xã hội, 2005 Origin and usage "Nguyễn" is the spelling of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the Han character 阮 (, ). The same Han character is often romanized as ''Ruǎn'' in Mandarin, ''Yuen'' in Cantonese, ''Gnieuh'' or ''Nyoe¹'' in Wu Chinese, or ''Nguang'' in Fuzhou dialect, Hokchew. . Hanja reading ( Korean language, Korean) is 완 (''Wan'') or 원 (''Won'') and in Hiragana, it is げん (''Gen''), old reading as け゚ん (Ngen). The first recorded mention of a person surnamed Nguyen is a 317 CE description of a journey to Giao Châu undertaken by Eastern Jin dynasty (, ) officer and his family. Many events in Vietnamese history have contribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lê Văn Thịnh
Lê Văn Thịnh (, 1038 – 1096), courtesy name Mậu Phu (茂夫), was an official in the royal court of the Lý dynasty. Ranking first in the first imperial examination of the Lý dynasty, Lê Văn Thịnh was appointed tutor for Lý Nhân Tông and was gradually promoted to the position of chancellor of the Lý dynasty due to his achievements, especially in the negotiation with the Song dynasty about the return of occupied land by the Song army to Annam in 1086. Lê Văn Thịnh was charged with high treason in 1096 and was banished to the mountainous area. Today the fact about the 1096 event is still a matter of debate. Biography Lê Văn Thịnh he was born in 1038 at the Đông Cứu village, Gia Định district. In the second month of 1075, the emperor Lý Nhân Tông ordered the organization of the first imperial examination of the Lý dynasty, which was also the first contest based on Confucianist education in the history of Vietnam. Lê Văn Thịnh who ranked f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nam Định
Nam Định () is a city in the Red River Delta of northern Vietnam. It is the capital of Nam Định Province. The city of Nam Định is 90 km south-east of Vietnam's capital, Hanoi. From August 18–20 of each year, there is a festival held in Nam Định called the Cố Trạch. This celebration honors General Trần Hưng Đạo, a 13th-century national hero who led Vietnamese forces to victory over the invading Mongols. Sports Nam Định has two sports facilities, Thiên Trường Stadium (formerly Cuối Stadium) and Trần Quốc Toản Indoor Stadium, which are host to football and volleyball matches. Both sports centers are located on Hùng Vương Street. Hà Nam Ninh won the National Football Champions ( V.League) in 1985 with star player Nguyễn Văn Dũng. In 2001, Nam Định took second place in the National Championships, losing to Bình Định F.C. In 2007, the Nam Định football team changed its name to Đạm Phú Mỹ Nam Định and won its firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |