|
Cyclones Judy And Kevin
Cyclones Judy and Kevin were a pair of intense tropical cyclones that made landfall on the Pacific island nation of Vanuatu, within 48 hours of each other in March 2023. They were the fourth and fifth named storms of the 2022–23 South Pacific cyclone season respectively, as well as the second and third severe tropical cyclones of the season. By the end of February, Judy had affected the Solomon Islands, and shortly after, Kevin began to affect the country. The nations were pounded by powerful winds and destructive seas. Vanuatu was heavily affected, being struck by both cyclones two days apart. The government asked Australia and New Zealand for aid shortly after Judy's passage. During March 3, as Kevin was impacting the islands, a Magnitude 6.5 earthquake hit just west of Espiritu Santo, and then a Magnitude 5.5 earthquake aftershock hit the island shortly after. Nonetheless, no deaths or significant injuries have been reported in connection with either cyclone. Meteorologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about . The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population of live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts: either in the capital city of Suva; or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi—where tourism is the major local industry; or in Lautoka, where the Sugarcane, sugar-cane industry is dominant. The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain. The majority of Fiji's islands were formed by Volcano, volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Some geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubuai
Tubuai or Tupuai is the main island of the Austral Island group, located south of Tahiti. In addition to Tubuai, the group of islands include Rimatara, Rurutu, Raivavae, Rapa and the uninhabited Îles Maria. They are part of the Austral Islands in the far southwest of French Polynesia in the south Pacific Ocean. Tubuai island sustains a population of 2,217 people on 45 km2 of land.Répartition de la population en Polynésie française en 2017 Institut de la statistique de la Polynésie françaiseEnvironnement marin des îles Australes p. 205< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MetService
Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited (MetService - Te Ratonga Tirorangi) is the national meteorological service of New Zealand. MetService was established as a state-owned enterprise in 1992. It employs about 300 staff, and its headquarters are in Wellington, New Zealand. Prior to becoming an SOE, New Zealand's national meteorological service has existed in a number of forms since the appointment of the country's first Director of Meteorological Stations in August 1861. As New Zealand's national meteorological service, MetService produces and issues forecasts and official weather warnings on behalf of New Zealand's Ministry of Transport and is certified by the Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand. International media, aviation and energy business is conducted under the ''MetraWeather'' brand. MetService has been certified to the ISO 9001 standard since November 1995. History The weather forecasting service began in 1861, when a spate of shipwrecks prompted the Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efate
Efate (french: Éfaté) is an island in the Pacific Ocean which is part of the Shefa Province in Vanuatu. It is also known as Île Vate. Geography It is the most populous (approx. 66,000) island in Vanuatu. Efate's land area of makes it Vanuatu's third largest island. Its geological past was heavily volcanic, meaning that a lava shelf surrounds much of the island. Most inhabitants of Efate live in Port Vila, the national capital. Its highest mountain is Mount McDonald with a height of . History Captain James Cook named it Sandwich Island "in honour of my noble patron, the Earl of Sandwich" on his 1774 voyage on . During World War II, Efate served an important role as a United States military base. On March 13, 2015, Port Vila, the island's largest human settlement and the capital of Vanuatu, bore extensive damage from Cyclone Pam. Politics Efate became an independent commune in 1889 when residents declared the region as Franceville. However, by 1890 the commune was broke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
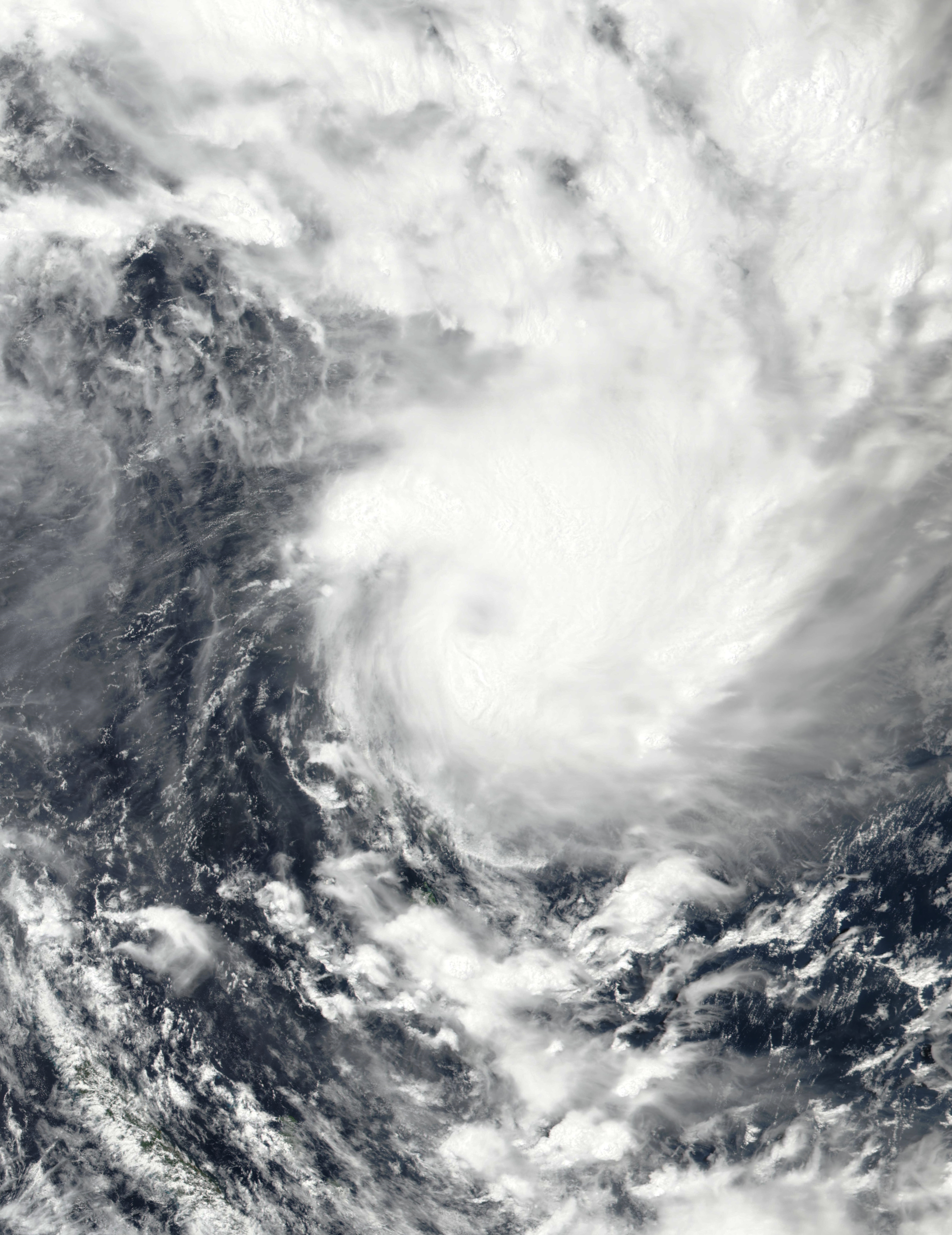
Judy 2023-02-28 0245Z
Judy is a short form of the name Judith. Judy may refer to: Places * Judy, Kentucky, village in Montgomery County, United States * Judy Woods, woodlands in Bradford, West Yorkshire, England, United Kingdom Animals * Judy (dog) (1936–1950), Royal Navy Second World War ship's dog awarded the Dickin Medal *Judy of Punch and Judy (dogs) (fl. 1946), British dog awarded the Dickin Medal * Judy the Beauty (foaled 2009), Canadian-American racehorse People and fictional characters * Judy (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Judy (surname) Music * ''Judy'' (Judy Garland album) (1956) * ''Judy'' (Judy Rodman album) (1986) * "Judy" (Elvis Presley song) (1961) * "Judy" (The Pipettes song) (2005) * "Judy" (Thomas Anders song) (1980) * "Judy", a song from the album '' Lost & Found (1961–62)'' by The Beach Boys * "Judy", a song from the album '' On the Double'' by Golden Earring * "Judy", a song from Tony Bennett's album '' When Lights Are Low'' by Hoagy Carmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatutaka
Fatutaka, Fatu Taka or Patu Taka (also known as Fataka and Mitre Island) is a small high island in the Solomon Islands province of Temotu in the south-west Pacific Ocean. The easternmost of the Solomon Islands, Fatutaka is located southeast of Anuta and can be seen from there in clear weather. Fatutaka and Anuta were discovered by Admiral Edward Edwards in 1791. The island, located at , is a small rocky outcropping, rising to an elevation of . The total land area of the island is . Human activities The island's soil is rocky, and not especially fertile, although it has in the past been used as a gardening location for the people of Anuta. The population of Anuta, the closest inhabited island, regularly sail to Fatutaka to eat and collect sea-birds and their eggs. The birds of Fatukaka have never been surveyed although the presence of Frigatebird, Eastern Reef Egret, Pacific Imperial Pigeon, and Emerald Dove have been reported. Geology Fatutaka is one of numerous volcani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale
Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basins they are located in. Only a few scales of classifications are used officially by the meteorological agencies monitoring the tropical cyclones, but other scales also exist, such as accumulated cyclone energy, the Power Dissipation Index, the Integrated Kinetic Energy Index, and the Hurricane Severity Index. Tropical cyclones that develop in the Northern Hemisphere are unofficially classified by the warning centres on one of three intensity scales. Tropical cyclones or subtropical cyclones that exist within the North Atlantic Ocean or the North-eastern Pacific Ocean are classified as either tropical depressions or tropical storms. Should a system intensify further and become a hurricane, then it will be classified on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, and is based on the estimated maximum sustained winds over a 1-minu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Category 1 South Pacific Tropical Cyclones
Category 1 is the lowest classification on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale and is used to classify tropical cyclones, that have 10-minute sustained winds of . tropical cyclones have peaked as Category 1 tropical cyclones in the South Pacific tropical cyclone basin, which is denoted as the part of the Pacific Ocean to the south of the equator and to the east of 160°E. This list does include any tropical cyclones that went on to peak as a Category 4 or 5 severe tropical cyclone, while in the Southern Pacific tropical cyclone basin. Background The South Pacific tropical cyclone basin is located to the south of the Equator between 160°E and 120°W. The basin is officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service and the New Zealand MetService, while other meteorological services such as the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, Météo-France as well as the United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center also monitor the basin. Within the basin a Category 3 severe tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scatterometer
A scatterometer or diffusionmeter is a scientific instrument to measure the return of a beam of light or radar waves scattered by diffusion in a medium such as air. Diffusionmeters using visible light are found in airports or along roads to measure horizontal visibility. Radar scatterometers use radio or microwaves to determine the normalized radar cross section (σ0, "sigma zero" or "sigma naught") of a surface. They are often mounted on weather satellites to find wind speed and direction, and are used in industries to analyze the roughness of surfaces. Optical Optical diffusionmeters are devices used in meteorology to find the optical range or the horizontal visibility. They consist of a light source, usually a laser, and a receiver. Both are placed at a 35° angle downward, aimed at a common area. Lateral scattering by the air along the light beam is quantified as an attenuation coefficient. Any departure from the clear air extinction coefficient (e.g. in fog) is measured an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)


