|
Cutaneous Mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, are sent to the central nervous system. Vertebrate mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli that result from physical interaction, including pressure and vibration. They are located in the skin, like other cutaneous receptors. They are all innervated by Aβ fibers, except the mechanorecepting free nerve endings, which are innervated by Aδ fibers. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can be categorized by what kind of sensation they perceive, by the rate of adaptation, and by morphology. Furthermore, each has a different receptive field. By sensation *The Slowly Adapting type 1 (SA1) mechanoreceptor, with the Merkel corpuscle end-organ (also known as Merkel discs) detect sustained p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Receptor
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord. The sensory information travels on the afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve, to the brain via the spinal cord. The stimulus can come from ''exteroreceptors'' outside the body, for example those that detect light and sound, or from ''interoreceptors'' inside the body, for example those that are responsive to blood pressure or the sense of body position. Types and function Different types of sensory neurons have different sensory receptors that respond to different kinds of stimuli. There are at least six external and two internal sensory receptors: External receptors External receptors that respond to stimuli from outside the body are called ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Nerve Ending
A free nerve ending (FNE) or bare nerve ending, is an unspecialized, afferent nerve fiber sending its signal to a sensory neuron. ''Afferent'' in this case means bringing information from the body's periphery toward the brain. They function as cutaneous nociceptors and are essentially used by vertebrates to detect noxious stimuli that often result in pain. Structure Free nerve endings are unencapsulated and have no complex sensory structures. They are the most common type of nerve ending, and are most frequently found in the skin. They penetrate the dermis and end in the stratum granulosum. FNEs infiltrate the middle layers of the dermis and surround hair follicles. Types Free nerve endings have different rates of adaptation, stimulus modalities, and fiber types. Rate of adaptation Different types of FNE can be rapidly adapting, intermediate adapting, or slowly adapting. A delta type II fibers are fast-adapting while A delta type I and C fibers are slowly adapting.Rolf-Detlef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
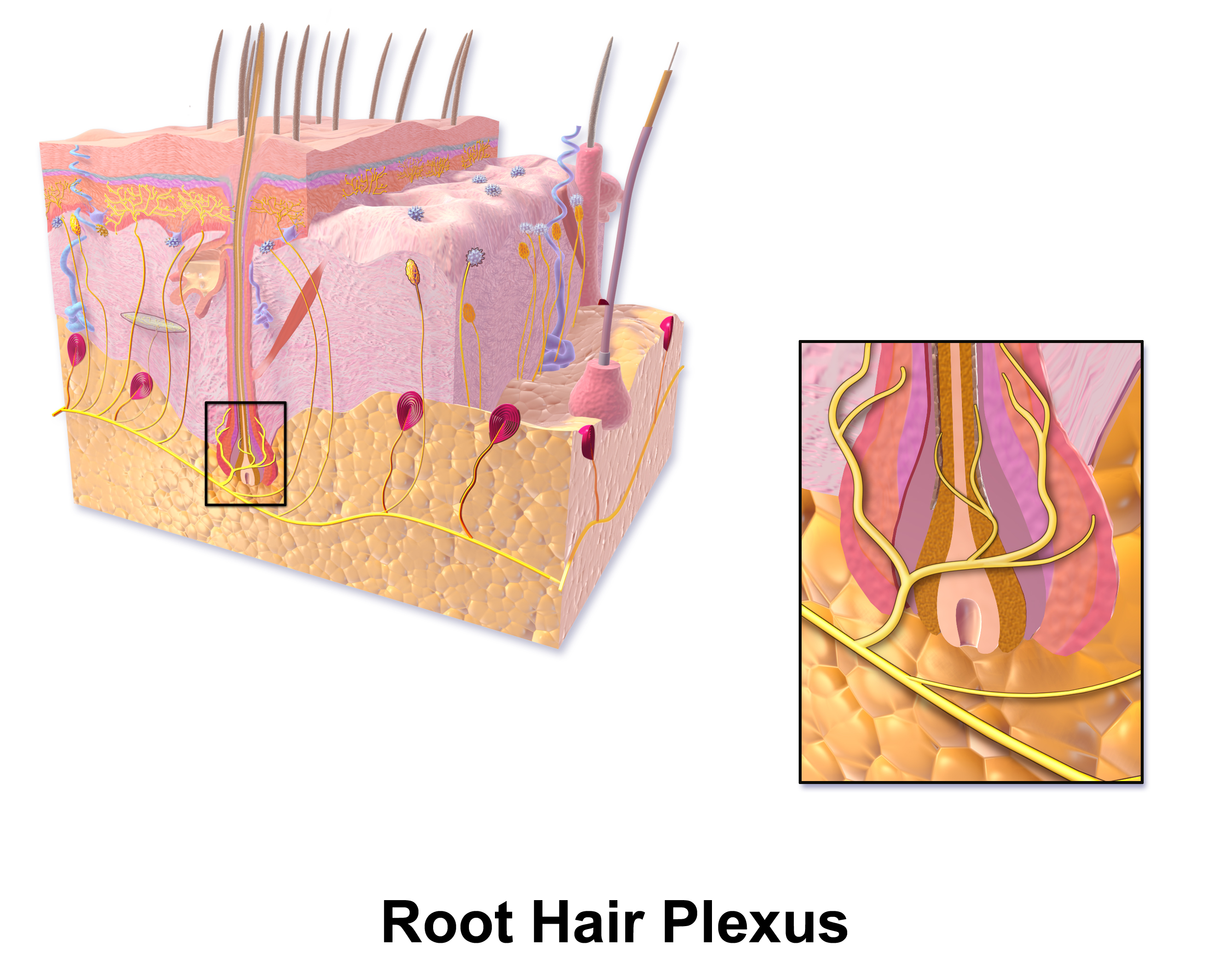
Hair Follicle Receptors
A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of nerve fiber endings and serves as a very sensitive mechanoreceptor for touch sensation. Each hair plexus forms a network around a hair follicle and is a receptor, which means it sends and receives nerve impulses to and from the brain when the hair moves. Endings of sensory nerve fibers which form a plexus around a hair follicle in hairy skin. They are mechanoreceptors conveying touch sensation. Specifically, crude touch and pressure sensation conveyed through the spinocervical tract, which is located in the posterior part of the lateral funiculus and terminates in the lateral cervical nucleus The lateral cervical nucleus is a scattered nucleus located dorsally in the lateral funiculus in the first three cervical segments of the spine. The spinocervical and spinothalamic tracts synapse in the lateral cervical nucleus; the spinocervical ....Nolte, John. Nolte’s The Human Brain E-Book: An Introduction to its Functional Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacinian Corpuscle End-organs
Pacinian corpuscle or lamellar corpuscle or Vater-Pacini corpuscle; is one of the four major types of mechanoreceptors (specialized nerve ending with adventitious tissue for mechanical sensation) found in mammalian skin. This type of mechanoreceptor is found in both glabrous (hairless) and hirsute (hairy) skins, viscera, joints and attached to periosteum of bone, primarily responsible for sensitivity to vibration. Few of them are also sensitive to quasi-static or low frequency pressure stimulus. Most of them respond only to sudden disturbances and are especially sensitive to vibration of few hundreds of Hz. The vibrational role may be used for detecting surface texture, e.g., rough vs. smooth. Most of the Pacinian corpuscles act as rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors. Groups of corpuscles respond to pressure changes, e.g. on grasping or releasing an object. Structure Pacinian corpuscles are larger and fewer in number than Meissner's corpuscle, Merkel cells and Ruffini's corpuscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ), also referred to as kinaesthesia (or kinesthesia), is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. It is sometimes described as the "sixth sense". Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinematic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other sensory systems, such as the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonic (physiology)
Tonic in physiology refers to a physiological response which is slow and may be graded. This term is typically used in opposition to a fast response. For instance, tonic muscles are contrasted by the more typical and much faster twitch muscles, while tonic sensory nerve endings are contrasted to the much faster phasic sensory nerve endings. Tonic muscles Tonic muscles are much slower than twitch fibers in terms of time from stimulus to full activation, time to full relaxation upon cessation of stimuli, and maximal shortening velocity.Kardong, K. 2008. Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution. 5th edition. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. These muscles are rarely found in mammals (only in the muscles moving the eye and in the middle ear), but are common in reptiles and amphibians. Tonic sensory receptors Tonic sensory input adapts slowly to a stimulushttp://caspar.bgsu.edu/~courses/Glossary.htm and continues to produce action potentials over the duration of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of events l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges. Acoustics Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gasses, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an ''acoustician'', while someone working in the field of acoustica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription or translation of genes, and post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecular events are the basic mechanisms controlling cell growth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereocilia
Stereocilia (or stereovilli or villi) are non-motile apical cell modifications. They are distinct from cilia and microvilli, but are closely related to microvilli. They form single "finger-like" projections that may be branched, with normal cell membrane characteristics. They contain actin. Stereocilia are found in the vas deferens, the epididymis, and the sensory cells of the inner ear. Structure Stereocilia are cylindrical and non-motile. They are much longer and thicker than microvilli, form single "finger-like" projections that may be branched, and have more of the characteristics of the cellular membrane proper. Like microvilli, they contain actin and lack an axoneme. This distinguishes them from cilia. They do not have a Basal body at their base since they do not contain microtubules. They may or may not be covered by a glycocalyx coating. They have no fixed arrangement, different to the structure present in kinocilium. Function Stereocilia are found in: *the vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea. The name cochlea derives . Structure The cochlea (plural is cochleae) is a spiraled, hollow, conical chamber of bone, in which waves propagate from the base (near the middle ear and the oval window) to the apex (the top or center of the spiral). The spiral canal of the cochlea is a section of the bony labyrinth of the inner ear that is approximately 30 mm long and makes 2 turns about the modiolus. The cochlear structures include: * Three ''scalae'' or chambers: ** the vestibular duct or ''scala vestibuli'' (containing perilymph), which lies superior to the cochlear duct and abuts the oval window ** the ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |