|
CureVac COVID-19 Vaccine
The CureVac COVID-19 vaccine (abbreviated CVnCoV) was a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by CureVac N.V. and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). The vaccine showed inadequate results in its Phase III trials with only 47% efficacy. In October 2021 CureVac abandoned further development and production plans for CVnCoV and refocused efforts on a cooperation with GlaxoSmithKline. Efficacy On 16 June 2021, CureVac said its vaccine showed 47% efficacy from its Phase IIb/III trial. Later, the final result data showed an efficacy of 48% against symptomatic disease in all age groups and, for people aged 18 to 60 years, an efficacy of 53% against symptomatic disease, 77% against moderate and severe disease and 100% against hospitalization and death, as no cases were detected in the study. This was based on interim analysis of 134 COVID cases in its Phase III study conducted in Europe and Latin America. The final analysis for the trials requires a minimum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a Novel coronavirus, provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is Contagious disease, contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1, SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
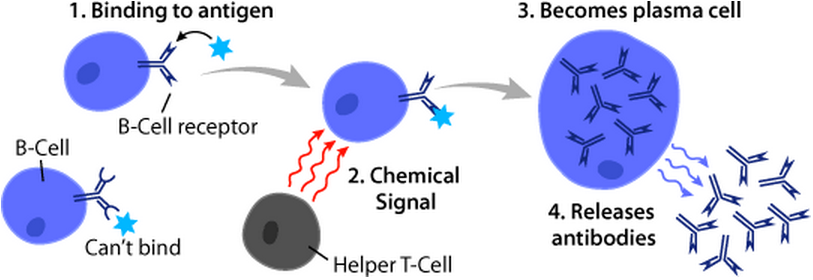
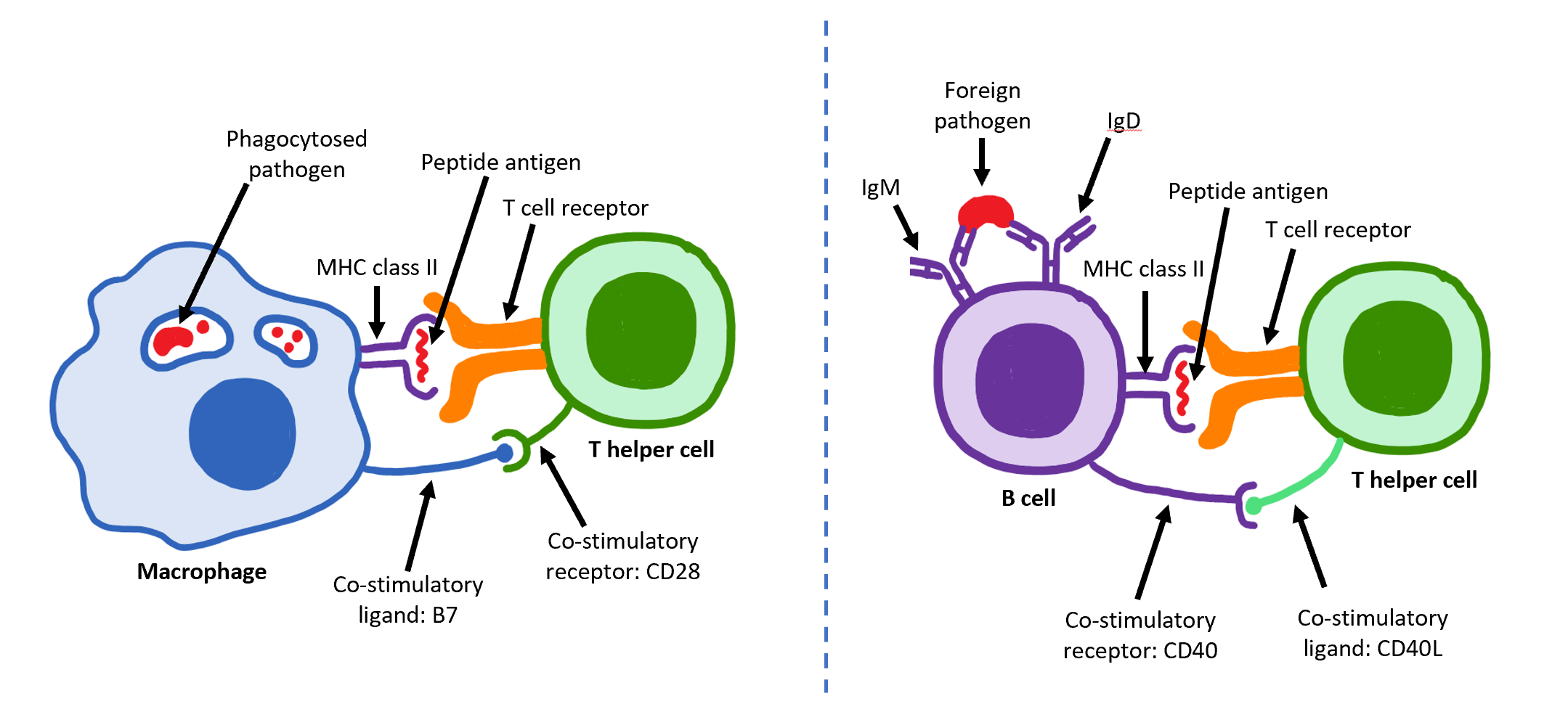
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convalescence
Convalescence is the gradual recovery of health and strength after illness or injury. It refers to the later stage of an infectious disease or illness when the patient recovers and returns to previous health, but may continue to be a source of infection to others even if feeling better. In this sense, "Healing, recovery" can be considered a synonymous term. This also sometimes includes Patient Care, patient care after a major surgery, under which they are required to visit the Physician, doctor for regular check-ups. Convalescent care facilities are sometimes recognized by the acronym TCF (Transitional Convalescent Facilities). See also * Drug rehabilitation, Rehabilitation, therapy to control a medical condition such as an addiction * Recuperation (recovery), a period of physical or mental recovery * Recuperation (sociology), a sociological concept * Relapse, reappearance of symptoms * Remission (medicine), Remission, absence of symptoms in chronic diseases References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutralizing Antibody
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralization renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, intracellular bacteria and microbial toxin. By binding specifically to surface structures (antigen) on an infectious particle, neutralizing antibodies prevent the particle from interacting with its host cells it might infect and destroy. Mechanism In order to enter cells, pathogens, such as circulating viral particles or extracellular bacteria, use molecules on their surfaces to interact with the cell surface receptors of their target cell which allows them to enter the cell and start their replication cycle. Neutralizing antibodies can inhibit infectivity by binding to the pathogen and blocking the molecules needed for cell entry. This can be due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine
The Moderna COVID19 vaccine (INN: elasomeran), sold under the brand name Spikevax, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by American company Moderna, the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA). Depending on the jurisdiction, it is authorized for use in people aged six months, twelve years, or eighteen years and older. It provides protection against COVID-19 which is caused by infection by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It is designed to be administered as two or three 0.5 mL doses given by intramuscular injection at an interval of at least 28 days apart. It is an mRNA vaccine composed of nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) encoding a spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. It is authorized for use at some level in many countries. In August and September 2022, bivalent versions of the vaccine (Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent) containing elasome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
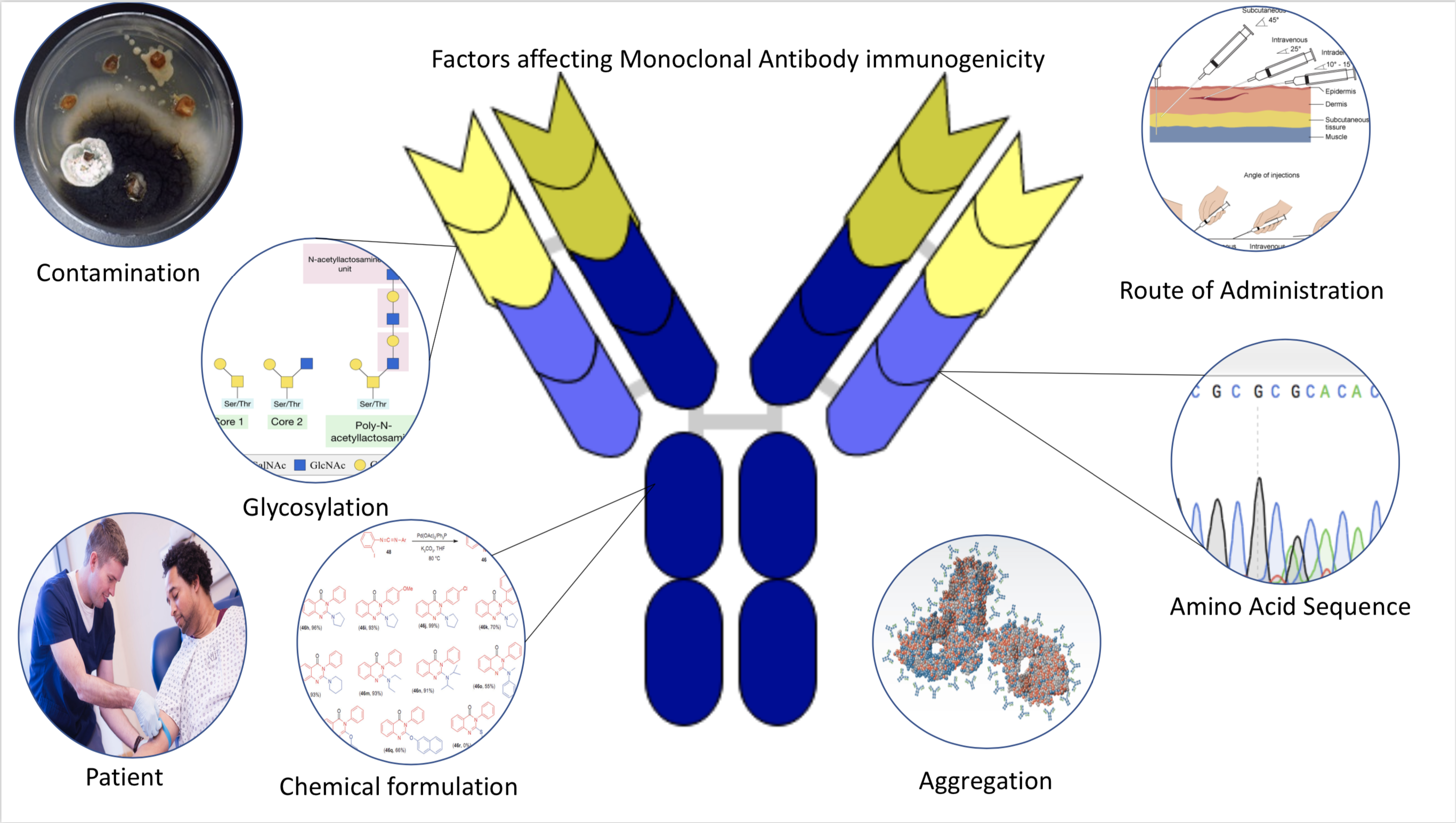
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal products for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use The Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding veterinary medicines. Text was copied from this source which is © ... References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |