|
Crocopoda
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. Archos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protorosauria
Protorosauria is an extinct polyphyletic group of archosauromorph reptiles from the latest Middle Permian (Capitanian stage) to the end of the Late Triassic (Rhaetian stage) of Asia, Europe and North America. It was named by the English anatomist and paleontologist Thomas Henry Huxley in 1871 as an order, originally to solely contain ''Protorosaurus''. Other names which were once considered equivalent to Protorosauria include Prolacertiformes and Prolacertilia. Protorosaurs are distinguished by their long necks formed by elongated cervical vertebrae, which have ribs that extend backward to the vertebrae behind them. Protorosaurs also have a gap between the quadrate bones and the jugal bones in the back of the skull near the jaw joint, making their skulls resemble those of lizards. While previously thought to be monophyletic, the group is now though to consist of various groups of basal archosauromorph reptiles that lie outside Crocopoda. Classification Protorosauria was consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreopricea
''Boreopricea'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile from the Early Triassic of arctic Russia. It is known from a fairly complete skeleton discovered in a borehole on Kolguyev Island, though damage to the specimen and loss of certain bones has complicated study of the genus. ''Boreopricea'' shared many similarities with various other archosauromorphs, making its classification controversial. Various studies have considered it a close relative of ''Prolacerta'', tanystropheids, both, or neither. ''Boreopricea'' is unique among early archosauromorphs due to possessing contact between the jugal and squamosal bones at the rear half of the skull. History ''Boreopricea funerea'' was named and described by Soviet paleontologist L. P. Tatarinov in 1978. It was primarily based on a fairly complete skull and skeleton collected in 1972 from a borehole at Kolguyev Island in the Arctic Ocean. This holotype specimen, PIN 3708/1, included bones from most of the body, apart from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
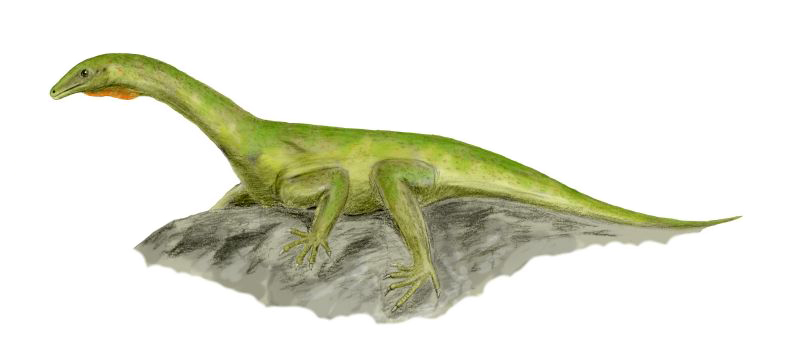
Prolacertidae
Prolacertidae is an extinct family of archosauromorph reptiles that lived during the Early Triassic epoch. It was named in 1935 by the British palaeontologist Francis Rex Parrington to include the species ''Prolacerta broomi'' of South Africa and Antarctica. In 1979 a second species, '' Kadimakara australiensis'', was described from Australia. Several other genera, such as ''Macrocnemus'', ''Pamelaria'' and ''Prolacertoides'', have also been assigned to this family in the past, but these have been placed elsewhere by later studies, leaving ''Prolacerta'' and ''Kadimakara'' as the only well-supported members. The prolacertids were historically placed within the paraphyletic group Prolacertiformes along with other basal, long-necked archosauriforms like ''Protorosaurus'' and the tanystropheids. However, more recent research has shown that the prolacertids were only distantly related to other "prolacertiforms", and were instead among the closest relatives of Archosauriformes. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
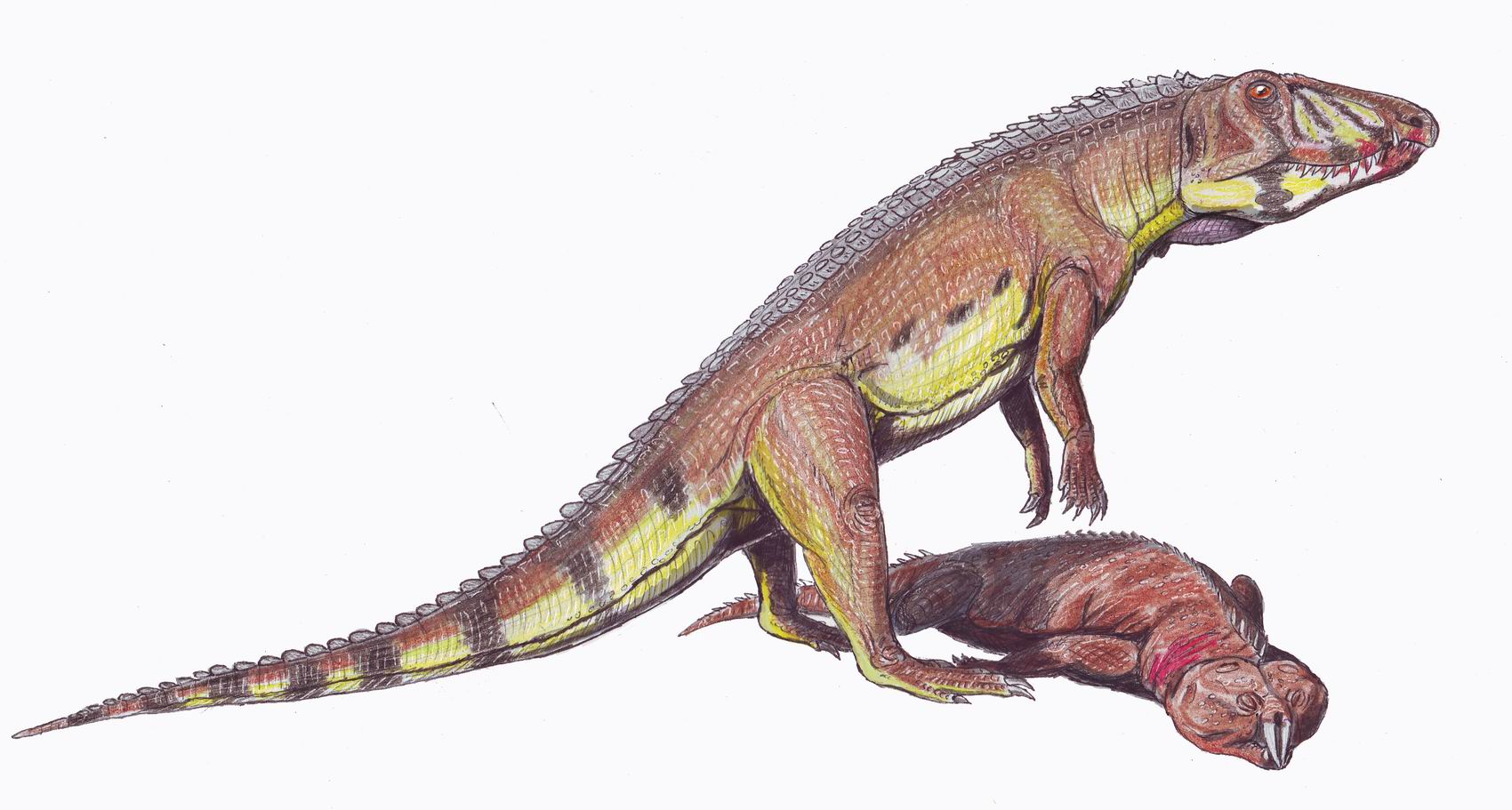
Allokotosauria
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivorous archosauromorphs was recovered by Sterling J. Nesbitt, John J. Flynn, Adam C. Pritchard, J. Michael Parrish, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and André R. Wyss in 2015. The name Allokotosauria is derived from Greek meaning "strange reptiles" in reference to unexpected grouping of early archosauromorph with a high disparity of features typically associated with herbivory. History Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2015) defined the group as a stem-based taxon containing ''Azendohsaurus madagaskarensis'' and '' Trilophosaurus buettneri'' and all taxa more closely related to them than to ''Tanystropheus longobardicus'', ''Proterosuchus fergusi'', ''Protorosaurus speneri'' or ''Rhynchosaurus articeps''. Therefore, Allokotosauria includes the families Azendoh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
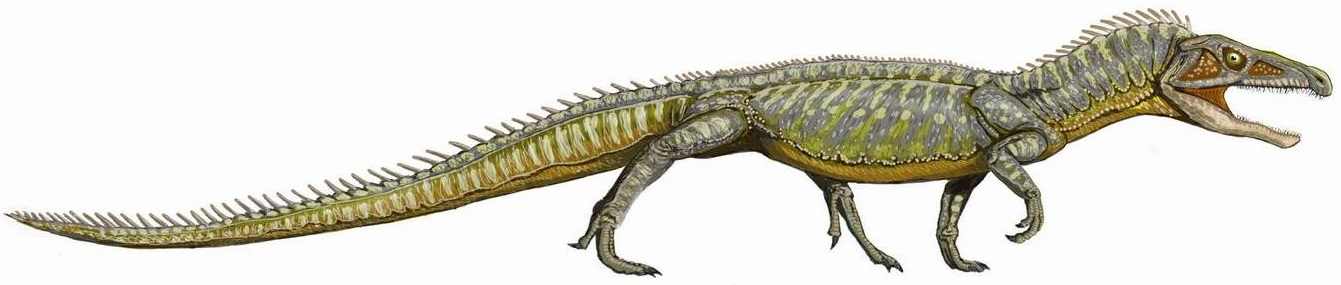
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aenigmastropheus
''Aenigmastropheus'' is an extinct genus of early archosauromorph reptiles known from the middle Late Permian Usili Formation of Songea District, southern Tanzania. It contains a single species, ''Aenigmastropheus parringtoni'', known solely from UMZC T836, a partial postcranial skeleton of a mature individual. It was collected in 1933, and first described in 1956, as a "problematic reptile" due to its unique morphology. Therefore, a binomial name was erected for this specimen in 2014. ''Aenigmastropheus'' was probably fully terrestrial. Discovery Fossils of ''Aenigmastropheus'' were first described by the British paleontologist Dr. Francis Rex Parrington in 1956, in an article titled as "A problematic reptile from the Upper Permian". Parrington reported collecting these remains in the Ruhuhu Valley in the Songea District of southern Tanzania in 1933, and considered them to come from a single individual. This specimen, UMZC T836, in currently housed at the University Museum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teyujagua
''Teyujagua'' (named for Teyú Yaguá, a legendary beast from local Guaraní mythology) is an extinct genus of small, probably semi-aquatic archosauromorph reptile that lived in Brazil during the Early Triassic period. The genus contains the type and only known species, ''T. paradoxa''. It is known from a well-preserved skull, and probably resembled a crocodile in appearance. It was an intermediary between the primitive archosauromorphs and the more advanced Archosauriformes, revealing the mosaic evolution of how the key features of the archosauriform skull were acquired. ''Teyujagua'' also provides additional support for a two-phase model of archosauriform radiation, with an initial diversification in the Permian followed by a second adaptive radiation in the Early Triassic. Description ''Teyujagua'' is known only from a well preserved skull with four associated cervical vertebrae, the only known postcranial material, but it is inferred to have been a small, carnivorous quadrupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmaniosaurus
''Tasmaniosaurus'' ('lizard from Tasmania', although this genus is not a true lizard) is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile known from the Knocklofty Formation (Early Triassic) of West Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. The type species is ''T. triassicus''. This genus is notable not only due to being one of the most complete Australian Triassic reptiles known, but also due to being a very close relative of Archosauriformes. Once believed to be a proterosuchid, this taxon is now believed to have been intermediate between advanced non-archosauriform archosauromorphs such as ''Prolacerta'', and basal archosauriforms such as ''Proterosuchus''. Features traditionally used to define Archosauria and later Archosauriformes, such as the presence of an antorbital fenestra and serrated teeth, are now known to have evolved prior to those groups due to their presence in ''Tasmaniosaurus''. History and Classification First named as a '' nomen nudum'' in 1974, the genus received a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |