|
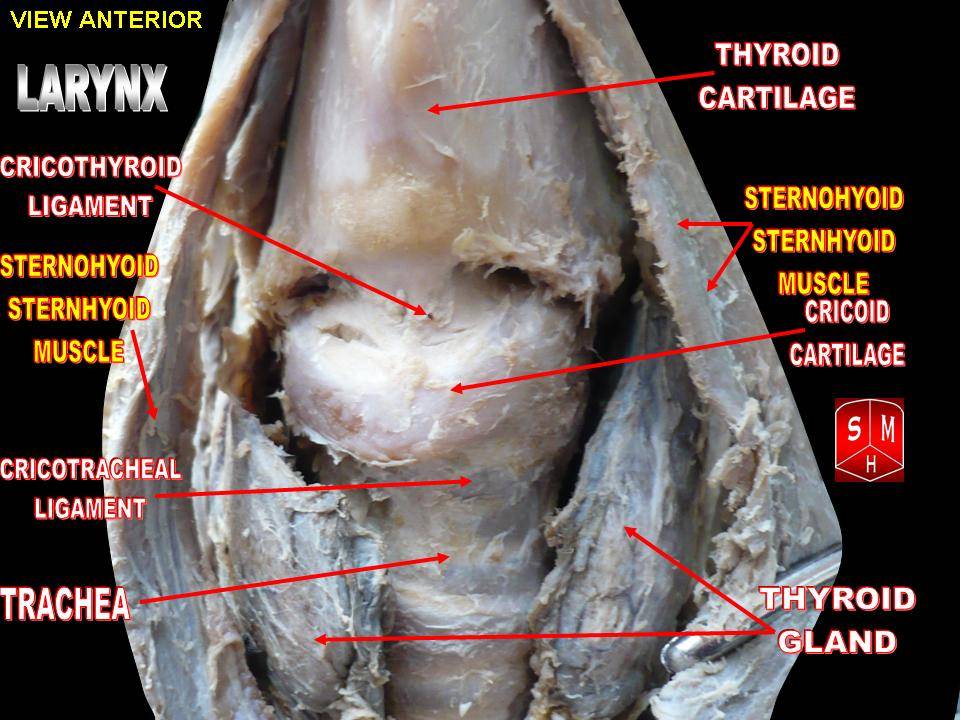
Cricoid
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech. Structure The cricoid cartilage sits just inferior to the thyroid cartilage in the neck, at the level of the C6 vertebra, and is joined to it medially by the median cricothyroid ligament and postero-laterally by the cricothyroid joints. Inferior to it are the rings of cartilage around the trachea (which are not continuous – rather they are C-shaped with a gap posteriorly). The cricoid is joined to the first tracheal ring by the cricotracheal ligament, and this can be felt as a more yielding area between the firm thyroid cartilage and firmer cricoid. It is also anatomically related to the thyroid gland; although the thyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricoid Pressure
Cricoid pressure, also known as the Sellick manoeuvre or Sellick maneuver, is a technique used in endotracheal intubation to try to reduce the risk of regurgitation. The technique involves the application of pressure to the cricoid cartilage at the neck, thus occluding the esophagus which passes directly behind it. Cricoid pressure should not be confused with the "BURP" (Backwards Upwards Rightwards Pressure) manoeuvre, which is used to improve the view of the glottis during laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, rather than to prevent regurgitation. As the name implies, the BURP manoeuvre requires a clinician to apply pressure on the thyroid cartilage posteriorly, then cephalad (upwards) and, finally, laterally towards the patient's right. History and technique In 1961 Brian Arthur Sellick (1918–1996), an anaesthetist, published the paper ''Cricoid pressure to control regurgitation of stomach contents during induction of anesthesia—preliminary communication'', describing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sellick Manoeuvre
Cricoid pressure, also known as the Sellick manoeuvre or Sellick maneuver, is a technique used in endotracheal intubation to try to reduce the risk of regurgitation. The technique involves the application of pressure to the cricoid cartilage at the neck, thus occluding the esophagus which passes directly behind it. Cricoid pressure should not be confused with the "BURP" (Backwards Upwards Rightwards Pressure) manoeuvre, which is used to improve the view of the glottis during laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, rather than to prevent regurgitation. As the name implies, the BURP manoeuvre requires a clinician to apply pressure on the thyroid cartilage posteriorly, then cephalad (upwards) and, finally, laterally towards the patient's right. History and technique In 1961 Brian Arthur Sellick (1918–1996), an anaesthetist, published the paper ''Cricoid pressure to control regurgitation of stomach contents during induction of anesthesia—preliminary communication'', describing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate Ventilation (physiology), ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an tracheal tube, endotracheal tube is passed through the mouth and larynx, vocal apparatus into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Other methods of intubation involve surgery and include the cricothyrotomy (used almost exclusively in emergency circumstances) and the tracheotomy, used primarily in situations where a prolonged need for airw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Sequence Induction
In advanced airway management, rapid sequence induction (RSI) – also referred to as rapid sequence intubation or as rapid sequence induction and intubation (RSII) or as crash induction – is a special process for endotracheal intubation that is used where the patient is at a high risk of pulmonary aspiration. It differs from other techniques for inducing general anesthesia in that several extra precautions are taken to minimize the time between giving the induction drugs and securing the tube, during which period the patient's airway is essentially unprotected. One important difference between RSI and routine tracheal intubation is that the anesthesiologist does not typically manually assist the ventilation of the lungs after the onset of general anesthesia and cessation of breathing, until the trachea has been intubated and the cuff has been inflated. Uses This procedure is used where general anesthesia must be induced before the patient has had time to fast long enough to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Isthmus
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricothyroid Ligament
The cricothyroid ligament (also known as the cricothyroid membrane or cricovocal membrane) is a ligament in the neck. It connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. It prevents these cartilages from moving too far apart. It is cut during an emergency cricothyrotomy to treat upper airway obstruction. Structure The cricothyroid ligament is composed of two parts: * the median cricothyroid ligament along the midline (a thickening of the cricothyroid membrane). It is a flat band of white connective tissue that connects the front parts of the contiguous margins of the cricoid and thyroid cartilages. It is a thick and strong ligament, narrow above and broad below. Each lateral ligament is known as the conus elasticus. * the lateral cricothyroid ligaments on each side (these are also called conus elasticus). Each is overlapped on either side by laryngeal muscles. The conus elasticus (which means elastic cone in Latin) is the lateral portion of the cricothyroid ligament. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricothyroid Muscle
The cricothyroid muscle is the only tensor muscle of the larynx aiding with phonation. It is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve. Its action tilts the thyroid forward to help tense the vocal cords. Structure The cricothyroid muscle originates from the anterolateral aspect of the cricoid cartilage, and inserts to the inferior cornu and lower lamina of the thyroid cartilage. Innervation This muscle is the only laryngeal muscle innervated by the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve known as the superior laryngeal nerve. Function The cricothyroid muscle produces tension and elongation of the vocal cords. They draw up the arch of the cricoid cartilage and tilt back the upper border of the cricoid cartilage lamina. The distance between the vocal processes and the angle of the thyroid is increased, and the folds are consequently elongated, resulting in higher pitch phonation. They work as antagonists to the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles. Clinical significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Cartilage
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the ''laryngeal skeleton'', the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx (only the cricoid cartilage encircles it). Structure The thyroid cartilage is a hyaline cartilage structure that sits in front of the larynx and above the thyroid gland. The cartilage is composed of two halves, which meet in the middle at a peak called the laryngeal prominence, also called the Adam's apple. In the midline above the prominence is the superior thyroid notch. A counterpart notch at the bottom of the cartilage is called the inferior thyroid notch. The two halves of the cartilage that make out the outer surfaces extend obliquely to cover the sides of the trachea. The posterior edge of each half articulates with the cricoid cartilage inferiorly at a joint called the cricothyroid joint. The most posterior part of the cartilage also has two projection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are small, paired intrinsic muscles of the larynx that extend between cricoid cartilage to the arytenoid cartilages in the larynx. Structure Origin and insertion The posterior cricoarytenoid originates from the posterior surface of the posterior quadrate lamina of the cricoid cartilage. It inserts onto the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage. Its distinct medial and lateral bellies insert onto opposite surfaces of the muscular process. Nerve supply The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are supplied by the anterior division of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (CN X). Sometimes, different parts of the muscle (such as the medial and lateral muscle bellies) are supplied by separate branches. This may vary between 1 and 6 branches, usually 2 or 3. These may connect within the muscle. Function The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles are the only muscles to open the vocal cords. By rotating the arytenoid cartila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. It is epithelium lined with column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usually as a result of a viral illness affecting other parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |