|
Counting Sort
Counting is the process of determining the number of elements of a finite set of objects; that is, determining the size of a set. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a (mental or spoken) counter by a unit for every element of the set, in some order, while marking (or displacing) those elements to avoid visiting the same element more than once, until no unmarked elements are left; if the counter was set to one after the first object, the value after visiting the final object gives the desired number of elements. The related term ''enumeration'' refers to uniquely identifying the elements of a finite (combinatorial) set or infinite set by assigning a number to each element. Counting sometimes involves numbers other than one; for example, when counting money, counting out change, "counting by twos" (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, ...), or "counting by fives" (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, ...). There is archaeological evidence suggesting that humans have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Children's Number Blocks Being Used For Learning To Count - 51069936953
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor (law), minor, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority (there are exceptions such as, for example, the consume and purchase of alcoholic beverage even after said age of majority), regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adults. Children generally have fewer Children's rights, rights and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, Metaphor, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finger Counting
Finger-counting, also known as dactylonomy, is the act of counting using one's fingers. There are multiple different systems used across time and between cultures, though many of these have seen a decline in use because of the spread of Arabic numerals. Finger-counting can serve as a form of manual communication, particularly in marketplace trading – including hand signaling (open outcry), hand signaling during open outcry in floor trading – and also in hand games, such as Morra (game), morra. Finger-counting is known to go back to ancient Egypt at least, and probably even further back. notes that as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, in Egypt's Old Kingdom, in the Pyramid texts' "Spell for obtaining a ferry-boat", the ferryman might object "Did you bring me a man who cannot number his fingers?". This spell was needed to cross a canal of the nether-world, as detailed in the Book of the Dead. Historical counting Complex systems of dactylonomy were used in the ancient world. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sennight
A week is a unit of time equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for short cycles of days in most parts of the world. The days are often used to indicate common work days and rest days, as well as days of worship. Weeks are often mapped against yearly calendars. There are just over 52 weeks in a year. The term "week" may also be used to refer to a sub-section of the week, such as the workweek and weekend. Ancient cultures had different "week" lengths, including ten days in Egypt and an eight-day week for Etruscans. The Etruscan week was adopted by the ancient Romans, but they later moved to a seven-day week, which had spread across Western Asia and the Eastern Mediterranean due to the influence of the Christian seven-day week, which is rooted in the Jewish seven-day week. In AD 321, Emperor Constantine the Great officially decreed a seven-day week in the Roman Empire, including making Sunday a public holiday. This later spread across Europe, then the rest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fortnight
A fortnight is a unit of time equal to 14 days (two weeks). The word derives from the Old English term , meaning "" (or "fourteen days", since the Anglo-Saxons counted by nights). Astronomy and tides In astronomy, a ''lunar fortnight'' is half a lunar synodic month, which is equivalent to the mean period between a full moon and a new moon (and vice versa). This is equal to 14.77 days. It gives rise to a lunar fortnightly tidal constituent (see: Long-period tides). Analogs and translations In many languages, there is no single word for a two-week period, and the equivalent terms "two weeks", "14 days", or "15 days" ( counting inclusively) have to be used. * Celtic languages: in Welsh, the term ''pythefnos'', meaning "15 nights", is used. This is in keeping with the Welsh term for a week, which is ''wythnos'' ("eight nights"). In Irish, the term is ''coicís''. * Similarly, in Greek, the term δεκαπενθήμερο (''dekapenthímero''), meaning "15 days", is used. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quinquagesima
Quinquagesima (), in the Western Christian Churches, is the last pre-Lenten Sunday, being the Sunday before Ash Wednesday, and the first day of Carnival (also known as Shrovetide). It is also called Quinquagesima Sunday, Quinquagesimae, Estomihi, Shrove Sunday, Pork Sunday, or the Sunday next before Lent. Being the Lord's Day before the start of the Lenten season, it is known for meat consumption as people feast before starting their fast on Ash Wednesday, the first day of Lent. Historically Lutheran countries such as Denmark mark Quinquagesima Sunday as the peak of the Fastelavn. After attending the Divine Service on Shrove Sunday, congregants enjoy Shrovetide buns (fastelavnsboller). Children often dress up and collect money from people while singing. Christians in these nations carry Shrovetide rods (fastelavnsris), which "branches decorated with sweets, little presents, etc., that are used to decorate the home or give to children." In the Revised Common Lectionary the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christian Liturgical Calendar
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year, ecclesiastical calendar, or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be observed, and which portions of scripture are to be read. Distinct liturgical colours may be used in connection with different seasons of the liturgical year. The dates of the festivals vary somewhat among the different churches, although the sequence and logic is largely the same. Liturgical cycle The liturgical cycle divides the year into a series of seasons, each with their own mood, theological emphases, and modes of prayer, which can be signified by different ways of decorating churches, colours of paraments and vestments for clergy, scriptural readings, themes for preaching and even different traditions and practices often observed personally or in the home. In churches that follow the liturgical year, the scripture passages for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, their original calendar was established by their legendary first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones, and idesseem to have derived from the new moon, the first-quarter moon, and the full moon respectively. To a late date, the Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
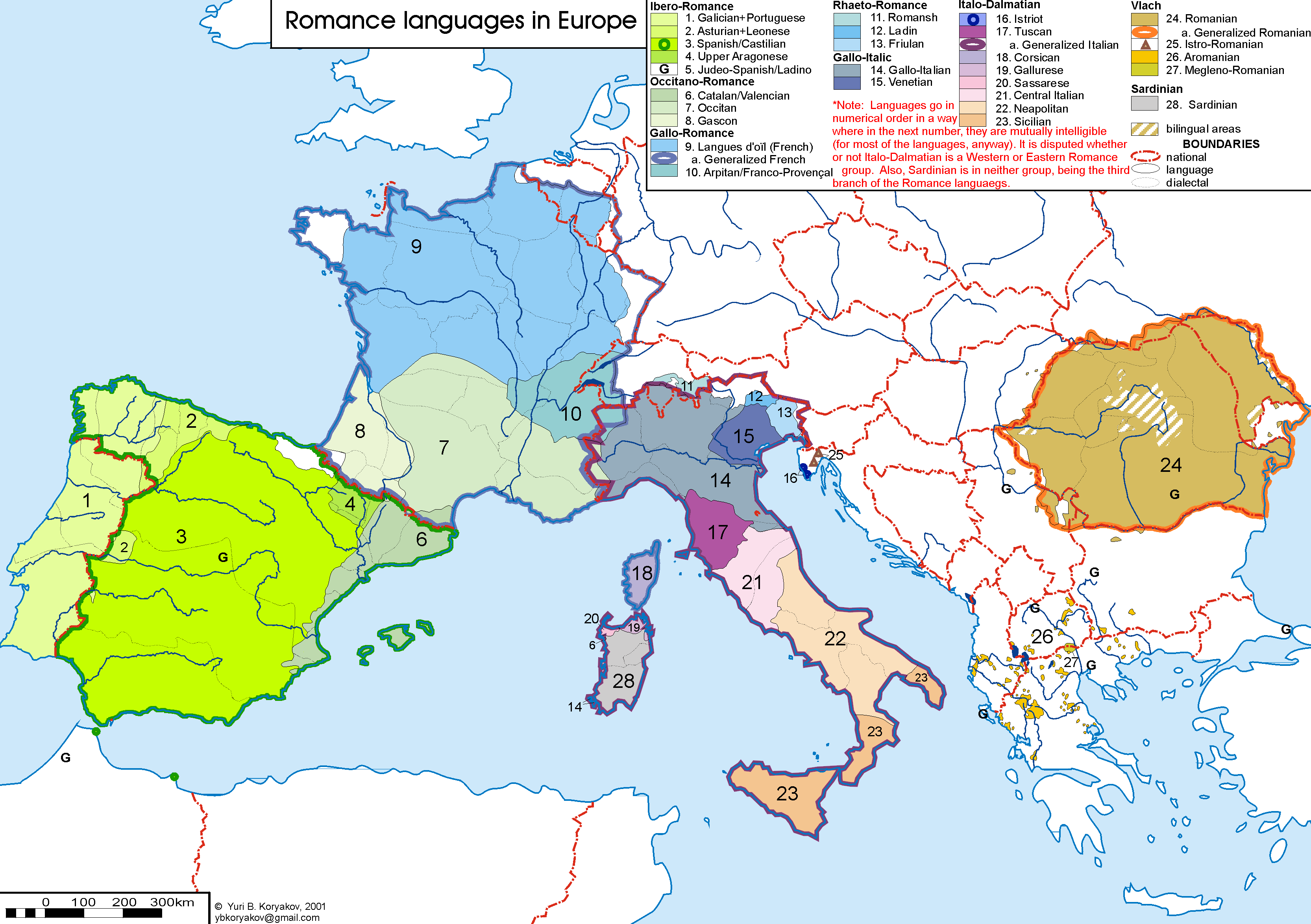
Romance Language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, #Romulus, their original calendar was established by their Roman legend, legendary list of kings of Rome, first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days inclusive counting, counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a Roman commerce, public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational calendar, observational lunar calendar, lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones (calendar), nones, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Off-by-one Error
An off-by-one error or off-by-one bug (known by acronyms OBOE, OBOB, OBO and OB1) is a logic error that involves a number that differs from its intended value by 1. An off-by-one error can sometimes appear in a mathematics, mathematical context. It often occurs in computer programming when a control flow#Loops, loop iterates one time too many or too few, usually caused by the use of non-strict inequality (≤) as the terminating condition where strict inequality (<) should have been used, or vice versa. Off-by-one errors also stem from confusion over zero-based numbering. Cases Looping over arrays Consider an array data type, array of items, and items ''m'' through ''n'' (inclusive) are to be processed. How many items are there? An intuitive answer may be , but that is off by one, exhibiting a #Fencepost error, fencepost error; the correct answer is . For this reason, ranges in computing are often represented by half-open intervals; the ra ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. An abacus consists of a two-dimensional array of Sliding (motion), slidable beads (or similar objects). In their earliest designs, the beads could be loose on a flat surface or sliding in grooves. Later the beads were made to slide on rods and built into a frame, allowing faster manipulation. Each rod typically represents one Numerical digit, digit of a multi-digit number laid out using a positional numeral system such as base ten (though some cultures used different numerical bases). Roman Empire, Roman and East Asian abacuses use a system resembling bi-quinary coded decimal, with a top deck (containing one or two beads) representing fives and a bottom deck (containing four or five beads) representing ones. Natural numbers are normally use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |