|
Cotton Dell
Cotton Dell is a nature reserve of the Staffordshire Wildlife Trust. It is a wooded valley area near the village of Cotton and about north of the village of Oakamoor, in Staffordshire, England. History The Cotton estate was owned in the 1700s by the politician Thomas Gilbert; he lived here from 1795, and tended the woodlands. In 1868 the woodlands became the property of Cotton College. The college closed in 1987, and the estate was sold by 1999, Cotton Dell then becoming a nature reserve."Discovering Cotton Dell". Leaflet by ''Staffordshire Wildlife Trust''. Description Car parking is at the Staffordshire County Council picnic area at Oakamoor, half a mile from the reserve. The area of the reserve is . There are paths through the site, which, in the valley terrain, are steep in places. Cotton Brook flows through the valley, and there is a path following the course of the brook. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton, Staffordshire
Cotton is a village and civil parish in Staffordshire, England. It is about north-east of Cheadle. Cotton Hall, originally built in the 17th century, was the home of Cotton College from 1863 until its closure in 1987. Buildings Cotton Hall Cotton Hall, which dates from 1630, was bought by Thomas Gilbert (1688–1742). His son, the politician Thomas Gilbert (c.1719–1798) inherited the building, and it was largely rebuilt. In 1844 it was bought by John Talbot, 16th Earl of Shrewsbury, and he offered it in 1846 to Frederick William Faber as a rural retreat for his small Roman Catholic community, called the Brothers of the Will of God, in Birmingham.Cotton Hall , his life and books. Accessed 28 August 2016.Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad-leaved Tree
A broad-leaved, broad-leaf, or broadleaf tree is any tree within the diverse botanical group of angiosperms that has flat leaves and produces seeds inside of fruits. It is one of two general types of trees, the other being a conifer, a tree with needle-like or scale-like leaves and seeds borne in woody cones. Broad-leaved trees are sometimes known as hardwoods. Most deciduous trees are broad-leavedLee, S. and A. RafloTrees and Water. Virginia Water Resources Research Center. Virginia Tech. but some are coniferous, like larches. U.S. Department of Agriculture Tree types Gallery |
Nature Reserves In Staffordshire
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
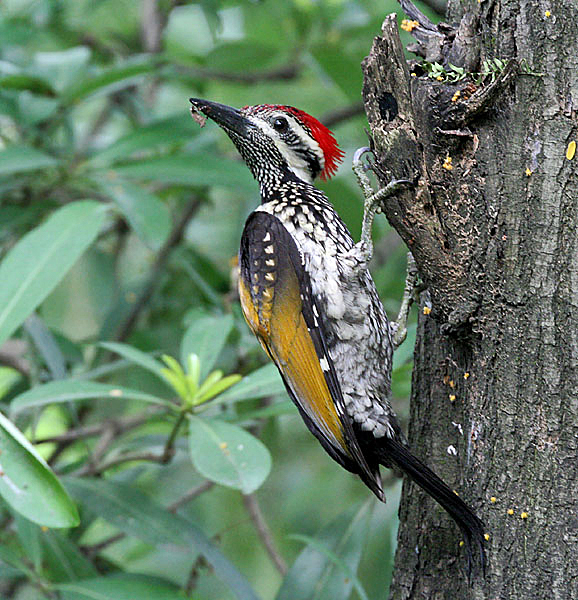
Woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions. Most species live in forests or woodland habitats, although a few species are known that live in treeless areas, such as rocky hillsides and deserts, and the Gila woodpecker specialises in exploiting cacti. Members of this family are chiefly known for their characteristic behaviour. They mostly forage for insect prey on the trunks and branches of trees, and often communicate by drumming with their beaks, producing a reverberatory sound that can be heard at some distance. Some species vary their diet with fruits, birds' eggs, small animals, tree sap, human scraps, and carrion. They usually nest and roost in holes that they excavate in tree trunks, and their abandoned holes are of importance to other cavity-nesting birds. They sometimes com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
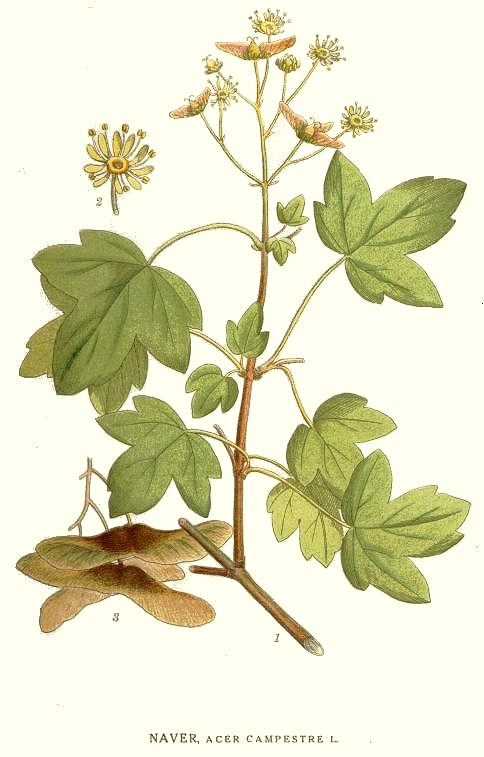
Field Maple
''Acer campestre'', known as the field maple, is a flowering plant species in the family Sapindaceae. It is native to much of continental Europe, Britain, southwest Asia from Turkey to the Caucasus, and north Africa in the Atlas Mountains. It has been widely planted, and is introduced outside its native range in Europe and areas of USA and Western Australia with suitable climate. Description It is a deciduous tree reaching tall, with a trunk up to in diameter, with finely fissured, often somewhat corky bark. The shoots are brown, with dark brown winter buds. The leaves are in opposite pairs, long (including the petiole) and broad, with five blunt, rounded lobes with a smooth margin. Usually monoecious, the flowers are produced in spring at the same time as the leaves open, yellow-green, in erect clusters across, and are insect-pollinated. The fruit is a samara with two winged achenes aligned at 180°, each achene is wide, flat, with a wing. The two varieties, not accept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holly
''Ilex'' (), or holly, is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen or deciduous trees, shrubs, and climbers from tropics to temperate zones worldwide. The type species is '' Ilex aquifolium'', the common European holly used in Christmas decorations and cards. Description The genus ''Ilex'' is divided into three subgenera: *''Ilex'' subg. ''Byronia'', with the type species ''Ilex polypyrena'' *''Ilex'' subg. ''Prinos'', with 12 species *''Ilex'' subg. ''Ilex'', with the rest of the species The genus is widespread throughout the temperate and subtropical regions of the world. It includes species of trees, shrubs, and climbers, with evergreen or deciduous foliage and inconspicuous flowers. Its range was more extended in the Tertiary period and many species are adapted to laurel forest habitats. It occurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech-oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 to 60 known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are a typically rather short-lived pioneer species widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates. Description Birch species are generally small to medium-sized trees or shrubs, mostly of northern temperate and boreal climates. The simple leaves are alternate, singly or doubly serrate, feather-veined, petiolate and stipulate. They often appear in pairs, but these pairs are really borne on spur-like, two-leaved, lateral branchlets. The fruit is a small samara, although the wings may be obscure in some species. They differ from the alders (''Alnus'', another genus in the family) in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class (biology), class, Pinopsida. All Neontology, extant conifers are perennial plant, perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include Cedrus, cedars, Pseudotsuga, Douglas-firs, Cupressaceae, cypresses, firs, junipers, Agathis, kauri, larches, pines, Tsuga, hemlocks, Sequoioideae, redwoods, spruces, and Taxaceae, yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecology, ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordshire Wildlife Trust
The Staffordshire Wildlife Trust is a wildlife trust covering the county of Staffordshire, England. Organisation and activities It is one of 46 Wildlife Trusts; each is a registered charity and is a member of the Royal Society of Wildlife Trusts. The Staffordshire Wildlife Trust was founded in 1969. It has about 160 members of staff, overseen by a board of trustees. The Trust is supported by a network of volunteers."About us" ''Staffordshire Wildlife Trust''. Retrieved 31 October 2022. The Trust has two s: the Wolseley Centre, near |
Ancient Woodland
In the United Kingdom, an ancient woodland is a woodland that has existed continuously since 1600 or before in England, Wales and Northern Ireland (or 1750 in Scotland). Planting of woodland was uncommon before those dates, so a wood present in 1600 is likely to have developed naturally. In most ancient woods, the trees and shrubs have been cut down periodically as part of the management cycle. Provided that the area has remained as woodland, the stand is still considered ancient. Since it may have been cut over many times in the past, ancient woodland does not necessarily contain very old trees. For many species of animal and plant, ancient woodland sites provide the sole habitat, and for many others, conditions on these sites are much more suitable than those on other sites. Ancient woodland in the UK, like rainforest in the tropics, is home to rare and threatened species. For these reasons ancient woodland is often described as an irreplaceable resource, or 'critical natural ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton College
Cotton College was a Roman Catholic boarding school in Cotton, Staffordshire, United Kingdom. It was also known as ''Saint Wilfrid's College''. The school buildings were centred on Cotton Hall, a country house used by religious communities from the 1840s until the school moved there in 1873. The school closed in 1987 and the site is now derelict. The school and its chapel (St Wilfrid's church) are both Grade II listed buildings.Cotton College, Cotton from British listed buildings, retrieved 22 December 2014 History of the school The school was founded in 1763 at – now ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)