|
Corythoraptor Jacobsi
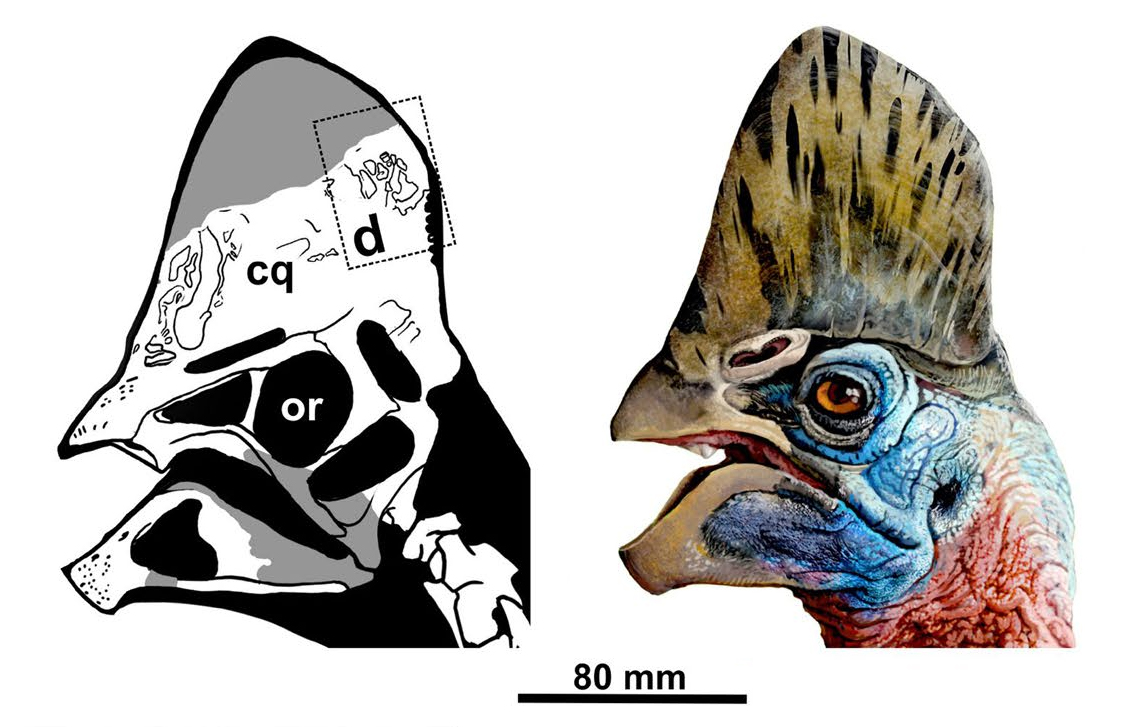
''Corythoraptor'' () is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian Nanxiong Formation of South China. It contains one species, ''C. jacobsi'', known from a single well-preserved skeleton, and named after paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs. It bears a tall crest similar to that of the modern cassowary, and possibly had a similar functionality of display and resonance to detect lower-frequency sounds. Like other oviraptorids, the bones of ''Corythoraptor'' were heavily pneumatized with many air pockets. Microanalysis of the bones indicates seasonal growth spurts, and the type specimen probably died at the age of 6 or 7, meaning growth continued into at least the 8th year of development. The type specimen reached in length. Oviraptorids may have predominantly inhabited arid environments and ate xerophytic (drought-resistant) plants, nuts, and seeds. However, ''Corythoraptor'' coexisted with six other oviraptorid genera, and they may have all eaten different foods ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganzhou
Ganzhou (), alternately romanized as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Jiangxi province, China, bordering Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, and Hunan to the west. Its administrative seat is at Zhanggong District. History Early settlement and administration In 201 CE, Emperor Gaozu of Han established a county in the territory of modern Ganzhou. In 236 CE, during the Three Kingdoms period, the was established in the area. In the early years, Han Chinese settlement and authority in the area was minimal and largely restricted to the Gan River basin. The river, a tributary of the Yangtze via Poyang Lake, provided a route of communication from the north as well as irrigation for rice farming. Sui dynasty In 589 CE, during the Sui dynasty, the was abolished, and the area was reorganized as Qianzhou. During the Song, immigration from the north bolstered the local population and drove local aboriginal tribes into admixing with the nornterners. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the of typically allow , |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyesocket
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corythoraptor Casque Restoration
''Corythoraptor'' () is a genus of Oviraptoridae, oviraptorid dinosaur from the Maastrichtian, late Maastrichtian Nanxiong Formation of South China. It contains one species, ''C. jacobsi'', known from a single well-preserved skeleton, and named after paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs. It bears a tall crest similar to that of the modern cassowary, and possibly had a similar functionality of display (zoology), display and resonance to detect lower-frequency sounds. Like other oviraptorids, the bones of ''Corythoraptor'' were heavily skeletal pneumaticity, pneumatized with many air pockets. Microanalysis of the bones indicates seasonal growth spurts, and the type specimen probably died at the age of 6 or 7, meaning growth continued into at least the 8th year of development. The type specimen reached in length. Oviraptorids may have predominantly inhabited arid environments and ate xerophytic (drought-resistant) plants, nuts, and seeds. However, ''Corythoraptor'' coexisted with six othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Methodist University
, mottoeng = "The truth will make you free" , established = , type = Private research university , accreditation = SACS , academic_affiliations = , religious_affiliation = United Methodist Church , president = R. Gerald Turner , provost = Elizabeth G. Loboa , coor = , students = 12,373 (fall 2020) , undergrad = 6,827 (fall 2020) , postgrad = 5,546 (fall 2020) , faculty = 1,151; 754 full time (Fall 2019) , endowment = $2.0 billion (2021)As of June 30, 2020. , city = Dallas , state = Texas , country = United States , campus = Large City , campus_size= (main) , colors = SMU Red SMU Blue , sports_nickname = Mustangs , athletics_affiliations = NCAA Division I FBS – AAC , mascot = Peruna , website = , logo = Southern Methodist University logo.svg , logo_upright = .8 , free_label2 = Newspaper , free2 = ''The Daily Campus'' , free_label = Other campuses , free = Taos Southern Methodist University (SMU) is a private research university in Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heyuannia
''Heyuannia'' ("from Heyuan") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, in what is now China and Mongolia. It was the first oviraptorid found in China; most others were found in neighbouring Mongolia. Two species are known: ''H. huangi'', named by Lü Junchang in 2002 from the Dalangshan Formation; and ''H. yanshini'', originally named as a separate genus ''Ingenia'' from the Barun Goyot Formation by Rinchen Barsbold in 1981, and later renamed to ''Ajancingenia'' in 2013 due to the preoccupation of ''Ingenia''. The latter name was eventually discarded due to various ethical issues surrounding the author. Discovery and naming ''H. huangi'' The type species, ''Heyuannia huangi'', was named and described by Lü Junchang in 2002. The generic name refers to the city of Heyuan. The specific name honours Huang Dong, the director of the Heyuan Museum. The holotype, HYMV1-1, was discovered in Guangdong near Huangsha in layers of the Dalang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Pose
Non-avian dinosaur and bird fossils are frequently found in a characteristic posture consisting of head thrown back, tail extended, and mouth wide open. The cause of this posture—often called a "death pose"—has been a matter of scientific debate. Traditional explanations ranged from strong ligaments in the animal's neck desiccating and contracting to draw the body into the pose, to water currents arranging the remains in the position. Faux and Padian suggested in 2007 that the live animal was suffering opisthotonus during its death throes, and that the pose is not the result of any post-mortem process at all. They also reject the idea of water as responsible for randomly arranging the bodies in a "death pose", as different parts of the body and the limbs can be in different directions, which they found unlikely to be the result of moving water.Padian K & Faux M (2007)"The opisthotonic posture of vertebrate skeletons: post-mortem contraction or death throes?" ''Paleobiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
