|
Coroneia
Koroneia ( el, Κορώνεια, before 1915: Κουτουμουλάς - ''Koutoumoulas'') is a village and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Livadeia, of which it is a municipal unit. The population of the municipal unit was 3,170 at the 2011 census.Detailed census results 2011 Geography The municipal unit Koroneia consists of the following communities: Agios Georgios (the seat of the former municipality), Agia Anna, Agia Triada, Alalkomenes and Koroneia. The ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center of Boeotia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Coronea (394 BC)
The Battle of Coronea in 394 BC, also Battle of Coroneia, was a battle in the Corinthian War, in which the Spartans and their allies under King Agesilaus II defeated a force of Thebans and Argives that was attempting to block their march back into the Peloponnese. It ranks among the deadliest of the Hoplite battles, despite its comparative obscurity, when matched up against more famous battles like the Battle of Delium in 424, and the Battle of Mantinea in 362. Prelude The Corinthian War began in 395 BC when Thebes, Argos, Corinth, and Athens, with Persian support and funding, united to oppose Spartan intervention in Locris and Phocis. At the start of the war, Agesilaus was in Ionia, campaigning against the Persians. When hostilities opened, he was recalled with his forces, and began an overland march through Thrace and central Greece back to the Peloponnese. Entering Boeotia, he was opposed by a force composed primarily of Thebans, allied Boeotians, and Argives. Agesilaus's fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; grc-gre, Ἀγησίλαος ; c. 442 – 358 BC) was king of Sparta from c. 399 to 358 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC. Despite the traditional secrecy fostered by the Spartiates, the reign of Agesilaus is particularly well-known thanks to the works of his friend Xenophon, who wrote a large history of Greece (the '' Hellenica'') covering the years 411 to 362 BC, therefore extensively dealing with Agesilaus' rule. Xenophon furthermore composed a panegyric biography of his friend, perhaps to clean his memory from the criticisms voiced against him. Another historical tradition—much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livadeia
Livadeia ( el, Λιβαδειά ''Livadiá'', ; grc, Λεβάδεια, Lebadeia or , ''Lebadia'') is a town in central Greece. It is the capital of the Boeotia regional district. Livadeia lies north-west of Athens, west of Chalkida, south-east of Lamia, east-south-east of Amfissa, and east-north-east of Nafpaktos. The town lies some west of Greek National Road 3, to which it is linked by National Road 48. The area around Livadeia is mountainous, with farming activities mainly confined to the valleys. The area has traditionally been associated with the production and processing of cotton and tobacco, as well as the cultivation of cereal crops and the raising of livestock. The city also known for having participated in the War of Troy in allegiance with Mycenae. Livadeia is home to Levadiakos FC, members of the Greek Superleague. Geography The municipality of Livadeia covers an area of , the municipal unit of Livadeia and the community . Municipality The municipality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronus (Greek Mythology)
In Greek mythology, the name Coronus (Ancient Greek: Κόρωνος means "crooked, curved") may refer to: *Coronus, king of the Lapiths, the son of Caeneus and counted among the Argonauts. In some accounts his father was Actor. His own children were Leonteus and Lysidice. He led a war against King Aegimius and was killed by Heracles. *Coronus, king of Sicyon, son of Apollo and Chrysorthe, and father of Lamedon and Corex. Coronus inherited the kingdom of Sicyon from his maternal grandfather Orthopolis. Corex succeeded to his father's power, but himself left no heirs so the kingdom was usurped by Epopeus, after whose death it went back to Lamedon. *Coronus, the Corinthian son of Thersander. He and his brother Haliartus were adopted by Athamas after the latter had lost all of his own sons. He was given land by Athamas and founded Coroneia. *Coronus, father of Anaxirhoe, herself mother of Hyrmine *Coronus, father of Asteria, herself possible mother of Idmon.Scholia on Apollonius Rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
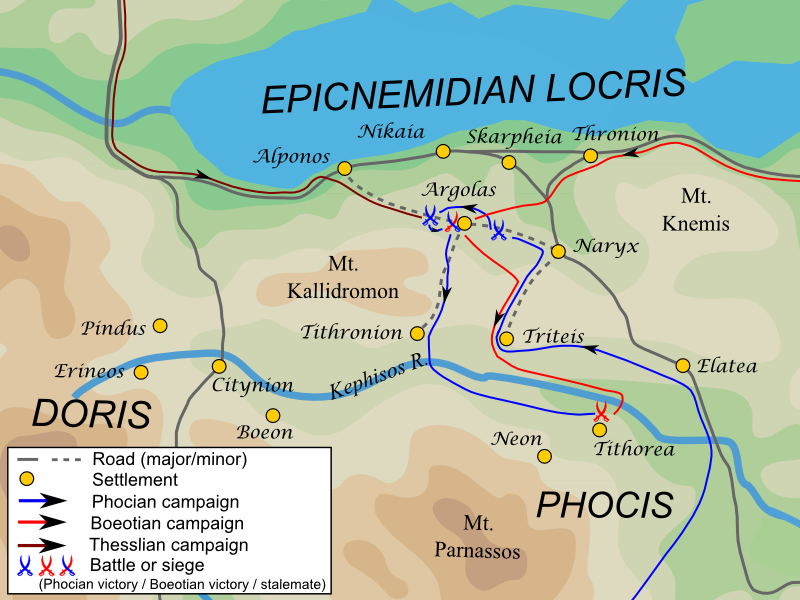
Onomarchus
Onomarchus ( grc, Ὀνόμαρχος) was general of the Phocians in the Third Sacred War, brother of Philomelus and son of Theotimus. After his brother's death he became commander of the Phocians and pursued a warmongering policy until his final defeat. Commander of the Phocians Onomarchus commanded a division of the Phocian army under his brother, Philomelus, in the action at Tithorea, in which Philomelus perished. After the battle Onomarchus gathered the remains of the Phocian army and retreated to Delphi. An assembly of the people was held, in which Onomarchus strongly urged the prosecution of the war—in opposition to the counsels of the more moderate party. In the winter of 354 / 353 BC, the Phocians decided to make Onomarchus supreme commander, in place of Philomelus. As far as the funding of his campaign was concerned, Onomarchus went a step further than his brother and predecessor, who had 'borrowed' from the sacred treasures of Delphi, keeping, however, scrupulou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Sacred War
The Third Sacred War (356–346 BC) was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians. The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League (dominated at that moment by Thebes), for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. Thus, although the Phocians suffered several major defeats, they were able to continue the war for many years, until eventually all parties were nearing exhaustion. Philip II used the distraction of the other states to increase his power in northern Greece, in the process becoming ruler of Thessaly. In the end, Philip's growing power, and the exhaustion of the other states, allowed him to impose a peaceful settlement of the war, marking a major step in the rise of Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argive
Argos (; el, Άργος ; grc, label=Ancient and Katharevousa, Ἄργος ) is a city in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center for the area. Since the 2011 local government reform it has been part of the municipality of Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 138.138 km2. It is from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour. A settlement of great antiquity, Argos has been continuously inhabited as at least a substantial village for the past 7,000 years. A resident of the city of Argos is known as an Argive ( , ; grc-gre, Ἀργεῖος). However, this term is also used to refer to those ancient Greeks generally who assaulted the city of Troy during the Trojan War; the term is more widely applied by the Homeric bards. Numerous ancient monuments can be found in the city today. Agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Greece (region)
Central Greece ( el, Περιφέρεια Στερεάς Ελλάδας, translit=Periféria Stereás Elládhas, , colloquially known as Ρούμελη (''Roúmeli'')) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. The region occupies the eastern half of the traditional Geographic regions of Greece, region of Central Greece, including the island of Euboea. To the south it borders the regions of Attica (region), Attica and the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, to the west the region of West Greece and to the north the regions of Thessaly and Epirus (region), Epirus. Its capital city is Lamia (city), Lamia. Administration The region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with Thessaly, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of Thessaly and Central Greece based at Larissa. The region is based at Lamia (city), Lamia and is divided into five regional units o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; grc-gre, Ἥρα, Hḗrā; grc, Ἥρη, Hḗrē, label=none in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Olympus, sister and wife of Zeus, and daughter of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. One of her defining characteristics in myth is her jealous and vengeful nature in dealing with any who offend her, especially Zeus' numerous adulterous lovers and illegitimate offspring. Her iconography usually presents her as a dignified, matronly figure, upright or enthroned, crowned with a ''polos'' or diadem, sometimes veiled as a married woman. She is the patron goddess of lawful marriage. She presides over weddings, blesses and legalises marital unions, and protects women from harm during childbirth. Her sacred animals include the cow, cuckoo and the peacock. She is sometimes shown holding a pomegranate, as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Thebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_2017_(detail).jpg)



_Pompeian_Art.jpg)
