|
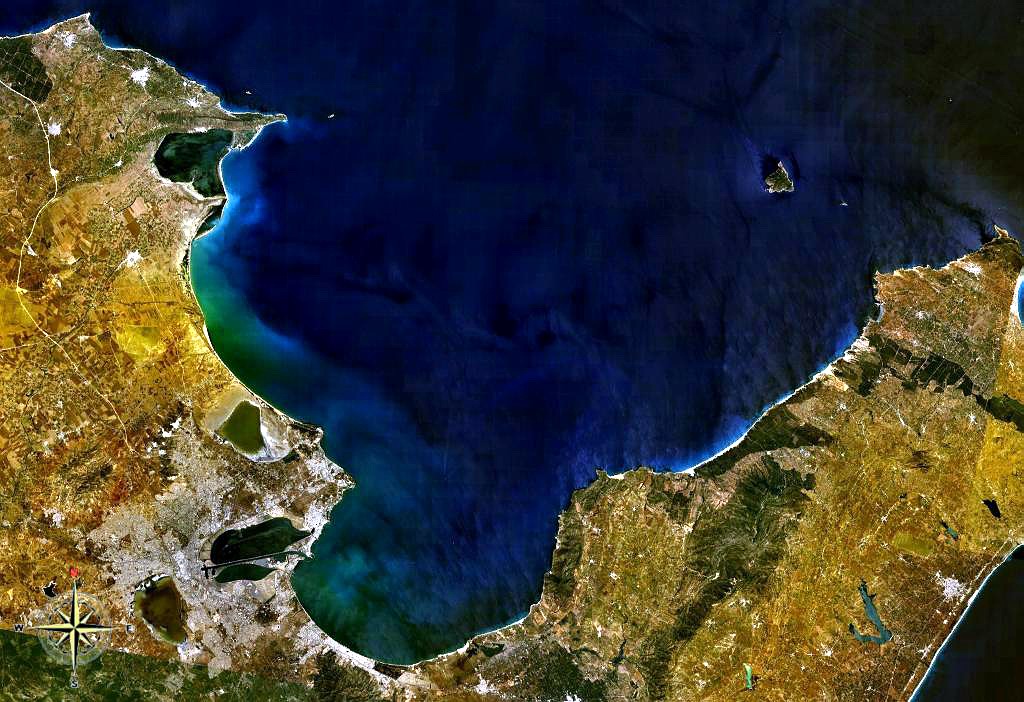
Coronation Gulf
Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf. The northwest point is Cape Krusenstern (not the Cape Krusenstern in Alaska). South of that is Richardson Bay and the mouths (from west to east) of the Rae River, Richardson River and the large Coppermine River, Napaaktoktok River, and the Asiak River. The Tree River enters at the south center. At the southeast end is the large Bathurst Inlet Bathurst Inlet, officially Kiluhiqtuq, is a deep inlet located along the northern coast of the Canadian mainland, at the east end of Coronation Gulf, into which the Burnside and Western rivers empty. The name, or its native equivalent ''Kingo .... At the northeast end is Cape Flinders on the Kent Peninsula. In the center of the gulf lies the Duke of York Archipelago. The gulf was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Indicating Coronation Gulf, Nunavut, Canada
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as Physical body, objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to Context (language use), context or Scale (map), scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Flinders
{{KitikmeotNU-geo-stub ...
Cape Flinders is a headland in the northern Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is located on the western point of the Kent Peninsula, now known as Kiillinnguyaq. The cape was named by Sir John Franklin in 1821 after the navigator Matthew Flinders. References Flinders Flinders may refer to: Places Antarctica * Flinders Peak, near the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula Australia New South Wales * Flinders County, New South Wales * Shellharbour Junction railway station, Shellharbour * Flinders, New South Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulfs Of Kitikmeot Region
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Chann .... See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large national audience. Daily broadsheet editions are printed for D.C., Maryland, and Virginia. The ''Post'' was founded in 1877. In its early years, it went through several owners and struggled both financially and editorially. Financier Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy in 1933 and revived its health and reputation, work continued by his successors Katharine and Phil Graham (Meyer's daughter and son-in-law), who bought out several rival publications. The ''Post'' 1971 printing of the Pentagon Papers helped spur opposition to the Vietnam War. Subsequently, in the best-known episode in the newspaper's history, reporters Bob Woodward and Carl Bernstein led the American press's investigation into what became known as the Watergate scandal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCGS Amundsen
CCGS ''Amundsen''CCGS stands for Canadian Coast Guard Ship is a and Arctic research vessel operated by the Canadian Coast Guard. The vessel entered service in 1979 as ''Franklin'' and was renamed ''Sir John Franklin'' in 1980 and served as such until 1996. Declared surplus, the vessel was used as an accommodation ship in Labrador in 1996 and placed in reserve in 2000. In 2003, the ship was reactivated and underwent conversion to an Arctic research vessel. The ship recommissioned as ''Amundsen''. Design and description The ''Pierre Radisson'' class were designed for Coast Guard operations in the Arctic Ocean.Maginley and Collin, p. 154 ''Amundsen'' has a standard displacement of and is fully loaded. The vessel has a gross tonnage of 5,911 and a net tonnage of 1,678. The ship is long overall with a beam of and a draught of .Saunders, p. 95 The vessel is propelled by two fixed-pitch propellers and one bow thruster powered by a diesel-electric system comprising six Alco M251 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MV Sea Adventurer
M/V ''Ocean Adventurer'' is an ice-capable expedition cruise ship operating commercial voyages to both polar regions, with Quark Expeditions of Seattle, WA, USA. The vessel was renamed on 1 October 2012, having previously been registered as "Clipper Adventurer". She is the sister ship to the MV ''Lyubov Orlova''. Built in 1975 in the former Yugoslavia as ''Alla Tarasova'', she underwent a $13 million refit in 1998 managed by Master Mariner AB, Sweden. During the summer of 2009 Adventure Canada of Mississauga, Ontario, Canada carried passengers through the Northwest Passage on the ''Clipper Adventurer''. On 27 August 2010, ''Clipper Adventurer'' ran aground of a supposedly uncharted rock in the waters of Nunavut's Coronation Gulf during a cruise. The collision damaged the ship's ballast and fuel tanks, leading pollution to be released into the Coronation Gulf. 128 passengers and 69 crew members were stranded until they were rescued by the CCGS ''Amundsen''. It was later found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard conditions for temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Arctic Expedition 1913–16
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Jenness
Diamond Jenness, (February 10, 1886, Wellington, New Zealand – November 29, 1969, Chelsea, Quebec, Canada) was one of Canada's greatest early scientists and a pioneer of Canadian anthropology. Early life (1886–1910) Family and childhood Diamond Jenness was the second youngest son in a middle-class family of ten children. His father's profession was that of a watchmaker/jeweler, though he also installed several clocks in municipal building towers in New Zealand. The family was encouraged to read, learn music, and engage in sports. Richling, in his biography “In Twilight and in Dawn,” writes that the young Jenness “was a proficient outdoorsman and an accomplished sharpshooter,” skills that helped prepare him for his experience in the arctic years later. Education At an early age, Jenness showed proficiency for learning. He earned his first scholarship at the age of twelve by entering a composition competition for children under fourteen. In those days, in New Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Martin Anderson
Rudolph Martin Anderson (June 30, 1876 – June 21, 1961) was an American born Canadian zoologist and explorer. Early life He was born in Decorah, Iowa in 1876, the son of John E. A. Anderson. He received a Ph.D. from the University of Iowa in 1906; his dissertation was entitled, ''The birds of Iowa''. Military service He was a veteran of the Spanish–American War, serving as a corporal in the 52nd Iowa Volunteer Infantry. He served with the 54th Infantry National Guard of Iowa from 1900 to 1906. He was a captain with the National Guard of Missouri from 1906 to 1908. Civilian career Anderson participated in the Stefansson-Anderson Arctic Expedition which explored Alaska and the northern Yukon from 1908 to 1912 and was part of the Canadian Arctic Expedition led by Vilhjalmur Stefansson from 1913 to 1916. Anderson joined the Explorers Club in New York in 1912, but resigned six years later. He assisted in the development of the Migratory Birds Convention signed by Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronation Of George IV
The coronation of George IV as King of the United Kingdom took place at Westminster Abbey, London, on 19 July 1821. Originally scheduled for 1 August of the previous year, the ceremony had been postponed due to the parliamentary proceedings of George's estranged wife, Caroline of Brunswick; because these failed to deprive Queen Caroline of her titles and obtain a divorce from the King, she was excluded from the ceremony. In accordance with George's lavish personal tastes, the coronation was the most extravagant ever staged and a number of the traditional elements of the ceremonial were conducted for the last time. Background George had acceded to the throne on 29 January 1820, on the death of his father, King George III, at Windsor Castle. The late king had been debilitated by illness for most of the previous decade and George had been appointed prince regent in his father's place in 1811. From the start of the Regency, Prince George, already notorious for his numerous mistresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |