|
Contextual Inquiry
Contextual inquiry (CI) is a user-centered design (UCD) research method, part of the contextual design methodology. A contextual inquiry interview is usually structured as an approximately two-hour, one-on-one interaction in which the researcher watches the user in the course of the user's normal activities and discusses those activities with the user. Description Contextual inquiry defines four principles to guide the interaction: * Context—Interviews are conducted in the user's actual workplace. The researcher watches users do their own work tasks and discusses any artifacts they generate or use with them. In addition, the researcher gathers detailed re-tellings of specific past events when they are relevant to the project focus. * Partnership—User and researcher collaborate to understand the user's work. The interview alternates between observing the user as he or she works and discussing what the user did and why. * Interpretation—The researcher shares interpretations a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User-centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) or user-driven development (UDD) is a framework of process (not restricted to interfaces or technologies) in which usability goals, user characteristics, environment, tasks and workflow of a product, service or process are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. These tests are conducted with/without actual users during each stage of the process from requirements, pre-production models and post production, completing a circle of proof back to and ensuring that "development proceeds with the user as the center of focus." Such testing is necessary as it is often very difficult for the designers of a product to understand intuitively the first-time users of their design experiences, and what each user's learning curve may look like. User-centered design is based on the understanding of a user, their demands, priorities and experiences and when used, is known to lead to an increased product usefulness and usability as it delivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contextual Design
Contextual design (CD) is a user-centered design process developed by Hugh Beyer and Karen Holtzblatt. It incorporates ethnographic methods for gathering data relevant to the product via field studies, rationalizing workflows, and designing human–computer interfaces. In practice, this means that researchers aggregate data from customers in the field where people are living and applying these findings into a final product.Beyer, H. & Holtzblatt, K. (1998). Contextual Design: Defining Customer-Centered Systems. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann. Contextual design can be seen as an alternative to engineering and feature driven models of creating new systems. Process overview The contextual design process consists of the following top-level steps: contextual inquiry, interpretation, data consolidation, visioning, storyboarding, user environment design, and prototyping. Collecting data – contextual inquiry Contextual inquiry is a field data collection technique used to capture detai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interview
An interview is a structured conversation where one participant asks questions, and the other provides answers.Merriam Webster DictionaryInterview Dictionary definition, Retrieved February 16, 2016 In common parlance, the word "interview" refers to a one-on-one conversation between an ''interviewer'' and an ''interviewee''. The interviewer asks questions to which the interviewee responds, usually providing information. That information may be used or provided to other audiences immediately or later. This feature is common to many types of interviews – a job interview or interview with a witness to an event may have no other audience present at the time, but the answers will be later provided to others in the employment or investigative process. An interview may also transfer information in both directions. Interviews usually take place face-to-face and in person but the parties may instead be separated geographically, as in videoconferencing or telephone interviews. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
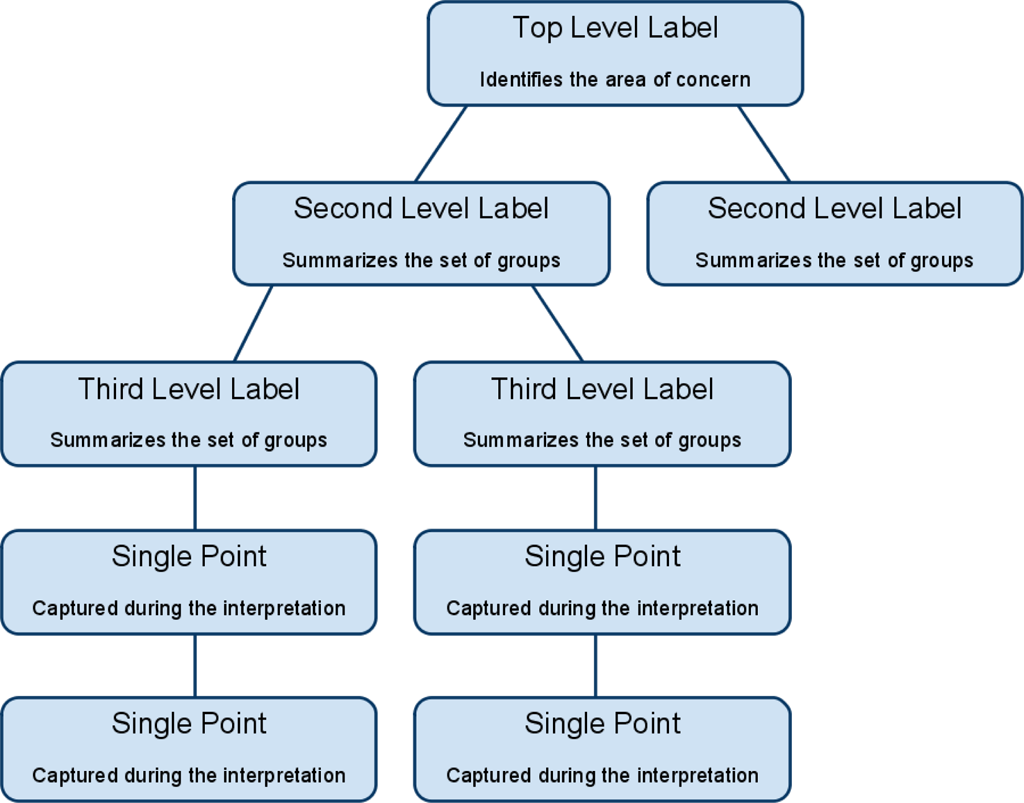
Affinity Diagram
The affinity diagram is a business tool used to organize ideas and data. It is one of the Seven Management and Planning Tools. People have been grouping data into groups based on natural relationships for thousands of years; however, the term affinity diagram was devised by Jiro Kawakita in the 1960s and is sometimes referred to as the KJ Method. The tool is commonly used within project management and allows large numbers of ideas stemming from brainstorming to be sorted into groups, based on their natural relationships, for review and analysis. It is also frequently used in contextual inquiry Contextual inquiry (CI) is a user-centered design (UCD) research method, part of the contextual design methodology. A contextual inquiry interview is usually structured as an approximately two-hour, one-on-one interaction in which the researcher w ... as a way to organize notes and insights from field interviews. It can also be used for organizing other freeform comments, such as open-ende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persona
A persona (plural personae or personas), depending on the context, is the public image of one's personality, the social role that one adopts, or simply a fictional character. The word derives from Latin, where it originally referred to a theatrical mask. On the social web, users develop virtual personas as online identities. Etymology The Latin word probably derived from the Etruscan word "", with the same meaning, and that from the Greek ('). Its meaning in the latter Roman period changed to indicate a "character" of a theatrical performance or court of law, when it became apparent that different individuals could assume the same role and that legal attributes such as rights, powers, and duties followed the role. The same individuals as actors could play different roles, each with its own legal attributes, sometimes even in the same court appearance. According to other sources, which also admit that the origin of the term is not completely clear, ''persona'' could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacit Knowledge
Tacit knowledge or implicit knowledge—as opposed to formal, codified or explicit knowledge—is knowledge that is difficult to express or extract, and thus more difficult to transfer to others by means of writing it down or verbalizing it. This can include personal wisdom, experience, insight, and intuition. For example, knowing that London is in the United Kingdom is a piece of ''explicit'' knowledge; it can be written down, transmitted, and understood by a recipient. In contrast, the ability to speak a language, ride a bicycle, knead dough, play a musical instrument, or design and use complex equipment requires all sorts of knowledge which is not always known ''explicitly'', even by expert practitioners, and which is difficult or impossible to explicitly transfer to other people. Overview Origin The term tacit knowing is attributed to Michael Polanyi's ''Personal Knowledge'' (1958). In his later work, ''The Tacit Dimension'' (1966), Polanyi made the assertion that "we ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Questionnaire
A questionnaire is a research instrument that consists of a set of questions (or other types of prompts) for the purpose of gathering information from respondents through survey or statistical study. A research questionnaire is typically a mix of close-ended questions and open-ended questions. Open-ended, long-term questions offer the respondent the ability to elaborate on their thoughts. The Research questionnaire was developed by the Statistical Society of London in 1838. Although questionnaires are often designed for statistical analysis of the responses, this is not always the case. Questionnaires have advantages over some other types of surveys in that they are cheap, do not require as much effort from the questioner as verbal or telephone surveys, and often have standardized answers that make it simple to compile data. However, such standardized answers may frustrate users as the possible answers may not accurately represent their desired responses. Questionnaires are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usability Test
Usability testing is a technique used in user-centered interaction design to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can be seen as an irreplaceable usability practice, since it gives direct input on how real users use the system. It is more concerned with the design intuitiveness of the product and tested with users who have no prior exposure to it. Such testing is paramount to the success of an end product as a fully functioning application that creates confusion amongst its users will not last for long. This is in contrast with usability inspection methods where experts use different methods to evaluate a user interface without involving users. Usability testing focuses on measuring a human-made product's capacity to meet its intended purposes. Examples of products that commonly benefit from usability testing are food, consumer products, websites or web applications, computer interfaces, documents, and devices. Usability testing measures the usability, or ease of use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. Ethnography in simple terms is a type of qualitative research where a person puts themselves in a specific community or organization in attempt to learn about their cultures from a first person point-of-view. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation—on the researcher participating in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scenario
In the performing arts, a scenario (, ; ; ) is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the ''commedia dell'arte'', it was an outline of entrances, exits, and action describing the plot of a play, and was literally pinned to the back of the scenery. It is also known as ''canovaccio'' or "that which is pinned to the canvas" of which the scenery was constructed. Surviving scenarios from the Renaissance contain little other than character names, brief descriptions of action, and references to specific lazzi with no further explanation. It is believed that a scenario formed the basis for a fully improvisational performance, though it is also likely that they were simple reminders of the plot for those members of the cast who were literate. Modern commedia troupes most often make use of a script with varying degrees of additional improvisation. In the creation of an opera or ballet, a scenario is often developed initially to indicate how the original so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–computer Interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is research in the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and computers. HCI researchers observe the ways humans interact with computers and design technologies that allow humans to interact with computers in novel ways. A device that allows interaction between human being and a computer is known as a "Human-computer Interface (HCI)". As a field of research, human–computer interaction is situated at the intersection of computer science, behavioral sciences, design, media studies, and several other fields of study. The term was popularized by Stuart K. Card, Allen Newell, and Thomas P. Moran in their 1983 book, ''The Psychology of Human–Computer Interaction.'' The first known use was in 1975 by Carlisle. The term is intended to convey that, unlike other tools with specific and limited uses, computers have many uses which often involve an open-ended dialogue between the user and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)