|
Constantin Meunier
Constantin Meunier (12 April 1831 – 4 April 1905) was a Belgian painter and sculptor. He made an important contribution to the development of modern art by elevating the image of the industrial worker, docker and miner to an icon of modernity. His work is a reflection of the industrial, social and political developments of his day and represents a compassionate and committed view of man and the world. Early life and education Constantin Meunier was born in the traditionally working-class area of Etterbeek in Brussels. His family was poor and suffered from the negative economic impact caused by the Belgian Revolution which had taken place the year before Meunier's birth. Meunier's father committed suicide when he was just four years old.Constantin Meuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
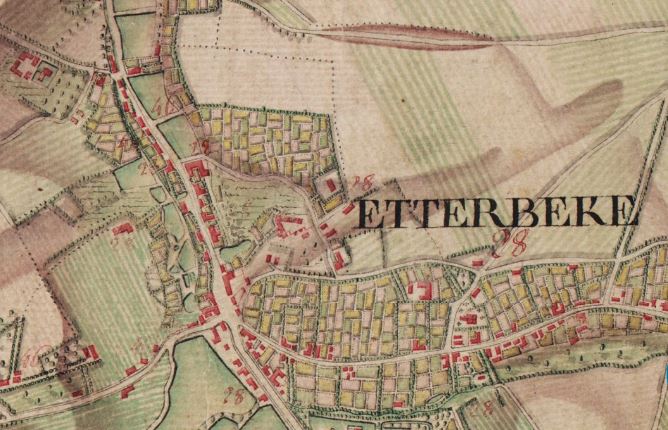
Etterbeek
Etterbeek (French: ; Dutch: ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). The main university campus of Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) is called ''Campus Etterbeek'', although it is geographically not within Etterbeek but in the adjacent Ixelles. History Origins and etymology According to legend, Saint Gertrude of Nivelles, daughter of Pippin of Landen, founded a chapel there in the 8th century. A document by Holy Roman Emperor Otto I, dated 966, mentions the church of ''Iatrebache''. The name ''Ietrebecca''—possibly from the Celtic root ''ett'' meaning "rapid movement" and the Dutch word ''beek'' meaning "stream"—is found for the first time in a document dated 1127. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasants' War (1798)
The Peasants' War (french: Guerre des Paysans, nl, Boerenkrijg, german: Klöppelkrieg, lb, Klëppelkrich) was a peasant revolt in 1798 against the French occupiers of the Southern Netherlands, a region which now includes Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Germany. The French had annexed the region in 1795 and control of the region was officially ceded to the French after the Treaty of Campo Formio in 1797. The revolt is considered part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Motivations for war After the Southern Netherlands was annexed by France, the French revolutionaries began to implement their policies regarding the Catholic Church. The Civil Constitution of the Clergy required that priests take an oath of allegiance to the state. Priests who refused such an oath (non-juring priests) were considered to be enemies of the state and could be removed from their positions and homes. Additionally, in early 1798, the French Council of Five Hundred passed a law requiring compulsory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society Of Sculptors, Painters And Gravers
The International Society of Sculptors, Painters and Gravers was a union of professional artists that existed from 1898 to 1925, "To promote the study, practice, and knowledge of sculpture, painting, etching, lithographing, engraving, and kindred arts in England or elsewhere...". It came to be known simply as The International.Philip Athill (January 1985)The International Society of Sculptors, Painters and Gravers ''The Burlington Magazine'' 127(982): 21-29+33. The society organised exhibitions, some for members only and some open to others, and social events such as musical evenings and soirées. The exhibitions were held in a number of London venues, and in other cities around England, including Nottingham and Manchester. Its founder and first president was James McNeill Whistler. On his death, the presidency was taken up by Auguste Rodin, with John Lavery as vice-president. The society contributed £500 towards the cost of Whistler's memorial. Formation The society was initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
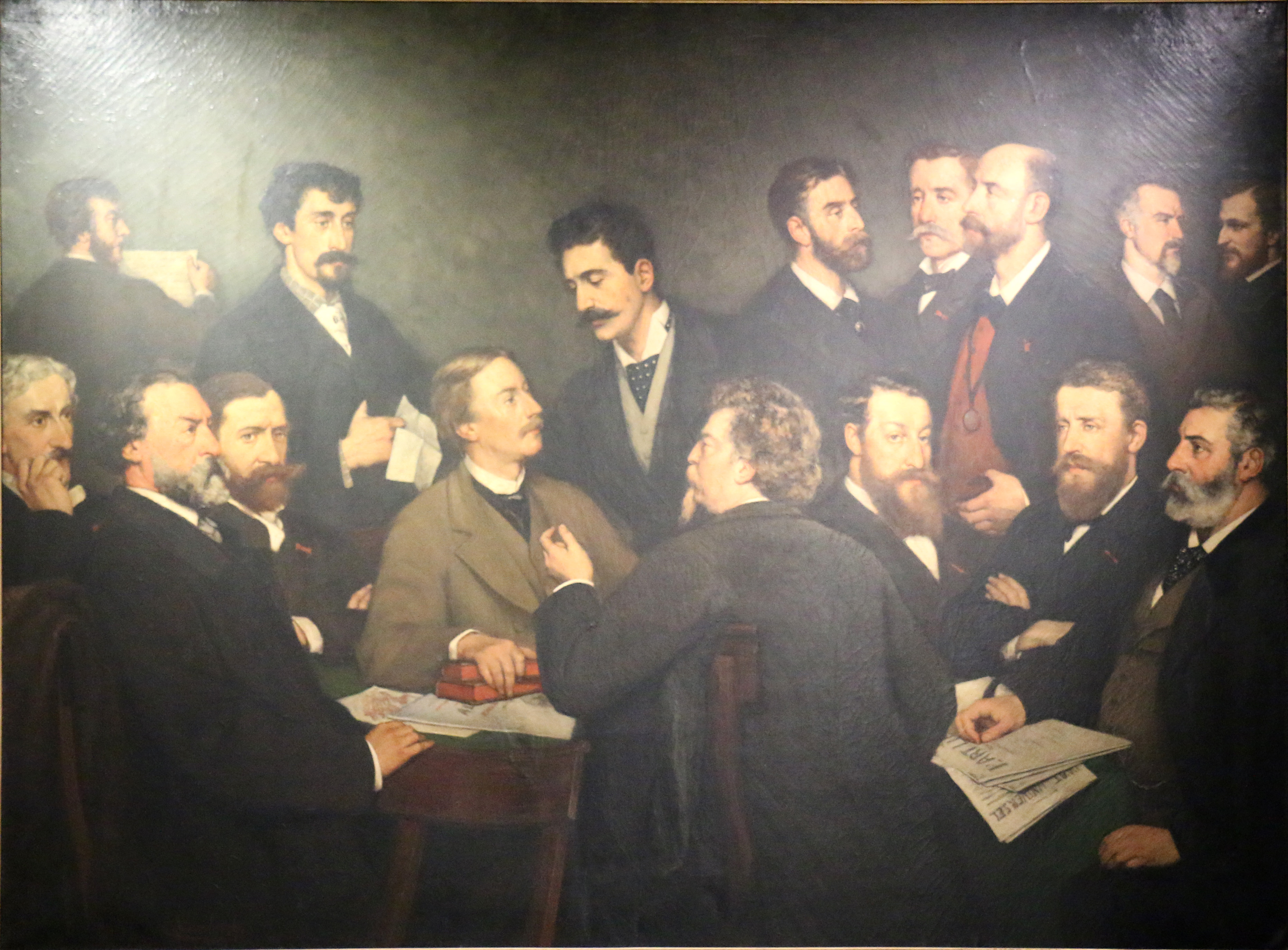
Société Libre Des Beaux-Arts
The Société Libre des Beaux-Arts ("Free Society of Fine Arts") was an organization formed in 1868 by Belgian artists to react against academicism and to advance Realist painting and artistic freedom. Based in Brussels, the society was active until 1876, by which time the aesthetic values it espoused had infiltrated the official Salon. It played a formative role in establishing avant-gardism in Belgium. History The first exhibition of the Free Society was held in 1868 to provide an alternative art space beyond the Salon. Three exhibitions were held in 1872. The society's manifesto was written by Camille van Camp and published 31 January, 1869. It promoted the "free and individual interpretation of nature" characteristic of Realist art, along with avant-garde concepts such as "struggle, change, freedom, progress, originality and tolerance." The society published the periodicals ''L'Art Libre'', a bi-monthly review (1871–72), and ''L'Art Universel'' (1873–76). In the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre Charpentier
Alexandre-Louis-Marie Charpentier (1856–1909) was a French sculptor, medalist, craftsman, and cabinet-maker. Life and work From working-class origins and apprenticed to an engraver as a young man, he became a studio assistant to the innovative medallist Hubert Ponscarme. Along with Ponscarme, Louis-Oscar Roty, and other artists, Charpentier advanced a resurgence of art in French medal design. Charpentier's patrons included André Antoine, for whom he designed theatre programmes. Charpentier experimented with a wide variety of formats and materials—tin, marble, wood, leather, and terra cotta work, the latter executed by ceramic artisan Emile Müller. He opened several cabinet shops and designed many sets of furniture. Many of his custom designs for fixtures (doorknobs, door plates, window handles and the like) were subsequently mass-produced and commercially sold. Several of Charpentier's works are part of the Musée d'Orsay collection. Social circle Carpentier' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of theatrical naturalism. He was a major figure in the political liberalization of France and in the exoneration of the falsely accused and convicted army officer Alfred Dreyfus, which is encapsulated in his renowned newspaper opinion headlined '' J'Accuse…!'' Zola was nominated for the first and second Nobel Prize in Literature in 1901 and 1902. Early life Zola was born in Paris in 1840 to François Zola (originally Francesco Zolla) and Émilie Aubert. His father was an Italian engineer with some Greek ancestry, who was born in Venice in 1795, and engineered the Zola Dam in Aix-en-Provence; his mother was French. The family moved to Aix-en-Provence in the southeast when Émile was three years old. Four years later, in 1847, his fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Van Der Stappen
Charles van der Stappen (also Karl van der Stappen; 19 September 1843 – 21 October 1910), was a Belgian sculptor, born in Saint-Josse-ten-Noode. Life Educated at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels (1859–1868), van der Stappen's contribution to the Brussels Salon was "The Faun's Toilet" of 1869, and thereafter he began to produce work of a high and novel order in every class of sculpture, and soon, along with Paul de Vigne, became recognized as the leader of the section of the new Belgian school of sculpture which infused models derived from Greek and Roman models and the art of the Italian Renaissance with naturalistic detail and fleeting action. His best-known funeral monuments are those to Alexandre Gendebien (1874) and Baron Coppens, at Sheel (1875). His statues include ''William the Silent,'' set up at the Petit Sablon Square, and two in the Brussels Museum, ''The Man with the Sword,'' and "The Sphinx". The bronze group ''Ompdrailles'' was acquired b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Garden Of Brussels
The Botanical Garden of Brussels (french: Jardin botanique de Bruxelles, nl, Kruidtuin van Brussel) is a former botanical garden in Brussels, Belgium. It was created in 1826 and stood on the Rue Royale/Koningsstraat in Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, near Brussels' Northern Quarter financial district, until its relocation in 1938 to the National Botanic Garden of Belgium in Meise, Flemish Brabant. Since 1984, the main orangery building has been a cultural complex and music venue of the French Community of Belgium known as Le Botanique. It can be accessed from Brussels-North railway station and Botanique/Kruidtuin metro station on lines 2 and 6 of the Brussels Metro. History Origins (–1830) A first plant garden (french: Jardin des plantes, link=no, nl, Plantentuin, link=no) had existed since the French rule of Belgium in 1797, at a different location, along Brussels' first wall, in the Hôtel de Nassau—a building belonging to the former Palace of Coudenberg where the É ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Father Damien
Father Damien or Saint Damien of Molokai, SS.CC. or Saint Damien De Veuster ( nl, Pater Damiaan or '; 3 January 1840 – 15 April 1889), born Jozef De Veuster, was a Roman Catholic priest from Belgium and member of the Congregation of the Sacred Hearts of Jesus and Mary, a missionary religious institute. He was recognized for his ministry, which he led from 1873 until his death in 1889, in the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi to people with leprosy (Hansen's disease), who lived in government-mandated medical quarantine in a settlement on the Kalaupapa Peninsula of Molokai. During this time, he taught the Catholic faith to the people of Hawaii. Father Damien also cared for the patients and established leaders within the community to build houses, schools, roads, hospitals, and churches. He dressed residents' ulcers, built a reservoir, made coffins, dug graves, shared pipes, and ate poi with them, providing both medical and emotional support. After eleven years caring for the physical, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Marteleur
''Le Marteleur'' (; variously translated as ''The Hammerman'' or ''The Drop Forger'') is a bronze sculpture by Belgian sculptor Constantin Meunier. It depicts a hammerman holding a pair of pincers and wearing an apron, cap, and spats. Created in 1886, several casts of the statue exist, including one on the campus of Columbia University. History ''Le Marteleur'' was contemporaneous with the Belgian strike of 1886, considered by historians to be the first time the Belgian working class achieved significant concessions from the national government. Inspired by the "plastic grandeur of the industrial worker," Meunier's work reflected the political and economic developments of his day in his depiction of the hammerer: while the realism of the statue indicated the difficulty of the worker's labor, the ''contrapposto'' posture of its subject, borrowed from Classical and Renaissance sculpture, idealized and elevated him. The plaster cast of the statue was exhibited at the Parisian Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |