|
Conditional Symmetric Instability
Conditional symmetric instability, or CSI, is a form of convective instability in a fluid subject to temperature differences in a uniform rotation frame of reference while it is thermally stable in the vertical and dynamically in the horizontal (inertial stability). The instability in this case develop only in an inclined plane with respect to the two axes mentioned and that is why it can give rise to a so-called "slantwise convection" if the air parcel is almost saturated and moved laterally and vertically in a CSI area. This concept is mainly used in meteorology to explain the mesoscale formation of intense precipitation bands in an otherwise stable region, such as in front of a warm front. The same phenomenon is also applicable to oceanography. Principle Hydrostatic stability An air particle at a certain altitude will be stable if its adiabatically modified temperature during an ascent is equal to or cooler than the environment. Similarly, it is stable if its temperature is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
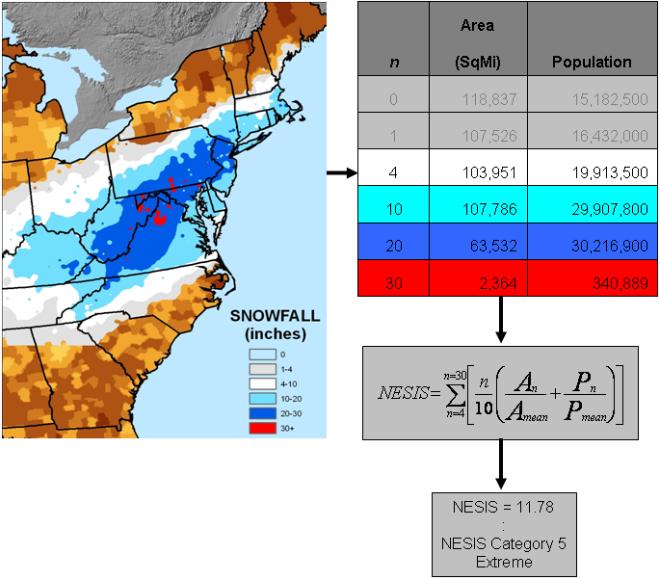
Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale
The Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale (NESIS) was created to measure snowstorms in the U.S. Northeast in much the same way the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale records hurricane intensity and the Enhanced Fujita Scale with tornadoes. The Scale NESIS was created by Paul Kocin of The Weather Channel and Louis Uccellini of the National Weather Service, classifies storms in one of five ways that range from ''Notable'' (the weakest designation) to ''Significant'', ''Major'', ''Crippling'', and ''Extreme''. storms have on the economy and transportation throughout the major cities in the Northeastern United States as well as the country as a whole.http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/snow-and-ice/nesis.phpref The variables measured on the scale include area, amount of snowfall, and the number of people living in the path of the storm. These numbers are calculated into a raw data number ranging from "1" for an insignificant fall to over "10" for a massive snowstorm. Based on these raw numbers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Corporation For Atmospheric Research
The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) is a US nonprofit consortium of more than 100 colleges and universities providing research and training in the atmospheric and related sciences. UCAR manages the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and provides additional services to strengthen and support research and education through its community programs. Its headquarters, in Boulder, Colorado, include NCAR's Mesa Laboratory, designed by I.M. Pei. UCAR was established in 1959 by faculty from 14 leading universities to support and nourish the atmospheric sciences. They were motivated by a newly recognized need for pooled observational and computational facilities and a strong research staff, which together would allow the academic community to carry out complex, long-term scientific programs beyond the reach of individual universities. This group’s first major action, in partnership with the National Science Foundation, was to establish NCAR. Since then, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average of one gigajoule of energy. This discharge may produce a wide range of electromagnetic radiation, from heat created by the rapid movement of electrons, to brilliant flashes of visible light in the form of black-body radiation. Lightning causes thunder, a sound from the shock wave which develops as gases in the vicinity of the discharge experience a sudden increase in pressure. Lightning occurs commonly during thunderstorms as well as other types of energetic weather systems, but volcanic lightning can also occur during volcanic eruptions. The three main kinds of lightning are distinguished by where they occur: either inside a single thundercloud (intra-cloud), between two clouds (cloud-to-cloud), or between a cloud and the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus (from Latin ''cumulus'', "heaped" and ''nimbus'', "rainstorm") is a dense, towering vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful buoyant air currents. Above the lower portions of the cumulonimbus the water vapor becomes ice crystals, such as snow and graupel, the interaction of which can lead to hail and to lightning formation, respectively. When occurring as a thunderstorm these clouds may be referred to as thunderheads. Cumulonimbus can form alone, in clusters, or along squall lines. These clouds are capable of producing lightning and other dangerous severe weather, such as tornadoes, hazardous winds, and large hailstones. Cumulonimbus progress from overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds and may further develop as part of a supercell. Cumulonimbus is abbreviated Cb. Appearance Towering cumulonimbus clouds are typically accompanied by smaller cumulus clouds. The cumulonimbus base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convective Available Potential Energy
In meteorology, convective available potential energy (commonly abbreviated as CAPE), is the integrated amount of work that the upward (positive) buoyancy force would perform on a given mass of air (called an air parcel) if it rose vertically through the entire atmosphere. Positive CAPE will cause the air parcel to rise, while negative CAPE will cause the air parcel to sink. Nonzero CAPE is an indicator of atmospheric instability in any given atmospheric sounding, a necessary condition for the development of cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds with attendant severe weather hazards. Mechanics CAPE exists within the conditionally unstable layer of the troposphere, the free convective layer (FCL), where an ascending air parcel is warmer than the ambient air. CAPE is measured in joules per kilogram of air (J/kg). Any value greater than 0 J/kg indicates instability and an increasing possibility of thunderstorms and hail. Generic CAPE is calculated by integrating vertically the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapse Rate
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. ''Lapse rate'' arises from the word ''lapse'', in the sense of a gradual fall. In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 °C/km (5.4 °F per 1,000 ft). It corresponds to the vertical component of the spatial gradient of temperature. Although this concept is most often applied to the Earth's troposphere, it can be extended to any gravitationally supported parcel of gas. Definition A formal definition from the ''Glossary of Meteorology'' is: :The decrease of an atmospheric variable with height, the variable being temperature unless otherwise specified. Typically, the lapse rate is the negative of the rate of temperature change with altitude change: :\Gamma = -\frac where \Gamma (sometimes L) is the lapse rate given in units of temperature divided by units of altitude, ''T'' is temperature, and ''z'' is altitude. Convection and adiabatic expansio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratiform ).
{{Disambiguation ...
Stratiform may refer to: * Any of the stratus family of clouds (fog, stratus clouds, altostratus clouds, cirrostratus clouds, nimbostratus clouds) and the precipitation coming from them. * Any occurrence of layered strata (see stratigraphic unit A stratigraphic unit is a volume of rock of identifiable origin and relative age range that is defined by the distinctive and dominant, easily mapped and recognizable petrographic, lithologic or paleontologic features (facies) that characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condensed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the purposes of protection, safety, and general information. It is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch of the Department of Commerce, and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland, within the Washington metropolitan area. The agency was known as the United States Weather Bureau from 1890 until it adopted its current name in 1970. The NWS performs its primary task through a collection of national and regional centers, and 122 local Weather Forecast Offices (WFOs). As the NWS is an agency of the U.S. federal government, most of its products are in the public domain and available free of charge. History Calls for the creation of a government weather bureau began as early as 1844, when the electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Vorticity
In fluid mechanics, potential vorticity (PV) is a quantity which is proportional to the dot product of vorticity and stratification. This quantity, following a parcel of air or water, can only be changed by diabatic or frictional processes. It is a useful concept for understanding the generation of vorticity in cyclogenesis (the birth and development of a cyclone), especially along the polar front, and in analyzing flow in the ocean. Potential vorticity (PV) is seen as one of the important theoretical successes of modern meteorology. It is a simplified approach for understanding fluid motions in a rotating system such as the Earth's atmosphere and ocean. Its development traces back to the circulation theorem by Bjerknes in 1898, which is a specialized form of Kelvin's circulation theorem. Starting from Hoskins et al., 1985, PV has been more commonly used in operational weather diagnosis such as tracing dynamics of air parcels and inverting for the full flow field. Even after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |