|
Compute Kernel
In computing, a compute kernel is a routine compiled for high throughput accelerators (such as graphics processing units (GPUs), digital signal processors (DSPs) or field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs)), separate from but used by a main program (typically running on a central processing unit). They are sometimes called compute shaders, sharing execution units with vertex shaders and pixel shaders on GPUs, but are not limited to execution on one class of device, or graphics APIs. Description Compute kernels roughly correspond to inner loops when implementing algorithms in traditional languages (except there is no implied sequential operation), or to code passed to internal iterators. They may be specified by a separate programming language such as " OpenCL C" (managed by the OpenCL API), as "compute shaders" written in a shading language (managed by a graphics API such as OpenGL), or embedded directly in application code written in a high level language, as in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve Hardware acceleration, hardware-accelerated Rendering (computer graphics), rendering. Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) began developing OpenGL in 1991 and released it on June 30, 1992. It is used for a variety of applications, including computer-aided design (CAD), video games, scientific visualization, virtual reality, and Flight simulator, flight simulation. Since 2006, OpenGL has been managed by the Non-profit organization, non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. Design The OpenGL specification describes an abstract application programming interface, application programming interface (API) for drawing 2D and 3D graphics. It is designed to be implemented mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shader (computer Graphics)
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene—a process known as '' shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of specialized functions in computer graphics special effects and video post-processing, as well as general-purpose computing on graphics processing units. Traditional shaders calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility. Most shaders are coded for (and run on) a graphics processing unit (GPU), though this is not a strict requirement. ''Shading languages'' are used to program the GPU's rendering pipeline, which has mostly superseded the fixed-function pipeline of the past that only allowed for common geometry transforming and pixel-shading functions; with shaders, customized effects can be used. The position and color ( hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast) of all pixels, vertices, and/or textu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SPIR-V
Standard Portable Intermediate Representation (SPIR) is an intermediate language for General-purpose computing on graphics processing units, parallel computing and graphics by Khronos Group. It is used in multiple execution environments, including the Vulkan graphics API and the OpenCL compute API, to represent a shader or Compute kernel, kernel. It is also used as an interchange language for cross compilation. SPIR-V is a new version of SPIR which was introduced in 2015 by the Khronos Group, and has since replaced the original SPIR, which was introduced in 2012. On September 19th 2024, Microsoft has announced plans to adopt SPIR-V as the DirectX, Direct3D Interchange format in place of DXIL, beginning support from Shader Model 7 on. Purpose The purposes of SPIR-V are to natively represent the primitives needed by compute and graphics; to separate high-level language from the interface to compute and graphics drivers; to be the distribution form, or distribute fully compiled bina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vulkan (API)
Vulkan is a cross-platform API and open standard for 3D graphics and computing. It was intended to address the shortcomings of OpenGL, and allow developers more control over the GPU. It is designed to support a wide variety of GPUs, CPUs and operating systems, and it is also designed to work with modern multi-core CPUs. Microsoft supports Vulkan 1.2 (and more) on Windows 10 and 11, with a downloadable compatibility pack. Overview Vulkan targets high-performance real-time 3D-graphics applications, such as video games and interactive media, and highly parallelized computing. Vulkan is intended to offer higher performance and more efficient CPU and GPU usage compared to the older OpenGL and Direct3D 11 APIs. It does so by providing a considerably lower-level API for the application than the older APIs, that more closely resembles how modern GPUs work. Vulkan is comparable to Apple's Metal API and Microsoft's Direct3D 12. In addition to its lower CPU usage, Vulkan is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scatter Gather (vector Addressing)
Gather/scatter is a type of Computer memory, memory addressing that at once collects (gathers) from, or stores (scatters) data to, multiple, arbitrary memory indices. Examples of its use include Sparse matrix, sparse linear algebra operations, sorting algorithms, fast Fourier transforms, and some computational graph theory problems. It is the vector equivalent of Addressing_mode#Base_plus_index, register indirect addressing, with gather involving indexed reads, and scatter, indexed writes. Vector processors (and some Single Instruction Multiple Data, SIMD units in CPUs) have hardware support for gather and scatter operations, as do many input/output systems, allowing large data sets to be transferred to main memory more rapidly. The concept is somewhat similar to vectored I/O, which is sometimes also referred to as scatter-gather I/O. This system differs in that it is used to map multiple sources of data from contiguous structures into a single stream for reading or writing. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synchronization (computer Science)
In computer science, synchronization is the task of coordinating multiple processes to join up or handshake at a certain point, in order to reach an agreement or commit to a certain sequence of action. Motivation The need for synchronization does not arise merely in multi-processor systems but for any kind of concurrent processes; even in single processor systems. Mentioned below are some of the main needs for synchronization: '' Forks and Joins:'' When a job arrives at a fork point, it is split into N sub-jobs which are then serviced by n tasks. After being serviced, each sub-job waits until all other sub-jobs are done processing. Then, they are joined again and leave the system. Thus, parallel programming requires synchronization as all the parallel processes wait for several other processes to occur. '' Producer-Consumer:'' In a producer-consumer relationship, the consumer process is dependent on the producer process until the necessary data has been produced. ''Exclusiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Operations
Atomic may refer to: * Of or relating to the atom, the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties * Atomic physics, the study of the atom * Atomic Age, also known as the "Atomic Era" * Atomic scale, distances comparable to the dimensions of an atom * Atom (order theory), in mathematics * Atomic (coffee machine), a 1950s stovetop coffee machine * Atomic (cocktail), a champagne cocktail * ''Atomic'' (magazine), an Australian computing and technology magazine * Atomic Skis, an Austrian ski producer Music * Atomic (band), a Norwegian jazz quintet * ''Atomic'' (Lit album), 2001 * ''Atomic'' (Mogwai album), 2016 * ''Atomic'', an album by Rockets, 1982 * ''Atomic'' (EP), by , 2013 * "Atomic" (song), by Blondie, 1979 * "Atomic", a song by Tiger Army from '' Tiger Army III: Ghost Tigers Rise'' See also * * * Atom (other) * Atomicity (database systems) * Atomism, philosophy about the basic building blocks of reality * Atomic C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Parallel
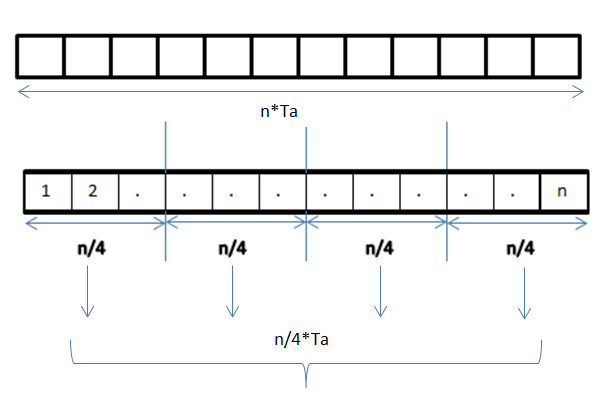
Data parallelism is parallelization across multiple processors in parallel computing environments. It focuses on distributing the data across different nodes, which operate on the data in parallel. It can be applied on regular data structures like arrays and matrices by working on each element in parallel. It contrasts to task parallelism as another form of parallelism. A data parallel job on an array of ''n'' elements can be divided equally among all the processors. Let us assume we want to sum all the elements of the given array and the time for a single addition operation is Ta time units. In the case of sequential execution, the time taken by the process will be ''n''×Ta time units as it sums up all the elements of an array. On the other hand, if we execute this job as a data parallel job on 4 processors the time taken would reduce to (''n''/4)×Ta + merging overhead time units. Parallel execution results in a speedup of 4 over sequential execution. The locality of data refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SIMD within a register (SWAR) Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation, compression and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Programming Paradigm
A programming paradigm is a relatively high-level way to conceptualize and structure the implementation of a computer program. A programming language can be classified as supporting one or more paradigms. Paradigms are separated along and described by different dimensions of programming. Some paradigms are about implications of the execution model, such as allowing Side effect (computer science), side effects, or whether the sequence of operations is defined by the execution model. Other paradigms are about the way code is organized, such as grouping into units that include both state and behavior. Yet others are about Syntax (programming languages), syntax and Formal grammar, grammar. Some common programming paradigms include (shown in hierarchical relationship): * imperative programming, Imperative code directly controls Control flow, execution flow and state change, explicit statements that change a program state ** procedural programming, procedural organized as function (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DirectCompute
Microsoft DirectCompute is an application programming interface (API) that supports running compute kernels on general-purpose computing on graphics processing units on Microsoft's Windows Vista, Windows 7 and later versions. DirectCompute is part of the Microsoft DirectX collection of APIs, and was initially released with the DirectX 11 API but runs on graphics processing units that use either DirectX 10 or DirectX 11. The DirectCompute architecture shares a range of computational interfaces with its competitors: OpenCL from Khronos Group, compute shaders in OpenGL, and CUDA from NVIDIA. The DirectCompute API brings enhanced multi-threading capabilities to leverage the emerging advanced compute resources. The API is designed for non-graphical applications to access and use GPU resources. Compute Pipeline The Compute pipeline is a type of graphics pipeline used for dispatching and executing compute shaders. Compute pipelines are run through compute command lists, which are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |