|
Computational Biology Department
The Computational Biology Department (CBD) is a division within the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. It is located in the Gates-Hillman Center. Established in 2007 by Robert F. Murphy as the Lane Center for Computational Biology with funding from Raymond J. Lane and Stephanie Lane, CBD became a department within the School of Computer Science in 2016. CBD faculty and students conduct research in genomics, systems biology, and biological imaging. Its faculty have served as president of the National Science Foundation, president of the International Society of Advanced Cytometry, and as a member of the National Institutes of Health Council of Councils; they have won awards such as the Overton Prize, a Guggenheim Fellowship, thOkawa Award a United States Air Force Young Investigator Award, and a Presidential Young Investigator Award. As part of the HHMI-NIBIB Interfaces Initiative, CBD received funding from Howa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Biology Department Logo
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as ''computers''. An especially well-known discipline of the study of computation is computer science. Physical process of Computation Computation can be seen as a purely physical process occurring inside a closed physical system called a computer. Examples of such physical systems are digital computers, mechanical computers, quantum computers, DNA computers, molecular computers, microfluidics-based computers, analog computers, and wetware computers. This point of view has been adopted by the physics of computation, a branch of theoretical physics, as well as the field of natural computing. An even more radical point of view, pancomputationalism (inaudible word), is the postulate of digital physics that argues that the evolution of the universe is itself a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overton Prize
The ISCB Overton Prize is a Awards in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, computational biology prize awarded annually for outstanding accomplishment by a scientist in the early to mid stage of his or her career. Laureates have made significant contribution to the field of computational biology either through research, education, service, or a combination of the three. The prize was established by the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB) in memory of a major contributor to the field of bioinformatics and member of the ISCB Board of Directors who died unexpectedly in 2000. The Overton Prize is traditionally awarded at the Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB) conference. Laureates Laureates include *2022 - *2021 - Barbara Engelhardt *2020 - *2019 - Christophe Dessimoz *2018 - Cole Trapnell *2017 - Christoph Bock *2016 - Debora Marks *2015 - Curtis Huttenhower *2014 - Dana Pe'er *2013 - Gonçalo Abecasis *2012 - Ziv Bar-Joseph *2011 - Olga Troya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathryn Roeder
Kathryn M. Roeder is an American statistician known for her development of statistical methods to uncover the genetic basis of complex disease and her contributions to mixture models, semiparametric inference, and multiple testing. Roeder holds positions as professor of statistics and professor of computational biology at Carnegie Mellon University, where she leads a project focused on discovering genes associated with autism. Education and career Roeder did her undergraduate studies at the University of Idaho, where she graduated in 1982 with a bachelor's degree in wildlife resources. Roeder worked as a biologist for a year in the Pacific Northwest before returning to academia for graduate studies in statistics. She completed her Ph.D. in 1988 at Pennsylvania State University; her dissertation, supervised by Bruce G. Lindsay, was ''Method of Spacings for Semiparametric Inference''. Roeder joined the faculty of Yale University in 1988 and earned tenure there. She remained at Yale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaime Carbonell
Jaime Guillermo Carbonell (July 29, 1953 – February 28, 2020) was a computer scientist who made seminal contributions to the development of natural language processing tools and technologies. His extensive research in machine translation resulted in the development of several state-of-the-art language translation and artificial intelligence systems. He earned his B.S. degrees in Physics and in Mathematics from MIT in 1975 and did his Ph.D. under Dr. Roger Schank at Yale University in 1979. He joined Carnegie Mellon University as an assistant professor of computer science in 1979 and lived in Pittsburgh from then. He was affiliated with the Language Technologies Institute, Computer Science Department, Machine Learning Department, and Computational Biology Department at Carnegie Mellon. His interests spanned several areas of artificial intelligence, language technologies and machine learning. In particular, his research focused on areas such as text mining (extraction, categorizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jian Ma (computer Scientist)
Jian Ma (Chinese: 马坚) is an American computer scientist and computational biologist. He is the Ray and Stephanie Lane Professor of Computational Biology in the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University. He is a faculty member in the Computational Biology Department. His lab develops machine learning algorithms to study the structure and function of the human genome. During his Ph.D. and postdoc training, he developed algorithms to reconstruct the ancestral mammalian genome. His research group has recently pioneered a series of new machine learning methods for 3D epigenomics and spatial genomics. He received an NSF CAREER award in 2011. In 2020, he was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship in Computer Science. He is an elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziv Bar-Joseph
Ziv Bar-Joseph is an Israeli computational biologist and Professor in the Computational Biology Department and the Machine Learning Department at the Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science. Education Bar-Joseph studied computer science at Bachelor of Science (1997) and Master of Science (1999) level, both at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He gained his PhD from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in computer science in 2003, under the supervision of David K. Gifford and Tommi S. Jaakkola. Following this, he was a postdoctoral associate at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and the Whitehead Institute. Research Bar-Joseph's research at Carnegie Mellon is primarily focused on developing computational methods to allow greater understanding of the interactions and dynamics of complex biological systems, particularly systems that change with time, such as the cell cycle. At MIT, Bar-Joseph's group developed a novel algorithm to disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
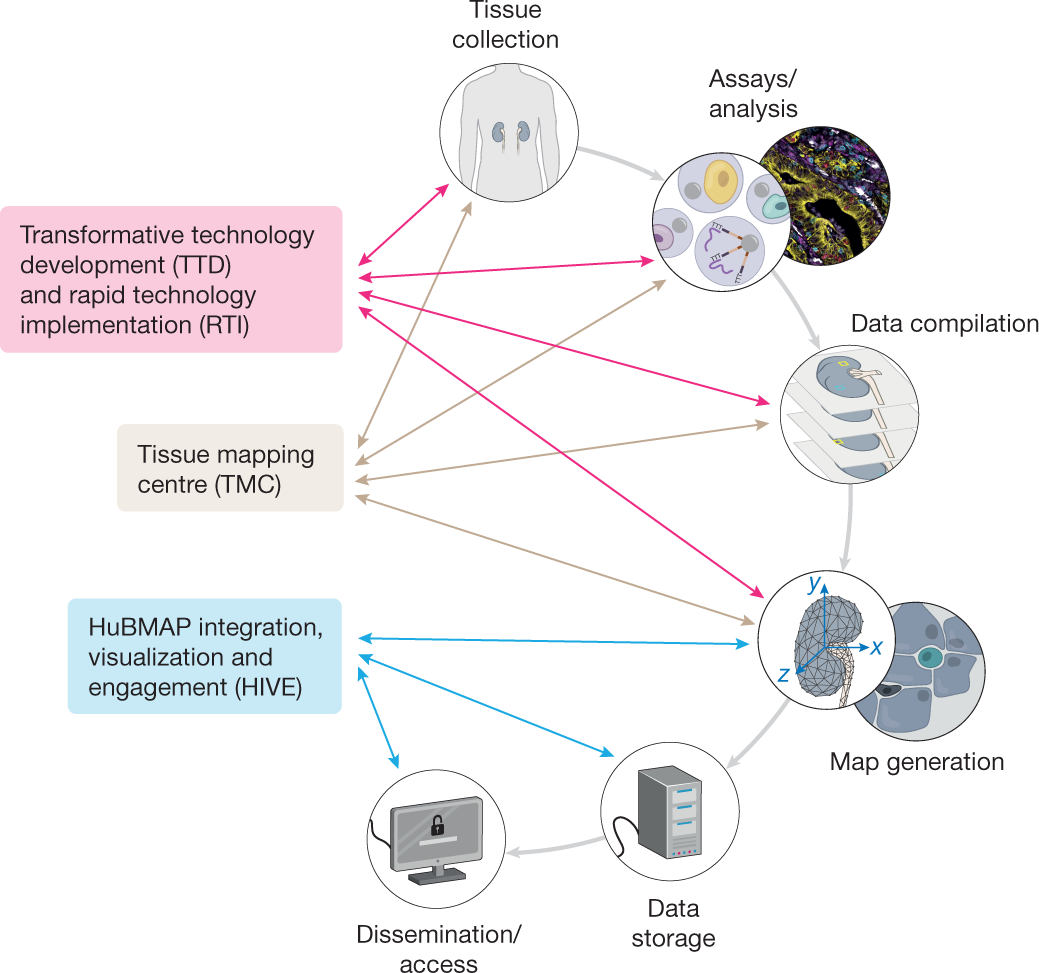
HuBMAP
The Human Biomolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) is a program funded by the US National Institutes of Health to characterize the human body at single cell resolution, integrated to other efforts such as the Human Cell Atlas. Among the products of the program is the Azimuth reference datasets for single-cell RNA seq data and the ASCT+B Reporter, a visualization tool for anatomical structures, cell types and biomarkers. Millitomes are used to create uniformly sized tissue blocks that match the shape and size of organs from HuBMAP's 3D Reference Object Library. The HuBMAP received 27 million US dollars The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from Dollar, other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American ... of funding from the NIH in 2020 and about 28.5 million in 2021. References External links Official website Biological databas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint CMU-Pitt Ph
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Classification The number of joints depends on if sesamoids are included, age of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) is a public state-related research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The university is composed of 17 undergraduate and graduate schools and colleges at its urban Pittsburgh campus, home to the university's central administration and around 28,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The 132-acre Pittsburgh campus includes various historic buildings that are part of the Schenley Farms Historic District, most notably its 42-story Gothic revival centerpiece, the Cathedral of Learning. Pitt is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". It is the second-largest non-government employer in the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. Pitt traces its roots to the Pittsburgh Academy founded by Hugh Henry Brackenridge in 1787. While the city was still on the edge of the American frontier at the time, Pittsburgh's rapid growth meant that a proper university was so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Biology
Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers. History Bioinformatics, the analysis of informatics processes in biological systems, began in the early 1970s. At this time, research in artificial intelligence was using network models of the human brain in order to generate new algorithms. This use of biological data pushed biological researchers to use computers to evaluate and compare large data sets in their own field. By 1982, researchers shared information via punch cards. The amount of data grew exponentially by the end of the 1980s, requiring new computational methods for quickly interpreting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Biomedical Imaging And Bioengineering
The National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), founded at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 2000, is located in Bethesda, Maryland. It is one of 27 institutes and centers that are part of NIH, an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). NIBIB programs accelerate the development and application of biomedical imaging and bioengineering technologies to study, diagnose, and treat human diseases. The institute is an engine and testbed for innovative biomedical technologies, which it generates at a robust rate; NIBIB is first among NIH institutes for patents generated per funding dollar. NIBIB-funded research integrates engineering and the physical sciences with the life sciences, building on opportunities and technical discoveries in biomedicine. The institute spearheads development of medical technologies that are better, faster, smaller, less costly and more accessible to people across the United States and around the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Hughes Medical Institute
The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) is an American non-profit medical research organization based in Chevy Chase, Maryland. It was founded in 1953 by Howard Hughes, an American business magnate, investor, record-setting pilot, engineer, film director, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most financially successful individuals in the world. It is one of the largest private funding organizations for biological and medical research in the United States. HHMI spends about $1 million per HHMI Investigator per year, which amounts to annual investment in biomedical research of about $825 million. The institute has an endowment of $22.6 billion, making it the second-wealthiest philanthropic organization in the United States and the second-best endowed medical research foundation in the world. HHMI is the former owner of the Hughes Aircraft Company – an American aerospace firm which was divested to various firms over time. History The institute was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
