|
Compaq Deskpro
The Compaq Deskpro is a line of business-oriented personal computers manufactured by Compaq, then discontinued after the merger with Hewlett-Packard. Models were produced containing microprocessors from the 8086 up to the x86-based Intel Pentium 4. History Deskpro (8086) and Deskpro 286 The original Compaq Deskpro (released in 1984), available in several disk configurations, is an XT-class PC equipped with an 8 MHz 8086 CPU and Compaq's unique display hardware that combined Color Graphics Adapter graphics with high resolution Monochrome Display Adapter text. As a result, it was considerably faster than the original IBM PC, the XT and the AT, and had a much better quality text display compared to IBM PCs which were equipped with either the IBM Monochrome Display Adapter or Color Graphics Adapter cards. Its hardware and BIOS were claimed to be 100% compatible with the IBM PC, like the earlier Compaq Portable. This compatibility had given Compaq the lead over companies l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Tower
In personal computing, a tower is a form of desktop computer whose case height is much greater than its width, thus having the appearance of an upstanding tower block, as opposed to a traditional desktop or "pizza box" computer whose width is greater than its height and appears lying flat. Although a tower case may be placed on top of the desk alongside the monitor and other peripherals, a far more common configuration is to place the case on the floor below the desk or in an under-desk compartment, in order to save desktop space for other items. Multiple subclasses of the tower form factor have been established to differentiate their varying heights, including full-tower, mid-tower, midi-tower and mini-tower; these classifications are nebulously defined and inconsistently applied by different manufacturers, however. Computer systems housed in the horizontal form factor—once popularized by the IBM PC in the 1980s but fallen out of mass use since the 1990s—have been given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Data Products
Columbia Data Products, Inc. (CDP) is a company which produced the first legally reverse-engineered IBM PC compatible, IBM PC clones. It faltered in that market after only a few years, and later reinvented itself as a Software development, software development company. History 1976–1986: As a hardware company Columbia Data Products was founded by William Diaz in 1976 in Columbia, Maryland. In 1980, Columbia Data Products made some Zilog Z80, Z80-based computers, most notably their Commander 900 series, which had several models some of which were multiprocessors and had graphics capabilities. CDP introduced the MPC 1600 "Multi Personal Computer," designed by David Howse, in June 1982. It was an exact functional copy of the IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC model 5150 except for the BIOS which was Clean room design, Clean room designed. IBM had published the Industry Standard Architecture, bus and BIOS specifications, wrongly assuming that this would not be enough to facilitate u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86 Compaq Computers
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor and its 8088 variant. The 8086 was introduced in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of Intel's 8-bit 8080 microprocessor, with memory segmentation as a solution for addressing more memory than can be covered by a plain 16-bit address. The term "x86" came into being because the names of several successors to Intel's 8086 processor end in "86", including the 80186, 80286, 80386 and 80486 processors. The term is not synonymous with IBM PC compatibility, as this implies a multitude of other computer hardware. Embedded systems and general-purpose computers used x86 chips before the PC-compatible market started, some of them before the IBM PC (1981) debut. , most desktop and laptop computers sold are based on the x86 architecture family, while mobile categories such as smartphones or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compaq Evo
The Compaq Evo is a series of business PCs (desktop and laptop) and thin clients made by Compaq and Hewlett-Packard following the 2002 merger. The Evo brand was introduced by Compaq in May 2001 as a business-oriented brand. It replaced the Deskpro brand of desktops and the Armada brand of notebooks. ''Evo'' was rebranded as ''HP Compaq'' which was used until 2013. It is not to be confused with the later Intel ''Evo'' branding for performant laptops. Design The Desktops were small and made to be positioned horizontally instead of vertically so that the monitor could be placed on top to save space. Most featured a sleek silver and black compact design. The early models were shipped with CD-ROM drives but Compaq shipped ''Evo''s with CD-RW drives and DVD-ROM drives. The design of some models were only allowed for one CD or DVD drive, but some models had bigger designs for 2 CD or DVD drives. Some models also shipped with a 3½ floppy drive, positioned below the CD or DVD drive. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
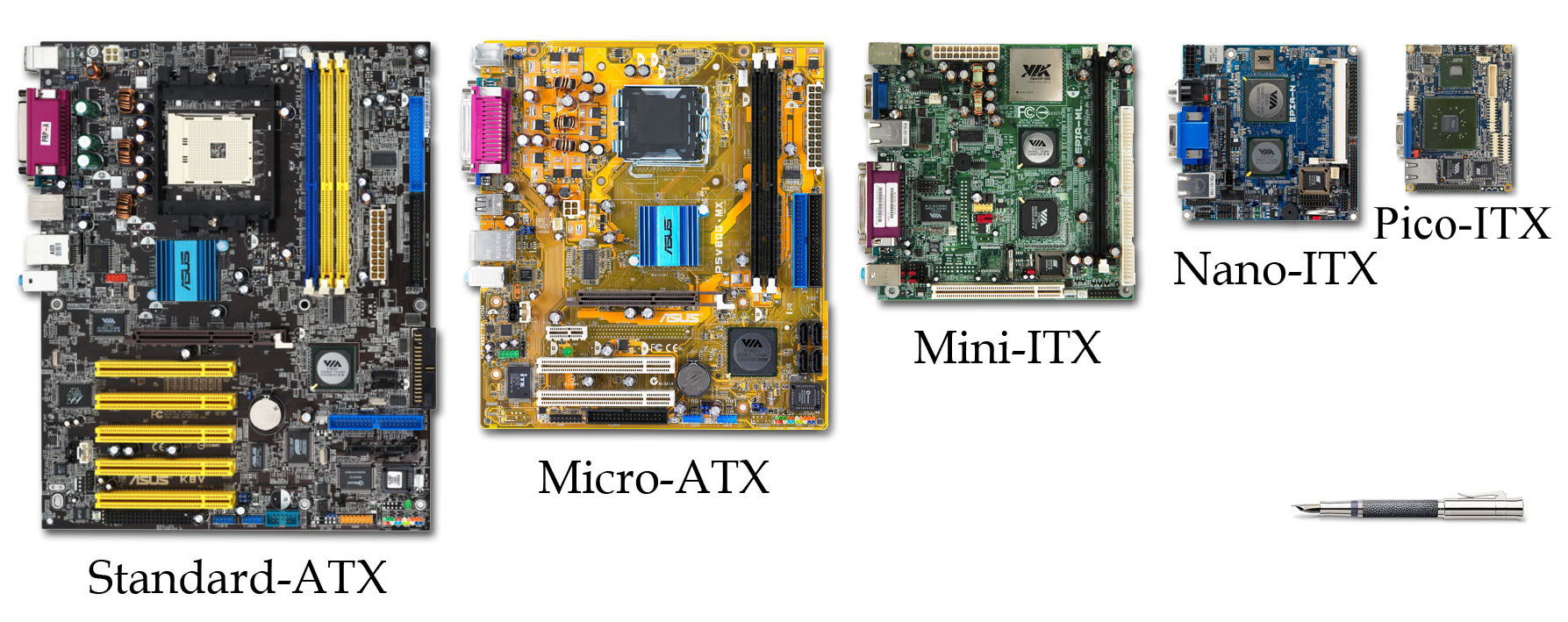
Small Form Factor (desktop And Motherboard)
Small form factor (SFF or SFX) is a term used for desktop computers, and their enclosures and motherboards, to indicate that they are designed in accordance with one of several standardized computer form factors intended to minimize the volume and footprint of a desktop computer compared to the standard ATX form factor. For comparison purposes, the size of an SFF case is usually measured in litres. SFFs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, including shoeboxes, cubes, and book-sized PCs. Their smaller and often lighter construction has made them popular as home theater PCs and as gaming computers for attending LAN parties. Manufacturers also emphasize the aesthetic and ergonomic design of SFFs since users are more likely to place them on top of a desk or carry them around. Advancements in component technology together with reductions in size means a powerful computer is no longer restricted to the huge towers of old. Small form factors do not include computing devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Factor (design)
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically been slower to evolve than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for compatibility of hardware from different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC/AT
The IBM Personal Computer/AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 80286 microprocessor. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of "AT" on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some sources expand the term as "Advanced Technology", including at least one internal IBM document. History IBM's 1984 introduction of the AT was seen as an unusual move for the company, which typically waited for competitors to release new products before producing its own models. At $4,000–6,000, it was only slightly more expensive than considerably slower IBM models. The announcement surprised rival executives, who admitted that matching IBM's prices would be difficult. No major competitor showed a comparable computer at COMDEX Las Vegas that year. Features The AT is IBM PC compatible, with the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse-engineered
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. It is essentially the process of opening up or dissecting a system to see how it works, in order to duplicate or enhance it. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: Information extraction, Modeling, and Review. Information extraction refers to the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling refers to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clean Room Design
Clean-room design (also known as the Chinese wall technique) is the method of copying a design by reverse engineering and then recreating it without infringing any of the copyrights associated with the original design. Clean-room design is useful as a defense against copyright infringement because it relies on independent creation. However, because independent invention is not a defense against patents, clean-room designs typically cannot be used to circumvent patent restrictions. The term implies that the design team works in an environment that is "clean" or demonstrably uncontaminated by any knowledge of the proprietary techniques used by the competitor. Typically, a clean-room design is done by having someone examine the system to be reimplemented and having this person write a specification. This specification is then reviewed by a lawyer to ensure that no copyrighted material is included. The specification is then implemented by a team with no connection to the original ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (abbreviated IW) is an information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a web-only publication. Its parent company today is International Data Group, and its sister publications include '' Macworld'' and ''PC World''. InfoWorld is based in San Francisco, with contributors and supporting staff based across the United States. Since its founding, ''InfoWorld''s readership has largely consisted of IT and business professionals. ''InfoWorld'' focuses on how-to, analysis, and editorial content from a mixture of experienced technology journalists and working technology practitioners. The site averages 4.6 million monthly page views and 1.1 million monthly unique visitors. History The magazine was founded by Jim Warren in 1978 as ''The Intelligent Machines Journal'' (IMJ). It was sold to IDG in late 1979. On 18 February 1980, the magazine name was changed to ''InfoWorld''. In 1986, the Robert X. Cringel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)