|
Columbia Plateau Aquifer System
The Columbia Plateau Aquifer system is a series of layered aquifers across ~44,000 mi2 of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. The aquifer system is on the Columbia Plateau, contained within the Cascades, Rocky Mountains, Okanogan Highlands, and the Blue Mountains.Burns, Erick R., Daniel T. Snyder, Jonathan V. Haynes, and Michael S. Waibel. "Groundwater Status and Trends for the Columbia Plateau Regional Aquifer System, Washington, Oregon, and Idaho" U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2012–5261, 2012. Web. These aquifers are bounded on the bottom by a layer of Miocene basaltic rock that can be up to 15,000 ft thick.Whitehead, R.L. "GROUND WATER ATLAS of the UNITED STATES Idaho, Oregon, Washington." U.S. Geological Survey HA 730-H, 1994. Web. The primary aquifers in the system are shallow, and unconfined. Water quality The primary source of water quality concerns was from agricultural outputs, especially in the southwestern area of the system where lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbia River. Geology During late Miocene and early Pliocene times, a flood basalt engulfed about of the Pacific Northwest, forming a large igneous province. Over a period of perhaps 10 to 15 million years, lava flow after lava flow poured out, ultimately accumulating to a thickness of more than 6,000 feet (1.8 km). As the molten rock came to the surface, the Earth's crust gradually sank into the space left by the rising lava. The Columbia River Basalt Group consists of seven formations: The Steens Basalt, Imnaha Basalt, Grande Ronde Basalt, Picture Gorge Basalt, Prineville Basalt, Wanapum Basalt, and Saddle Mountains Basalt. Many of these formations are subdivided into formal and informal members and flows. The subsidence of the crust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River Basalt Group
The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern Oregon and Washington, western Idaho, and part of northern Nevada. The basalt group includes the Steens and Picture Gorge basalt formations. Introduction During the middle to late Miocene epoch, the Columbia River flood basalts engulfed about of the Pacific Northwest, forming a large igneous province with an estimated volume of . Eruptions were most vigorous 17–14 million years ago, when over 99 percent of the basalt was released. Less extensive eruptions continued 14–6 million years ago. Erosion resulting from the Missoula Floods has extensively exposed these lava flows, laying bare many layers of the basalt flows at Wallula Gap, the lower Palouse River, the Columbia River Gorge and throughout the Channeled Scablands. The Columbia River Basalt Group is thought to be a potential link to the Chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
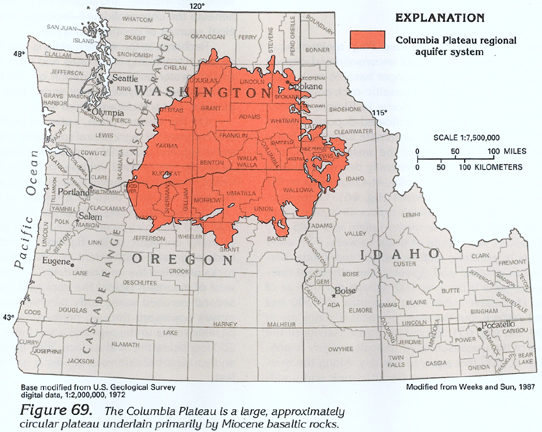
Columbia Plateau Aquifer Map
Columbia may refer to: * Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America Places North America Natural features * Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in the U.S. Pacific Northwest * Columbia River, in Canada and the United States ** Columbia Bar, a sandbar in the estuary of the Columbia River ** Columbia Country, the region of British Columbia encompassing the northern portion of that river's upper reaches *** Columbia Valley, a region within the Columbia Country ** Columbia Lake, a lake at the head of the Columbia River *** Columbia Wetlands, a protected area near Columbia Lake ** Columbia Slough, along the Columbia watercourse near Portland, Oregon * Glacial Lake Columbia, a proglacial lake in Washington state * Columbia Icefield, in the Canadian Rockies * Columbia Island (District of Columbia), in the Potomac River * Columbia Island (New York), in Long Island Sound Populated places ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdrafting
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. Groundwater depletion is comparable to a bank account in which more money is withdrawn than deposited. The primary cause of groundwater depletion is the excessive pumping of groundwater up from underground aquifers. There are two sets of yields: safe yield and sustainable yield. Safe yield is the amount of groundwater that can be withdrawn over a period of time without exceeding the long-term recharge rate or affecting the aquifer integrity. Sustainable yield is the amount of water extraction that can be sustained indefinitely without negative hydrological impacts, taking into account both recharge rate and surface water impacts. There are two types of aquifers: confined and unconfined. In confined aquifers, there is an overbearing layer called aquitard, which contains impermeable materials through wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquifers In The United States
This is a list of some aquifers in the United States. An aquifer is a geologic formation, a group of formations, or a part of a formation that contains sufficient saturated permeable material to yield significant quantities of water to groundwater wells and springs. List of notable aquifers * Ogallala Aquifer of the central United States is one of the world's great aquifers, but in places it is being rapidly depleted by growing municipal use, and continuing agricultural use. This huge aquifer, which underlies portions of eight states, contains primarily fossil water from the time of the last glaciation. Annual recharge, in the more arid parts of the aquifer, is estimated to total only about 10 percent of annual withdrawals. * Floridan Aquifer underlies the entire state of Florida as well as southern portions of Alabama, Georgia and South Carolina, and covers an area of 100,000 square miles. It developed millions of years ago during the late Paleocene to early Miocene per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |