|
Colmar Von Der Goltz
Wilhelm Leopold Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz (12 August 1843 – 19 April 1916), also known as ''Goltz Pasha'', was a Prussian Field Marshal and military writer. Military career Goltz was born in , East Prussia (later renamed Goltzhausen; now Ivanovka, in Polessky District, Kaliningrad Oblast), into the impoverished Von der Goltz noble family. He grew up at the manor house of Fabiansfelde near Preußisch Eylau, which had been bought by his father in 1844. His father spent some nineteen years in the Prussian Army without rising above the rank of lieutenant, and his efforts at farming were similarly unfruitful, and he eventually succumbed to cholera while on a trip to Danzig (now Gdańsk) when Colmar was six years old. Goltz entered the Prussian infantry in 1861 as a second lieutenant with the 5th East Prussian Infantry Regiment Number 41, in Königsberg (now Kaliningrad). During 1864 he was on border duty at Toruń, after which he entered the Berlin Military Academy, but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Masurians and Lithuanians formed minorities. From the 13th century, East Prussia was part of the monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Der Goltz
Von der Goltz is the name of an old and influential German noble family whose members occupied many important positions in the Kingdom of Prussia and later in the German Empire. History The family can trace their lineage from East Brandenburg back to 12th century. On 19 September 1786 the family was raised to the title of Count in Prussia by King Frederick William II.http://genealogy.euweb.cz/titles/g.html Notable members *Albert Graf von der Goltz (1893–1944), a German Oberst (colonel) killed in action during World War II *Augustus Frederick, Graf von der Goltz (1765–1818), First Prussian Minister for Foreign Affairs *Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz (1843–1916), Prussian Field Marshal and military writer *Gottfried von der Goltz (born 1964), German-Norwegian violinist and conductor *Gustav von Golz (1833–1908), Prussian general of the infantry *Horst von der Goltz (1884–?), German spy and actor *Kuno von der Goltz (1817–1897), Prussian general of the infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
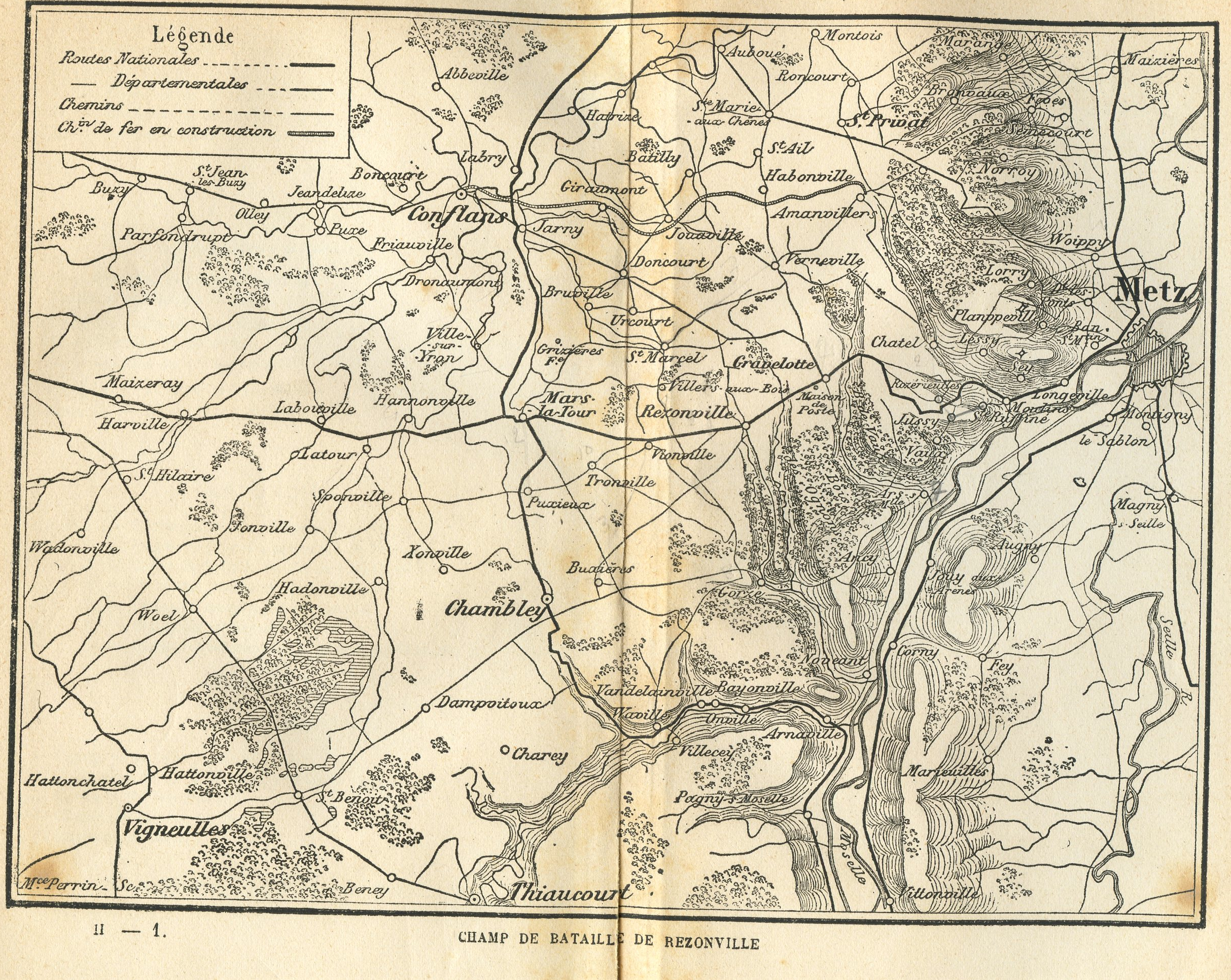
Battle Of Vionville
The Battle of Mars-la-Tour (also known as the Battle of Vionville or Battle of Rezonville) was fought on 16 August 1870, during the Franco-Prussian War, near the village of Mars-La-Tour in northeast France. One Prussian corps, reinforced by two more later in the day, encountered the entire French Army of the Rhine in a meeting engagement and, surprisingly, forced the Army of the Rhine to retreat toward the fortress of Metz. A cavalry patrol of the 1st Squadron of the 1st Hanoverian Dragoon Regiment No. 9, led by Rittmeister Oskar von Blumenthal, discovered that Marshal François Bazaine's 160,000-man Army of the Rhine was attempting to escape from Metz to join with French forces at Verdun. This intelligence prompted General Prince Friedrich Karl, commander of the Prussian Second Army, to order at 1900 on 15 August a grossly outnumbered group of 30,000 men of the advanced III Corps under General Constantin von Alvensleben to cut off the French line of retreat at Mars-la-Tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
II Corps (German Empire)
The II Army Corps / II AK (german: II. Armee-Korps) was a corps level command of the Prussian and then the Imperial German Armies from the 19th Century to World War I. It was established on 3 April 1820 with headquarters initially in Berlin. From 1837, the headquarters moved to Stettin (now Szczecin, Poland), back to Berlin in 1863, before finally settling in Stettin from 1870. The Corps catchment area included the Province of Pomerania, the district (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Bromberg from the Province of Posen and the Province of West Prussia. Later, the West Prussian districts were transferred to the new XVII Corps District. In peacetime, the Corps was assigned to the VIII Army Inspectorate, which became the 1st Army at the start of the First World War. The Corps headquarters was upgraded to form the headquarters of the South Army on 10 January 1915. The Corps was reformed post-war, before being finally disbanded in 1919. Austro-Prussian War The II Corps formed part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Frederick Charles
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Trautenau
The Battle of Trautenau (german: Schlacht bei Trautenau) or Battle of Trutnov was fought on 27 June 1866, during the Austro-Prussian War. It was the only battle of the war that ended in an Austrian victory over the Prussians, but at a large cost. Background The Prussian Second Army invading Bohemia had to split up in order to negotiate the difficult passes of the Giant Mountains. As they emerged on the Bohemian side, they met Austrian forces. At Nachod the Austrians were soundly beaten, but on the same day, as Adolf von Bonin’s I Corps emerged from the passes it was caught in the open on its way through Trautenau towards Pilníkov, where it hoped to link up with the First Army. The battle Bonin's vanguard cleared the passes during the late morning and entered Trautenau at 10:00. The Austrian X Corps, led by Ludwig von Gablenz, had broken camp at 8:00 and marched towards Trautenau to stop Bonin's advance. The Austrian troops arrived piecemeal with the Mondel brigade – wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Staff College
The Prussian Staff College, also Prussian War College (german: Preußische Kriegsakademie) was the highest military facility of the Kingdom of Prussia to educate, train, and develop general staff officers. Location It originated with the ''Akademie für junge Offiziere der Infanterie und Kavallerie'' (Academy for young officers of the infantry and cavalry) in 1801, later becoming known as the Allgemeine Kriegsschule (General War-School). It was officially re-founded by Gerhard von Scharnhorst in Berlin on October 15, 1810 as one of three officer colleges. Its building on Unter den Linden (1845/25), Berlin, was designed by Karl Friedrich Schinkel. Graduation Graduating from the ''Staff College'' was a prerequisite for appointment to the ''Prussian General Staff'' (later the German General Staff). Carl von Clausewitz enrolled as one of its first students in 1801 (before it was renamed), while other attendees included Field Marshals von Steinmetz, von Moltke, and von Blumentha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toruń
)'' , image_skyline = , image_caption = , image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg , image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg , nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town , pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship#Poland#Europe , pushpin_relief=1 , pushpin_label_position = top , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Voivodeship , subdivision_name1 = , leader_title = City mayor , leader_name = Michał Zaleski , established_title = Established , established_date = 8th century , established_title3 = City rights , established_date3 = 1233 , area_total_km2 = 115.75 , population_as_of = 31 December 2021 , population_total = 196,935 (16th) Data for territorial unit 0463000. , population_density_km2 = 1716 , population_metro = 297646 , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , coordinates = , elevation_m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and administrative centre of Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian semi-exclave between Lithuania and Poland. The city sits about west from mainland Russia. The city is situated on the Pregolya River, at the head of the Vistula Lagoon on the Baltic Sea, and is the only ice-free port of Russia and the Baltic states on the Baltic Sea. Its population in 2020 was 489,359, with up to 800,000 residents in the urban agglomeration. Kaliningrad is the second-largest city in the Northwestern Federal District, after Saint Petersburg, the third-largest city in the Baltic region, and the seventh-largest city on the Baltic Sea. The settlement of modern-day Kaliningrad was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was named in honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. A Baltic port city, it successively became the capital of the Królewiec Voivodeship, the State of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia and the provinces of East Prussia and Prussia. Königsberg remained the coronation city of the Prussian monarchy, though the capital was moved to Berlin in 1701. Between the thirteenth and the twentieth centuries, the inhabitants spoke predominantly German, but the multicultural city also had a profound influence upon the Lithuanian and Polish cultures. The city was a publishing center of Lutheran literature, including the first Polish translation of the New Testament, printed in the city in 1551, the first book in Lithuanian and the first Lutheran catechism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönfeld’s Buchhandlung (C. A. Werner), 1861, p. 71, 237.); Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. * , )Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)





.jpg)
.jpeg/1200px-Brama_Zuraw_W_Gdansku_(153003103).jpeg)