|
Colestilan
Colestilan ( INN, trade name BindRen) is a medication that acts as a phosphate binder and bile acid sequestrant. It is an ion-exchange resin, is an orally administered bile acid sequestrant that is being developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia and hyperphosphataemia. It has been launched in Japan for hypercholesterolaemia. For the treatment of hyperphosphataemia, it is launched in Austria, Germany, the Czech Republic, Portugal and the United Kingdom, is registered in the EU. Phase III development in paediatric patients with hyperphosphataemia associated with chronic kidney disease was underway in the UK and Germany. However, the company discontinued the development. In addition, the phase II development in type-2 diabetes mellitus and phase I development in hyperphosphataemia, in Japan, was also discontinued by the company. Phase III development for hyperphosphataemia was previously underway in the US. However, Mitsubishi Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colestilan Constituents
Colestilan ( INN, trade name BindRen) is a medication that acts as a phosphate binder and bile acid sequestrant. It is an ion-exchange resin, is an orally administered bile acid sequestrant that is being developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia and hyperphosphataemia. It has been launched in Japan for hypercholesterolaemia. For the treatment of hyperphosphataemia, it is launched in Austria, Germany, the Czech Republic, Portugal and the United Kingdom, is registered in the EU. Phase III development in paediatric patients with hyperphosphataemia associated with chronic kidney disease was underway in the UK and Germany. However, the company discontinued the development. In addition, the phase II development in type-2 diabetes mellitus and phase I development in hyperphosphataemia, in Japan, was also discontinued by the company. Phase III development for hyperphosphataemia was previously underway in the US. However, Mitsubishi Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Problem
Gastrointestinal diseases (abbrev. GI diseases or GI illnesses) refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Oral disease The oral cavity is part of the gastrointestinal system and as such the presence of alterations in this district can be the first sign of both systemic and gastrointestinal diseases. By far the most common oral conditions are plaque-induced diseases (e.g., gingivitis, periodontitis, dental caries). Oral symptoms can be similar to lesions occurring elsewhere in the digestive tract, with a pattern of swelling, inflammation, ulcers, and fissures. If these signs are present, then patients are more likely to also have anal and esophageal lesions and experience other extra-intestinal disease manifestations. Some diseases which involve other parts of the GI tract can manifest in the mouth, alone or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterohepatic Circulation
Enterohepatic circulation refers to the circulation of biliary acids, bilirubin, drugs or other substances from the liver to the bile, followed by entry into the small intestine, absorption by the enterocyte and transport back to the liver. Enterohepatic circulation is an especially important concept in the field of toxicology as many lipophilic xenobiotics undergo this process causing repeated liver damage. Biliary acids The circuit Hepatocytes metabolize cholesterol to cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. These lipid-soluble bile acids are conjugated (reversibly attached) mainly to glycine or taurine molecules to form water soluble primary conjugated bile acids, sometimes called "bile salts". These bile acids travel to the gall bladder during the interdigestive phase for storage and to the descending part of the duodenum via the common bile duct through the major duodenal papilla during digestion. 95% of the bile acids which are delivered to the duodenum will be recy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urate
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism (also often described as keto–enol tautomerism). Although the lactim form is expected to possess some degree of aromaticity, uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile Acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts. Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon (anatomy), colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts. They are roughly equal in concentration. The salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids. Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion Exchanger
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, the purification of chemicals and separation of substances. Ion exchange usually describes a process of purification of aqueous solutions using solid polymeric ion-exchange resin. More precisely, the term encompasses a large variety of processes where ions are exchanged between two electrolytes. Aside from its use to purify drinking water, the technique is widely applied for purification and separation of a variety of industrially and medicinally important chemicals. Although the term usually refers to applications of synthetic (man-made) resins, it can include many other materials such as soil. Typical ion exchangers are ion-exchange resins (functionalized porous or gel polymer), zeolites, montmorillonite, clay, and soil humus. Ion exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
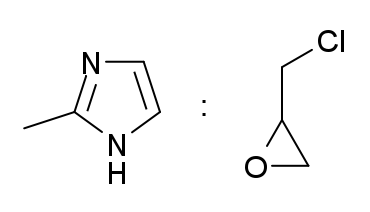
Epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organic solvents. It is a chiral molecule generally existing as a racemic mixture of right-handed and left-handed enantiomers. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive electrophilic compound and is used in the production of glycerol, plastics, epoxy glues and resins, epoxy diluents and elastomers. Production Epichlorohydrin is traditionally manufactured from allyl chloride in two steps, beginning with the addition of hypochlorous acid, which affords a mixture of two isomeric alcohols: : In the second step, this mixture is treated with base to give the epoxide: : In this way, more than 800,000 tons (1997) of epichlorohydrin are produced annually. Glycerol routes Epichlorohydrin was first described in 1848 by Marcellin Berthelot. The comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Methylimidazole
2-Methylimidazole is an organic compound that is structurally related to imidazole with the chemical formula CH3C3H2N2H. It is a white or colorless solid that is highly soluble in polar organic solvents and water. It is a precursor to a range of drugs and is a ligand in coordination chemistry. Synthesis and reactions It is prepared by condensation of glyoxal, ammonia and acetaldehyde, a Radziszewski reaction. Nitration gives 5-nitro derivative.Ebel, K., Koehler, H., Gamer, A. O., & Jäckh, R. "Imidazole and Derivatives." In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; 2002 Wiley-VCH, 2-Methylimidazole is a sterically hindered imidazole that is used to simulate the coordination of histidine to heme complexes. It can be deprotonated to make imidazolate-based coordination polymers. Applications 2-Methylimidazole is a precursor to the several members of the nitroimidazole antibiotics that are used to combat anaerobic bacterial and parasitic infections. File:Dimetridazole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon 6 and nylon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiepileptic
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs may block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to the voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GAT-1 GABA transporter, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gated calcium channels, SV2A, and α2δ. By blocking sodium or calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |