|
Coelodonta
''Coelodonta'' (, from the Greek κοιλία, ''koilía'' and οδούς, ''odoús'', "hollow tooth", in reference to the deep grooves of their molars) is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in Eurasia between 3.7 million years to 10,000 years before the present, in the Pliocene and the Pleistocene epochs. It is best known from the type species, the woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis''), which ranged throughout northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene. The earliest known species, ''Coelodonta thibetana,'' lived in Tibet during the Pliocene, with the genus spreading to the rest of Eurasia during the Pleistocene. Species Species recognised as members of ''Coelodonta'', according to Deng ''et al''. (2011), include: * ''Coelodonta thibetana'' (Deng et al. 2011): The most primitive species of the genus, inhabited the Tibetan Plateau during the Pliocene. * ''Coelodonta nihowanensis'' (Chow, 1978): A primitive species from northern China, it lived in the earliest Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. Taxonomy Woolly rhinoceros remains have been known long before the species was described, and were the basis for some mythical creatures. Native peoples of Siberia believed their horns were the claws of giant birds. A rhinoceros skull was found in Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. Taxonomy Woolly rhinoceros remains have been known long before the species was described, and were the basis for some mythical creatures. Native peoples of Siberia believed their horns were the claws of giant birds. A rhinoceros skull was found in Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelodonta Antiquitatis
''Coelodonta'' (, from the Greek κοιλία, ''koilía'' and οδούς, ''odoús'', "hollow tooth", in reference to the deep grooves of their molars) is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in Eurasia between 3.7 million years to 10,000 years before the present, in the Pliocene and the Pleistocene epochs. It is best known from the type species, the woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis''), which ranged throughout northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene. The earliest known species, ''Coelodonta thibetana,'' lived in Tibet during the Pliocene, with the genus spreading to the rest of Eurasia during the Pleistocene. Species Species recognised as members of ''Coelodonta'', according to Deng ''et al''. (2011), include: * ''Coelodonta thibetana'' (Deng et al. 2011): The most primitive species of the genus, inhabited the Tibetan Plateau during the Pliocene. * ''Coelodonta nihowanensis'' (Chow, 1978): A primitive species from northern China, it lived in the earliest Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelodonta Antiquitatis
''Coelodonta'' (, from the Greek κοιλία, ''koilía'' and οδούς, ''odoús'', "hollow tooth", in reference to the deep grooves of their molars) is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in Eurasia between 3.7 million years to 10,000 years before the present, in the Pliocene and the Pleistocene epochs. It is best known from the type species, the woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis''), which ranged throughout northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene. The earliest known species, ''Coelodonta thibetana,'' lived in Tibet during the Pliocene, with the genus spreading to the rest of Eurasia during the Pleistocene. Species Species recognised as members of ''Coelodonta'', according to Deng ''et al''. (2011), include: * ''Coelodonta thibetana'' (Deng et al. 2011): The most primitive species of the genus, inhabited the Tibetan Plateau during the Pliocene. * ''Coelodonta nihowanensis'' (Chow, 1978): A primitive species from northern China, it lived in the earliest Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
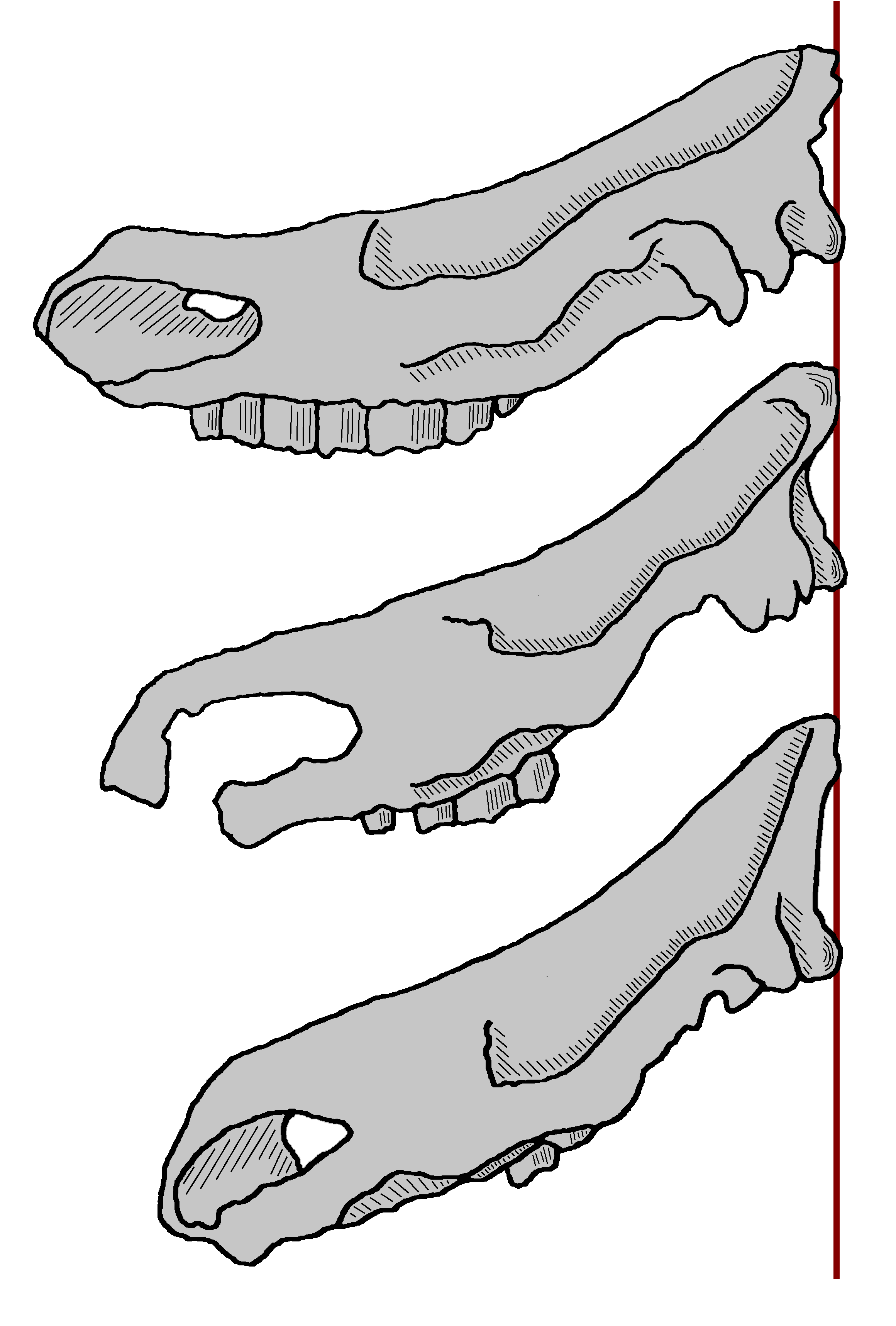
Coelodonta Thibetana
''Coelodonta thibetana'', the Tibetan woolly rhinoceros, is an extinct species of the genus Coelodonta native to western Himalayas that lived during the middle Pliocene epoch. ''C. thibetana'' is known from the holotype IVPP V15908, a partially complete skull including incomplete lower jaw preserved with full dentition. It was first named by Tao Deng, Xiaoming Wang, Mikael Fortelius, Qiang Li, Yang Wang, Zhijie J. Tseng, Gary T. Takeuchi, Joel E. Saylor, Laura K. Säilä and Guangpu Xie in 2011. Phylogeny The descriptors conducted a phylogenetic analysis of the five living rhinoceros A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species o ... species and thirteen extinct species. They qualify following cladogram, where ''C. thibetana'' was awarded a basal position within its genus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelodonta Tologoijensis
''Coelodonta tologoijensis'' is an extinct species of woolly rhino (''Coelodonta''). It was originally described as an Asian species. Subsequently one skull found in the Kyffhauser hills near the town of Bad Frankenhausen, Germany, was assigned to the species by researchers, which would make it the earliest known woolly rhino in Europe. The species was thought to have migrated to Europe between around 478,000 and 424,000 years ago during a cold, arid period. However, a 2022 study refuted the assignment of the Bad Frankenhausen skull to ''C. tologoijensis'', interpreting it as the skull of the woolly rhinoceros The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a me ... (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') instead. References Woolly rhino's ancient migrationBBC News, Monday, 17 November 2008 P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanorhinus Kirchbergensis
''Stephanorhinus kirchbergensis'', also known as Merck's rhinoceros or the forest rhinoceros, is an extinct species of rhino known from the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Pleistocene of Eurasia. One of the last members of the genus ''Stephanorhinus'', it is considered to be a typical component of the interglacial ''Palaeoloxodon'' large faunal assemblage in Europe. Among extant species of rhinoceroses it is most closely related to the Sumatran rhinoceros, while the well known woolly rhinoceros was another close relative. In the western part of its range, it was Sympatry, sympatric with ''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus''. Etymology and taxonomy The first part of the genus name is derived from that of Stephen I of Hungary, King Stephen I of Hungary, and the second part from 'rhinos' (ρινος, meaning "nose"), as with ''Dicerorhinus.'' The species name was given by :de:Georg Friedrich von Jäger, Georg Friedrich von Jäger in 1839 for Kirchberg an der Jagst in Baden-Württemberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatran Rhinoceros
The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis''), also known as the Sumatran rhino, hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Dicerorhinus''. It is the smallest rhinoceros, although it is still a large mammal; it stands high at the shoulder, with a head-and-body length of and a tail of . The weight is reported to range from , averaging . Like both African species, it has two horns; the larger is the nasal horn, typically , while the other horn is typically a stub. A coat of reddish-brown hair covers most of the Sumatran rhino's body. The Sumatran rhinoceros once inhabited rainforests, swamps and cloud forests in India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan. It is now critically endangered, with only five substantial populations in the wild: four in Suma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephanorhinus
''Stephanorhinus'' is an extinct genus of two-horned rhinoceros native to Eurasia and North Africa that lived during the Pliocene to Late Pleistocene. Species of ''Stephanorhinus'' were the predominant and often only species of rhinoceros in much of temperate Eurasia, especially Europe, for most of the Pleistocene. Two species of ''Stephanorhinus'' – Merck's rhinoceros (''S. kirchbergensis'') and the narrow-nosed rhinoceros (''S. hemitoechus'') – persisted into the last glacial period. Etymology The first part of the name, ''Stephano-'', honours Stephen I, the first king of Hungary. (The genus name was coined by Kretzoi, a Hungarian.) The second part is from (Greek for "nose"), a typical suffix of rhinoceros genus names. Taxonomy The taxonomic history of ''Stephanorhinus'' is long and convoluted, as many species are known by numerous synonyms and different genera – typically ''Rhinoceros'' and ''Dicerorhinus'' – for the 19th and most of the early 20th century. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao Deng
Deng Tao (; born June 1963) is a Chinese palaeontologist at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, who has made important fossil discoveries on Cenozoic mammals. He is a professor of vertebrate palaeontology, deputy director of the Academic Committee, and deputy director of Key Laboratory of Evolutionary Systematics of Vertebrates at IVPP. Education Deng was born in Yibin, Sichuan, China. He studied at Peking University from where he obtained BS in 1984. He completed MS from Southwest Petroleum University in 1994. He obtained PhD from the Northwest University in 1997. Professional career Deng works at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology as a researcher and PhD supervisor. His specialization is in the study of mammalian fossils, biostratigraphy, and environmental changes during the Late Cenozoic. Deng currently assumes several positions, including deputy director for the Academic Committ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |