|
Code 128
Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 15417:2007. It is used for alphanumeric or numeric-only barcodes. It can encode all 128 characters of ASCII and, by use of an extension symbol (FNC4), the Latin-1 characters defined in ISO/IEC 8859-1.. It generally results in more compact barcodes compared to other methods like Code 39, especially when the texts contain mostly digits. GS1-128 (formerly known as UCC/EAN-128) is a subset of Code 128 and is used extensively worldwide in shipping and packaging industries as a product identification code for the container and pallet levels in the supply chain. Specification A Code 128 barcode has seven sections: # Quiet zone # Start symbol # Encoded data # Check symbol (mandatory) # Stop symbol # Final bar (often considered part of the stop symbol) # Quiet zone The check symbol is calculated from a weighted sum (modulo 103) of all the symbols. Subtypes Code 128 includes 108 symbols: 103 data symbols, 3 sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Character
The null character (also null terminator) is a control character with the value zero. It is present in many character sets, including those defined by the Baudot and ITA2 codes, ISO/IEC 646 (or ASCII), the C0 control code, the Universal Coded Character Set (or Unicode), and EBCDIC. It is available in nearly all mainstream programming languages. It is often abbreviated as NUL (or NULL, though in some contexts that term is used for the null pointer). In 8-bit codes, it is known as a null byte. The original meaning of this character was like NOP—when sent to a printer or a terminal, it has no effect (some terminals, however, incorrectly display it as space). When electromechanical teleprinters were used as computer output devices, one or more null characters were sent at the end of each printed line to allow time for the mechanism to return to the first printing position on the next line. On punched tape, the character is represented with no holes at all, so a new unpunched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
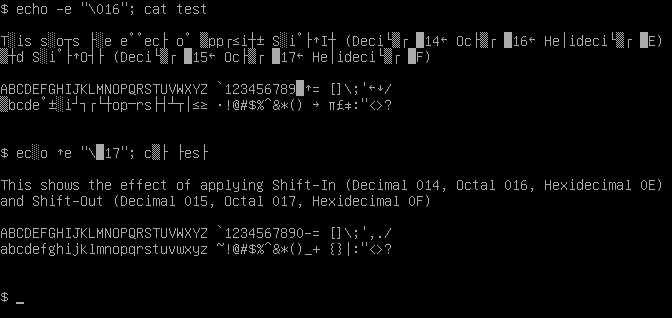
Shift In
Shift Out (SO) and Shift In (SI) are ASCII control characters 14 and 15, respectively (0x0E and 0x0F). These are sometimes also called "Control-N" and "Control-O". The original meaning of those characters provided a way to shift a coloured ribbon, split longitudinally usually with red and black, up and down to the other colour in an electro-mechanical typewriter or teleprinter, such as the Teletype Model 38, to automate the same function of manual typewriters. Black was the conventional ambient default colour and so was shifted "in" or "out" with the other colour on the ribbon. Later advancements in technology instigated use of this function for switching to a different font or character set and back. This was used, for instance, in the Russian character set known as KOI7-switched, where SO starts printing Russian letters, and SI starts printing Latin letters again. Similarly, they are used for switching between Katakana and Roman letters in the 7-bit version of the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shift Out
Shift Out (SO) and Shift In (SI) are ASCII control characters 14 and 15, respectively (0x0E and 0x0F). These are sometimes also called "Control-N" and "Control-O". The original meaning of those characters provided a way to shift a coloured ribbon, split longitudinally usually with red and black, up and down to the other colour in an electro-mechanical typewriter or teleprinter, such as the Teletype Model 38, to automate the same function of manual typewriters. Black was the conventional ambient default colour and so was shifted "in" or "out" with the other colour on the ribbon. Later advancements in technology instigated use of this function for switching to a different font or character set and back. This was used, for instance, in the Russian character set known as KOI7-switched, where SO starts printing Russian letters, and SI starts printing Latin letters again. Similarly, they are used for switching between Katakana and Roman letters in the 7-bit version of the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage Return
A carriage return, sometimes known as a cartridge return and often shortened to CR, or return, is a control character or mechanism used to reset a device's position to the beginning of a line of text. It is closely associated with the line feed and newline concepts, although it can be considered separately in its own right. Typewriters Originally, the term "carriage return" referred to a mechanism or lever on a typewriter. For machines where the type element was fixed and the paper held in a moving ''carriage'', this lever was on the left attached to the moving carriage, and operated after typing a line of text to cause the carriage to return to the far right so the type element would be aligned to the left side of the paper. The lever would also usually ''feed'' the paper to advance to the next line. Many electric typewriters such as IBM Electric or Underwood Electric made carriage return to be another key on the keyboard instead of a lever. The key was usually labeled "car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Feed
A page break is a marker in an electronic document that tells the document interpreter that the content which follows is part of a new page. A page break causes a form feed to be sent to the printer during spooling of the document to the printer. Thus it is one of the elements that contributes to pagination. Form feed Form feed is a page-breaking ASCII control character. It directs the printer to eject the current page and to continue printing at the top of another. Often, it will also cause a carriage return. The form feed character code is defined as 12 (0xC in hexadecimal), and may be represented as control+L or ^L. In a related use, control+L can be used to clear the screen in Unix shells such as bash. In the C programming language (and other languages derived from C), the form feed character is represented as '\f'. Unicode also provides the character as a printable symbol for a form feed (not as the form feed itself). The form feed character is considered whitespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Tab
The tab key (abbreviation of tabulator key or tabular key) on a keyboard is used to advance the cursor to the next tab stop. History The word ''tab'' derives from the word ''tabulate'', which means "to arrange data in a tabular, or table, form." When a person wanted to type a table (of numbers or text) on a typewriter, there was a lot of time-consuming and repetitive use of the space bar and backspace key. To simplify this, a horizontal bar was placed in the mechanism called the tabulator rack. Pressing the tab key would advance the carriage to the next tabulator stop. The original tabulator stops were adjustable clips that could be arranged by the user on the tabulator rack. Fredric Hillard filed a patent application for such a mechanism in 1900. The tab mechanism came into its own as a rapid and consistent way of uniformly indenting the first line of each paragraph. Often a first tab stop at 5 or 6 characters was used for this, far larger than the indentation used when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Feed
Newline (frequently called line ending, end of line (EOL), next line (NEL) or line break) is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line of text and the start of a new one. History In the mid-1800s, long before the advent of teleprinters and teletype machines, Morse code operators or telegraphists invented and used Morse code prosigns to encode white space text formatting in formal written text messages. In particular the Morse prosign (mnemonic reak ext) represented by the concatenation of literal textual Morse codes "B" and "T" characters sent without the normal inter-character spacing is used in Morse code to encode and indicate a ''new line'' or ''new section'' in a formal text message. Later, in the age of modern teleprinters, standardized character set control codes were developed to aid in white spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tab Key
The tab key (abbreviation of tabulator key or tabular key) on a keyboard is used to advance the cursor to the next tab stop. History The word ''tab'' derives from the word ''tabulate'', which means "to arrange data in a tabular, or table, form." When a person wanted to type a table (of numbers or text) on a typewriter, there was a lot of time-consuming and repetitive use of the space bar and backspace key. To simplify this, a horizontal bar was placed in the mechanism called the tabulator rack. Pressing the tab key would advance the carriage to the next tabulator stop. The original tabulator stops were adjustable clips that could be arranged by the user on the tabulator rack. Fredric Hillard filed a patent application for such a mechanism in 1900. The tab mechanism came into its own as a rapid and consistent way of uniformly indenting the first line of each paragraph. Often a first tab stop at 5 or 6 characters was used for this, far larger than the indentation used when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backspace
Backspace () is the keyboard key that originally pushed the typewriter carriage one position backwards and in modern computer systems moves the display cursor one position backwards,"Backwards" means to the left for left-to-right languages. deletes the character at that position, and shifts back the text after that position by one position. Typewriter In someMany typewriters don't advance accent characters, so that no backspace is needed. However, it is still used e.g. for combining "o" with "/". typewriters, a typist would, for example, type a lowercase letter A with acute accent (á) by typing a lowercase letter A, backspace, and then the acute accent key. This technique (also known as overstrike) is the basis for such spacing modifiers in computer character sets such as the ASCII caret (^, for the circumflex accent). Backspace composition no longer works with typical modern digital displays or typesetting systems.There is no reason why a digital display or typesetting system co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Character
A bell code (sometimes bell character) is a device control code originally sent to ring a small electromechanical bell on tickers and other teleprinters and teletypewriters to alert operators at the other end of the line, often of an incoming message. Though tickers punched the bell codes into their tapes, printers generally do not print a character when the bell code is received. Bell codes are usually represented by the label "BEL". They have been used since 1870 (initially in Baudot code). To maintain backward compatibility, video display terminals (VDTs) that replaced teletypewriters included speakers or buzzers to perform the same function, as did the personal computers that followed. Modern terminal emulators often integrate the warnings to the desktop environment (e.g., the macOS Terminal will play the system warning sound) and also often offer a silent ''visual bell'' feature that flashes the terminal window briefly. Representations In ASCII and Unicode the characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acknowledge Character
In data networking, telecommunications, and computer buses, an acknowledgment (ACK) is a signal that is passed between communicating processes, computers, or devices to signify acknowledgment, or receipt of message, as part of a communications protocol. The negative-acknowledgement (NAK or NACK) is a signal that is sent to reject a previously received message or to indicate some kind of error. Acknowledgments and negative acknowledgments inform a sender of the receiver's state so that it can adjust its own state accordingly. Many protocols contain checksums to verify the integrity of the payload and header. Checksums are used to detect data corruption. If a message is received with an invalid checksum (that is, the data received would have a different checksum than the message had), the receiver can know that some information was corrupted. Most often, when checksums are employed, a corrupted message received will either not be served an ACK signal, or will be served a NAK sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |