|
Coastal Reservoir
Coastal reservoir is a type of reservoir to store fresh water on sea coast area near a river delta. Saemanguem in South Korea, Marina Barrage in Singapore, Qingcaosha and Plover Cove in China, Delta Works in Netherlands, Thanneermukkom Bund in India etc. are a few existing coastal reservoirs. Advantages Unlike land-based water reservoirs, there is no land submergence in the case of coastal reservoirs. They store water without disturbing people and natural habitat by replacing standing salt water on the sea area by river flood water. The coastal reservoir area is separated from the sea by building earth dikes by dredging. Water is pumped from these reservoirs for irrigation, municipal and industrial purposes. Sometimes used for flood control and land reclamation from the sea coast. The social and environmental impacts of coastal reservoirs are negligible compared to land-based water reservoirs. The construction cost is a few times less than the cost of land-based reservoirs since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plover Cove Reservoir Form A Plane
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wader, wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae. Description There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "Dotterel (other), dotterel". The closely related lapwing subfamily, Vanellinae, comprises about 20 species. Plovers are found throughout the world, with the exception of the Sahara and the Polar regions of Earth, polar regions, and are characterised by relatively short bills. They hunt by sight, rather than by feel as longer-billed waders like snipes do. They feed mainly on insects, worms or other invertebrates, depending on the habitat, which are obtained by a run-and-pause technique, rather than the steady probing of some other wader groups. Plovers engage in false brooding, a type of distraction display. Examples include pretending to change position or to sit on an imaginary nest site. Species list in taxonomic sequence The International Ornithological Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil-storage Trade
The oil-storage trade, also referred to as contango, is a market strategy in which large, often vertically-integrated oil companies purchase oil for immediate delivery and storage—when the price of oil is low— and hold it in storage until the price of oil increases. Investors bet on the future of oil prices through a financial instrument, oil futures in which they agree on a contract basis, to buy or sell oil at a set date in the future. Crude oil is stored in salt mines, tanks and oil tankers. Investors can choose to take profits or losses prior to when the oil delivery date arrives or they can leave the contract in place and physical oil is delivered on the set date to an officially designated delivery point. In the United States, that is usually to Cushing, Oklahoma. When delivery dates approach, they close out existing contracts and sell new ones for future delivery of the same oil. The oil never moves out of storage. If the forward market is in "contango"—the forward p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolved Load
Dissolved load is the portion of a stream's total sediment load that is carried in solution, especially ions from chemical weathering. It is a major contributor to the total amount of material removed from a river's drainage basin, along with suspended load and bed load. The amount of material carried as dissolved load is typically much smaller than the suspended load, though this is not always the case, particularly when the available river flow is mostly harnessed for purposes such as irrigation or industrial uses. Dissolved load comprises a significant portion of the total material flux out of a landscape, and its composition is important in regulating the chemistry and biology of the stream water. The dissolved load is primarily controlled by the rate of chemical weathering, which depends on climate and weather conditions such as moisture and temperature. Dissolved load has many useful applications within the field of geology, including erosion, denudation, and reconstructing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Flows
Environmental flows describe the quantity, timing, and quality of water flows required to sustain freshwater and estuarine ecosystems and the human livelihoods and well being that depend on these ecosystems. In the Indian context river flows required for cultural and spiritual needs assumes significance. Through implementation of environmental flows, water managers strive to achieve a flow regime, or pattern, that provides for human uses and maintains the essential processes required to support healthy river ecosystems. Environmental flows do not necessarily require restoring the natural, pristine flow patterns that would occur absent human development, use, and diversion but, instead, are intended to produce a broader set of values and benefits from rivers than from management focused strictly on water supply, energy, recreation, or flood control. Rivers are parts of integrated systems that include floodplains and riparian corridors. Collectively these systems provide a large suit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
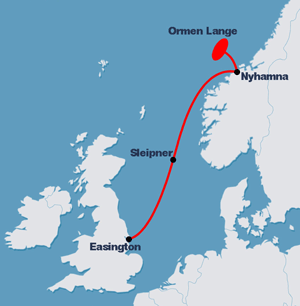
Submarine Pipeline
A submarine pipeline (also known as marine, subsea or offshore pipeline) is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench.Dean, p. 338-340Gerwick, p. 583-585 In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers.Palmer & King, p. 2-3 Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a ''flowline'' and a pipeline.Bai & Bai, p. 22 The former is an ''intrafield'' pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform ''within'' a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an ''export pipeline'', is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Electric Vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion (a hydrogen fuel cell, internal combustion engine, etc.). BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of internal combustion engines (ICEs) for propulsion. They derive all power from battery packs and thus have no internal combustion engine, fuel cell, or fuel tank. BEVs include – but are not limited to – motorcycles, bicycles, scooters, skateboards, railcars, watercraft, forklifts, buses, trucks, and cars. In 2016, there were 210 million electric bikes worldwide used daily. Cumulative global sales of highway-capable light-duty pure electric car vehicles passed the one million unit milestone in September 2016. , the world's top selling all-electric car in history is the Tesla Model 3, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell Vehicle
A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate electricity generally using oxygen from the air and compressed hydrogen. Most fuel cell vehicles are classified as zero-emissions vehicles that emit only water and heat. As compared with internal combustion vehicles, hydrogen vehicles centralize pollutants at the site of the hydrogen production, where hydrogen is typically derived from reformed natural gas. Transporting and storing hydrogen may also create pollutants. Fuel cells have been used in various kinds of vehicles including forklifts, especially in indoor applications where their clean emissions are important to air quality, and in space applications. The first commercially produced hydrogen fuel cell automobile, the Hyundai ix35 FCEV, was introduced in 2013, the Toyota Mirai followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or a translation for ''autobahn'', '' autoroute'', etc. According to Merriam Webster, the use of the term predates the 12th century. According to Etymonline, "high" is in the sense of "main". In North American and Australian English, major roads such as controlled-access highways or arterial roads are often state highways (Canada: provincial highways). Other roads may be designated "county highways" in the US and Ontario. These classifications refer to the level of government (state, provincial, county) that maintains the roadway. In British English, "highway" is primarily a legal term. Everyday use normally implies roads, while the legal use covers any route or path with a public right of access, including footpaths etc. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
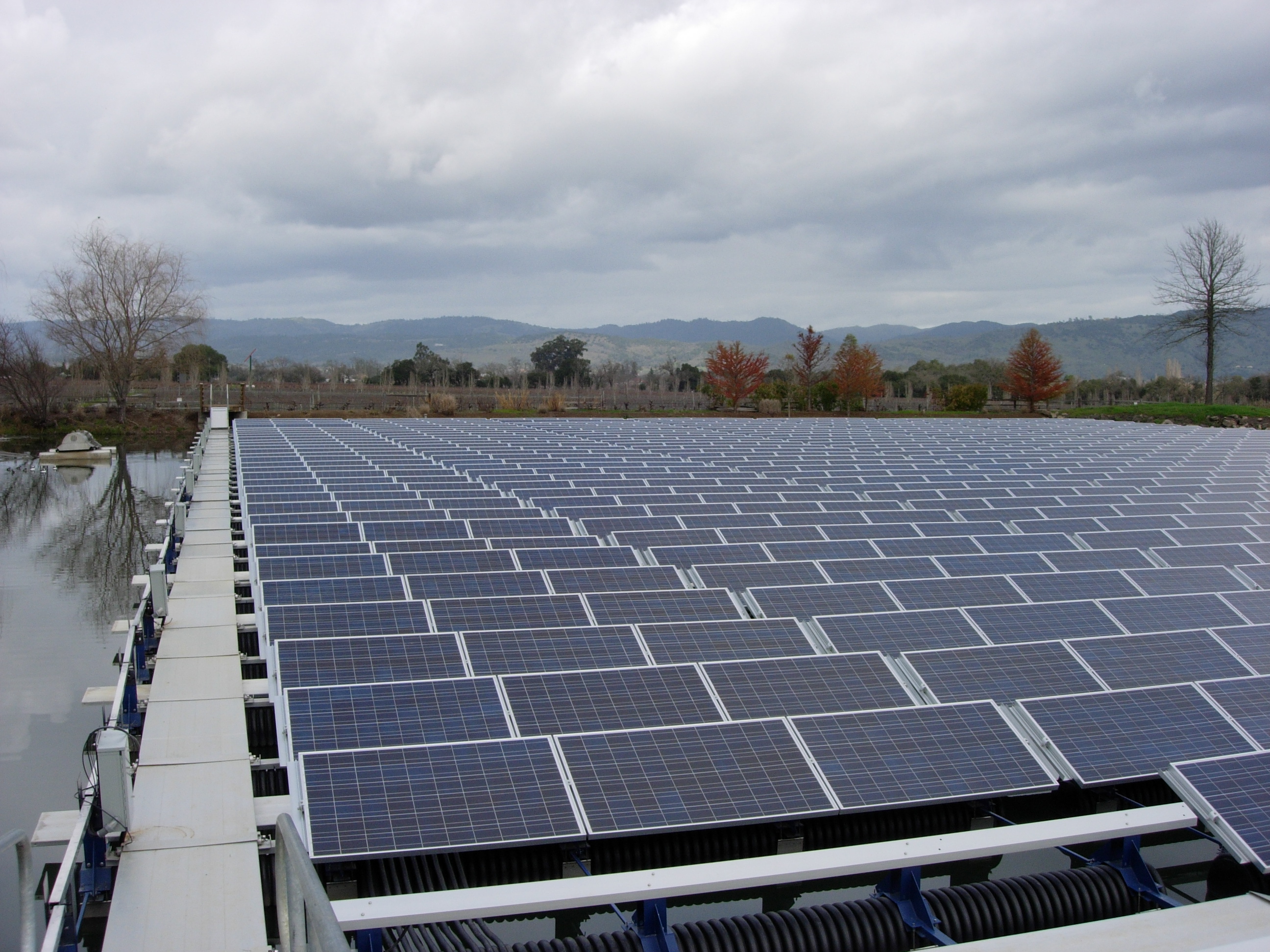
Floating Solar
Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, is solar panels mounted on a structure that floats on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake. The market for this renewable energy technology has grown rapidly since 2016. The first 20 plants with capacities of a few dozen kWp were built between 2007 and 2013. Installed power reached 3 GW in 2020, with 10 GW predicted by 2025. The costs for a floating system are 20-25% higher than for ground-mounted systems. Technology features There are several reasons for this development: #''No land occupancy'': The main advantage of floating PV plants is that they do not take up any land, except the limited surfaces necessary for electric cabinet and grid connections. Their price is comparable with land based plants, but floatovoltaics provide a good way to avoid land consumption. #''Installation and decommissioning'': Floating PV plants are more compact than land-based plants, their management is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Bore
{{disambiguation ...
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide. Tidal may also refer to: * ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple * Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim * TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music * Tidal (service), a music streaming service * Tidal, Manitoba, Canada ** Tidal station, Tidal, Manitoba See also * Tidal flow (traffic), the flow of traffic thought of as an analogy with the flow of tides * Tidal force, a secondary effect of the force of gravity and is responsible for the tides * Tide (other) A tide is the rise and fall of a sea level caused by the Moon's gravity and other factors. Tide may also refer to: Media * ''The Tide'' (Nigeria), a newspaper * ''Tide'' (TV series), 2019 Irish/Welsh/Scottish documentary series * WTKN, a radio s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the normal tidal level, and does not include waves. The main meteorological factor contributing to a storm surge is high-speed wind pushing water towards the coast over a long fetch. Other factors affecting storm surge severity include the shallowness and orientation of the water body in the storm path, the timing of tides, and the atmospheric pressure drop due to the storm. There is a suggestion that climate change may be increasing the hazard of storm surges. Some theorize that as extreme weather becomes more intense and sea level rises due to climate change, storm surge is expected to cause more risk to coastal populations. Communities and governments can adapt by building hard infrastructure, like surge barriers, soft infrastructure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_W_IMG_0104.jpg)




.jpg)

