|
Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial
A cluster-randomised controlled trial is a type of randomised controlled trial in which groups of subjects (as opposed to individual subjects) are randomised. Cluster randomised controlled trials are also known as cluster-randomised trials, group-randomised trials, and place-randomized trials. Cluster-randomised controlled trials are used when there is a strong reason for randomising treatment and control groups over randomising participants. Prevalence A 2004 Bibliometrics, bibliometric study documented an increasing number of publications in the medical literature on cluster-randomised controlled trials since the 1980s. Advantages Advantages of cluster-randomised controlled trials over individually randomised controlled trials include: * The ability to study interventions that cannot be directed toward selected individuals (e.g., a radio show about lifestyle changes) and the ability to control for "contamination" across individuals (e.g., one individual's changing behaviors may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomised Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing standard of care; these are then termed the 'experimental' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Behavioral Scientist
''American Behavioral Scientist'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes papers in the fields of social and behavioral sciences. The managing editor is Laura Lawrie. It was established in 1957 by Alfred de Grazia and is currently published by SAGE Publications, who acquired the journal from de Grazia. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Scopus and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... is 2.531, ranking it 41 out of 111 journals in the category "Social Sciences, Interdisciplinary" and 88 out of 130 journals in the category "Psychology, Clinical". References External links * {{Authority control SAGE Publishing aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliometrics
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in regard with scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Bibliometrics is closely associated with scientometrics, that is the analysis of scientific metrics and indicators, to the point that both fields largely overlap. Bibliometrics studies first appeared in the late 19th century. They have known a significative development after the Second World War in a context of "periodical crisis" and new technical opportunities offered by computing tools. In the early 1960s, the Science Citation Index of Eugene Garfield and the citation network analysis of Derek John de Solla Price laid the fundamental basis of a structured research program on bibliometrics. Citation analysis is a commonly used bibliometric method which is based on constructing the citation graph, a network or graph representation of the cita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National And International Statistical Services
The following is a list of national and international statistical services. Central national statistical services Nearly every country in the world has set a central public sector unit entirely devoted to the production, harmonisation and dissemination of official statistics that the public sector and the national community need to run, monitor and evaluate their operations and policies. This central statistical organisation does not produce every official statistic as other public sector organisations, like the national central bank or ministries in charge of agriculture, education or health, may be charged with producing and disseminating sector policy oriented statistical data. The statistical legislation and regulation generally attribute responsibilities and authorities according to statistical domains or functions in addition to those of the central unit. The table below lists these central statistical organisations by country. The United States has no central producing unit, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling Frame
In statistics, a sampling frame is the source material or device from which a sample is drawn. It is a list of all those within a population who can be sampled, and may include individuals, households or institutions. Importance of the sampling frame is stressed by Jessen and Salant and Dillman.Salant, Priscilla, and Don A. Dillman. "How to Conduct your own Survey: Leading professional give you proven techniques for getting reliable results" (1995) Obtaining and organizing a sampling frame In the most straightforward cases, such as when dealing with a batch of material from a production run, or using a census, it is possible to identify and measure every single item in the population and to include any one of them in our sample; this is known as ''direct element sampling''. However, in many other cases this is not possible; either because it is cost-prohibitive (reaching every citizen of a country) or impossible (reaching all humans alive). Having established the frame, there ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
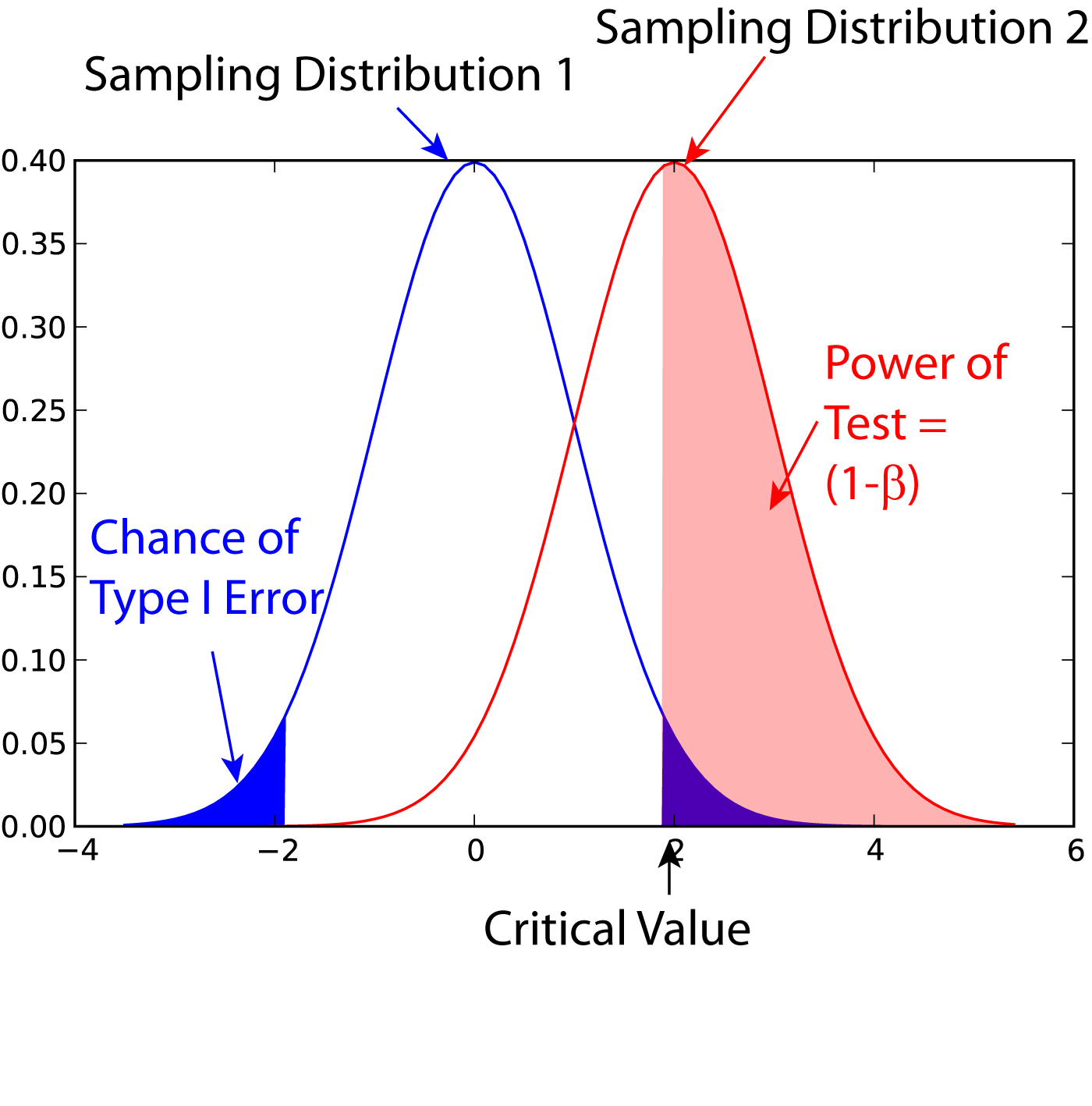
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraclass Correlation
In statistics, the intraclass correlation, or the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), is a descriptive statistic that can be used when quantitative measurements are made on units that are organized into groups. It describes how strongly units in the same group resemble each other. While it is viewed as a type of correlation, unlike most other correlation measures it operates on data structured as groups, rather than data structured as paired observations. The ''intraclass correlation'' is commonly used to quantify the degree to which individuals with a fixed degree of relatedness (e.g. full siblings) resemble each other in terms of a quantitative trait (see heritability). Another prominent application is the assessment of consistency or reproducibility of quantitative measurements made by different observers measuring the same quantity. Early ICC definition: unbiased but complex formula The earliest work on intraclass correlations focused on the case of paired measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Of A Test
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I And Type II Errors
In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error is the mistaken rejection of an actually true null hypothesis (also known as a "false positive" finding or conclusion; example: "an innocent person is convicted"), while a type II error is the failure to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false (also known as a "false negative" finding or conclusion; example: "a guilty person is not convicted"). Much of statistical theory revolves around the minimization of one or both of these errors, though the complete elimination of either is a statistical impossibility if the outcome is not determined by a known, observable causal process. By selecting a low threshold (cut-off) value and modifying the alpha (α) level, the quality of the hypothesis test can be increased. The knowledge of type I errors and type II errors is widely used in medical science, biometrics and computer science. Intuitively, type I errors can be thought of as errors of ''commission'', i.e. the researcher unluck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By Random assignment, randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing Standard of care#Medical standard of care, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zelen's Design
Zelen's design is an experimental design for randomized clinical trials proposed by Harvard School of Public Health statistician Marvin Zelen (1927-2014). In this design, patients are randomized to either the treatment or control group before giving informed consent. Because the group to which a given patient is assigned is known, consent can be sought conditionally. Overview In this design, those patients receiving standard care need not be consented for participation in the study other than possibly for privacy issues. On the other hand, those patients randomized to the experimental group are consented as usual, except that they are consenting to the certainty of receiving the experimental treatment only; alternatively these patients can decline and receive the standard treatment instead. In comparison, the current predominant design is for consent to be solicited prior to randomization. That is, eligible patients are asked if they would agree to participate in the clinical tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |