|
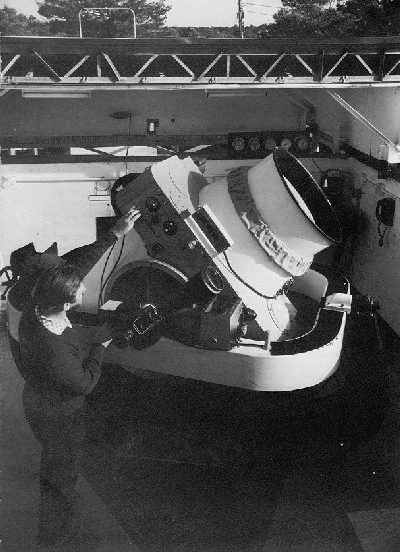
Cloudcroft Observatory
Cloudcroft Observatory, ( obs. code: V29) is an astronomical observatory located in the Lincoln National Forest near Cloudcroft, New Mexico, approximately northeast of Alamogordo. It is owned by the Tzec Maun Foundation, a private astronomical organization. Known as the Cloudcroft Electro-Optical Research Facility when it was built in 1962, it was owned by the U.S. Air Force (USAF) until 1982 and initially operated by the Air Force Avionics Laboratory (AFAL). It was used as part of a project to develop new techniques for detecting satellites with electronic imaging devices, which were eventually to replace Project Space Track's Baker-Nunn photographic system. From 1995 to 2002, the facility was known as the NASA Orbital Debris Observatory and hosted two telescopes funded and operated by NASA. History The site near Cloudcroft was selected by AFAL in 1961 after several months of site characterization, and construction began in 1962. First light of the Electro-Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Observatory Codes
This is a list of observatory codes (IAU codes or MPC codes) published by the Minor Planet Center. For a detailed description, ''see observations of small Solar System bodies Observations of minor planets as well as comets and natural satellites of the Solar System are made by astronomical observatories all over the world and reported to the Minor Planet Center (MPC), a service of the International Astronomical Unio ...''. List References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Observatory codes * Astronomy-related lists Technology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Telescope
The Newtonian telescope, also called the Newtonian reflector or just a Newtonian, is a type of reflecting telescope invented by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton, using a concave primary mirror and a flat diagonal secondary mirror. Newton's first reflecting telescope was completed in 1668 and is the earliest known functional reflecting telescope. The Newtonian telescope's simple design has made it very popular with amateur telescope makers. Description [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Otero County, New Mexico
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories In New Mexico
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Observatories
This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer in operation. While other sciences, such as volcanology and meteorology, also use facilities called observatories for research and observations, this list is limited to observatories that are used to observe celestial objects. Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Many modern telescopes and observatories are located in space to observe astronomical objects in wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot penetrate the Earth's atmosphere (such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays) and are thus impossible to observe using ground-based telescopes. Being above the atmosphere, these space observatories can also avoid the effects of atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEODSS
The United States Space Surveillance Network (SSN) detects, tracks, catalogs and identifies artificial objects orbiting Earth, e.g. active/inactive satellites, spent rocket bodies, or fragmentation debris. The system is the responsibility of United States Space Command and operated by the United States Space Force. Space surveillance accomplishes the following: * Predict when and where a decaying space object will re-enter the Earth's atmosphere; * Prevent a returning space object, which to radar looks like a missile, from triggering a false alarm in missile-attack warning sensors of the U.S. and other countries; * Chart the present position of space objects and plot their anticipated orbital paths; * Detect new artificial objects in space; * Correctly map objects traveling in Earth orbit; * Produce a running catalog of artificial space objects; * Determine ownership of a re-entering space object; * Inform NASA whether or not objects may interfere with the International Space S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-mirror Telescope
Liquid-mirror telescopes are telescopes with mirrors made with a reflective liquid. The most common liquid used is mercury, but other liquids will work as well (for example, low-melting alloys of gallium). The liquid and its container are rotated at a constant speed around a vertical axis, which causes the surface of the liquid to assume a paraboloidal shape. This parabolic reflector can serve as the primary mirror of a reflecting telescope. The rotating liquid assumes the same surface shape regardless of the container's shape; to reduce the amount of liquid metal needed, and thus weight, a rotating mercury mirror uses a container that is as close to the necessary parabolic shape as possible. Liquid mirrors can be a low-cost alternative to conventional large telescopes. Compared to a solid glass mirror that must be cast, ground, and polished, a rotating liquid-metal mirror is much less expensive to manufacture. Isaac Newton noted that the free surface of a rotating liquid forms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Mountain Observatory
Table Mountain Observatory (TMO) is an astronomical observation facility operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (California Institute of Technology). It is located in Big Pines, California, in Angeles National Forest near Wrightwood, north-northeast of Los Angeles, California, in the United States. TMO is part of JPL's Table Mountain Facility (TMF). The larger site hosts a number of non-astronomical projects. The site was first used by the Smithsonian Institution in 1924, which conducted atmospheric, solar, and astronomical observations for many years. JPL took over the lease in 1962. The observatory conducts high-precision astrometric observations to support NASA and international spacecraft mission navigation, confirmation and recovery of near-Earth objects such as comets and asteroids that may potentially impact the Earth, and technology development. The main-belt asteroid 84882 Table Mountain was named in honor of the observatory. List of discovered minor planets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
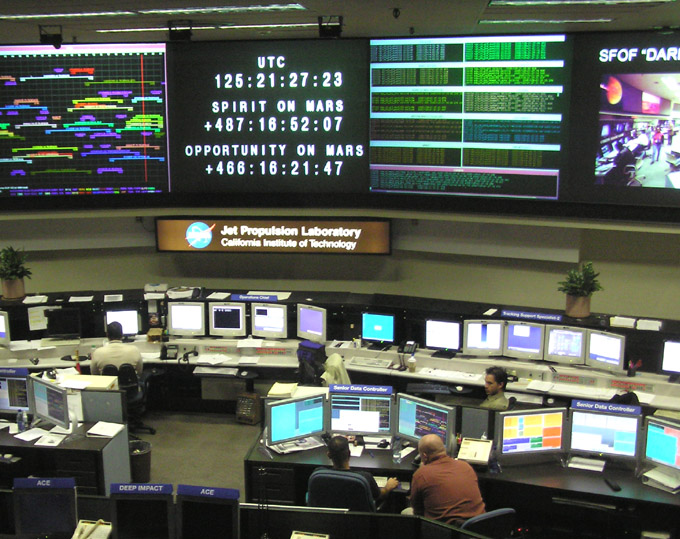
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States. Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA and managed by the nearby California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The laboratory's primary function is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating the NASA Deep Space Network. Among the laboratory's major active projects are the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the ''Perseverance'' rover and the '' Ingenuity'' Mars helicopter; the Mars Science Laboratory mission, including the ''Curiosity'' rover; the InSight lander (''Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport''); the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''; the ''Juno'' spacecraft orbiting Jupiter; the ''SMAP'' satellite for earth surface s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Solar Observatory
The National Solar Observatory (NSO) is a United States public research institute to advance the knowledge of the physics of the Sun. NSO studies the Sun both as an astronomical object and as the dominant external influence on Earth. NSO is headquartered in Boulder and operates facilities at two locations - at the 4-meter Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope in the Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, and at Sacramento Peak near Sunspot in New Mexico. NSO provides its observations to the scientific community. It operates facilities, develops advanced instrumentation both in-house and through partnerships, conducts solar research, and carries out educational and public outreach. Visiting the observatories The National Solar Observatory HQ is located on the campus of the University of Colorado, Boulder. It also has some staff on Maui, and Sacramento Peak. Telescopes operated by the observatory Haleakala Observatory * Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope Sacramento Peak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space And Missile Systems Center
Space Systems Command (SSC) is the United States Space Force's space development, acquisition, launch, and logistics field command. It is headquartered at Los Angeles Air Force Base, California and manages the United States' space launch ranges. Space Systems Command is the oldest military space organization in the United States Armed Forces, first established as the Western Development Division (WDD) on 1 April 1954 under Air Research and Development Command to manage the U.S. Air Force's ballistic missile program. It gained responsibility for spacecraft development in 1955 and was renamed the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division (AFBMD) in 1957. As part of Air Research and Development Command's transformation the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division's space and missile responsibilities were split, with the Space Systems Division (SSD) established in 1961. In 1967, the Space Systems Division was reorganized as the Space and Missile Systems Organization (SAMSO), absorbing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |