|
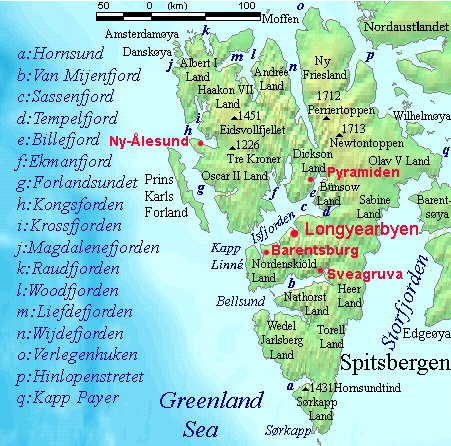
Climate Of Svalbard
Svalbard is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The climate of Svalbard is principally a result of its latitude, which is between 74ô¯ and 81ô¯ north. Climate is defined by the World Meteorological Organization as the average weather over a 30-year period. The North Atlantic Current moderates Svalbard's temperatures, particularly during winter, giving it up to higher winter temperature than similar latitudes in continental Russia and Canada. This keeps the surrounding waters open and navigable most of the year. The interior fjord areas and valleys, sheltered by the mountains, have fewer temperature differences than the coast, with about 2 ô¯C lower summer temperatures and 3 ô¯C higher winter temperatures. On the south of the largest island, Spitsbergen, the temperature is slightly higher than further north and west. During winter, the temperature difference between south and north is typically 5 ô¯C, and about 3 ô¯C in summer. Bear Island (''Bjû¡rnû¡ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard In Europe (-mini Map -rivers)
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74ô¯ to 81ô¯ north latitude, and from 10ô¯ to 35ô¯ east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Meteorological Institute
The Norwegian Meteorological Institute ( no, Meteorologisk institutt), also known internationally as MET Norway, is Norway's national meteorological institute. It provides weather forecasts for civilian and military uses and conducts research in meteorology, oceanography and climatology. It is headquartered in Oslo and has offices and stations in other cities and places. It has around 500 full-time staff and was founded in 1866. History The institute was founded on 1 December 1866 with the help of Norwegian astronomer and meteorologist Henrik Mohn who served as its director until 1913. He is credited with founding meteorological research in Norway. The abbreviation ''MET Oslo'' or ''MET OSLO'' has been used internationally for a long time; the World Meteorological Organization for example recommended in 1956 that its members standardized references to this institute as ''MET OSLO''.Abridged Final Report of the Session, Commission for Marine Meteorology, Secretariat of the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Vulnerability
Climate change vulnerability (or climate vulnerability or climate risk vulnerability) is defined as the "propensity or predisposition to be adversely affected" by climate change. It can apply to humans but also to natural systems (ecosystems). Human and ecosystem vulnerability are interdependent.IPCC, 2022Summary for Policymakers .-O. PûÑrtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, A. AlegrûÙa, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. LûÑschke, V. MûÑller, A. Okem (eds.) InClimate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change .-O. PûÑrtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. AlegrûÙa, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. LûÑschke, V. MûÑller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 3ã33, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.001. Climate change vulnerability encompasses "a variety of concepts and elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard Jan Mayen Temp (1750-2013)BE
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74th parallel north, 74ô¯ to 81st parallel north, 81ô¯ north latitude, and from 10th meridian east, 10ô¯ to 35th meridian east, 35ô¯ east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the Whaling, whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
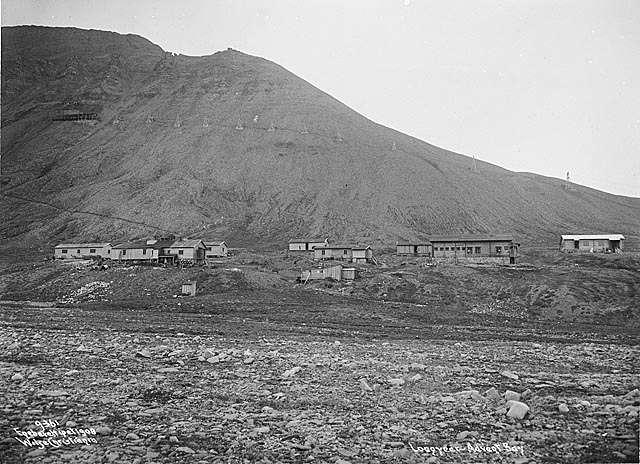
Sveagruva
Sveagruva (), or simply Svea, was a mining settlement in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard, lying at the head of Van Mijenfjord. It was the third largest settlement in the archipelago (after Longyearbyen and Barentsburg). Around 300 workers living in Longyearbyen commuted to Sveagruva for work on a daily or weekly basis. The mine was operated by Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani. There is no road to Longyearbyen or any other settlements, so travel is done by air from Svea Airport and coal transport by ship from a port southwest. Sveagruva closed in 2017 and currently has no permanent inhabitants. History The town was established in 1917 by Swedes. It was thereafter destroyed in 1944, but quickly re-established after World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesãincluding all of the great powersãforming two oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barentsburg
Barentsburg (russian: ÅůîÅçŧîÅÝîîÅ°) is the second-largest settlement in Svalbard, Norway, with about 455 inhabitants (). A coal mining town, the settlement is almost entirely made up of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians. History Rijpsburg, a now abandoned Dutch settlement on Spitsbergen on Cape Boheman (Bohemanflya), at the north site of Nordfjorden in the Isfjord, stood roughly diagonally opposite Longyearbyen. The Rotterdam-based Van der Eb and Dresselhuys Scheepvaartmaatschappij (ship-building company) built it in 1920, using prefabricated huts, for the mining of coal. Twelve Dutch staff and 52 German miners started mining coal here that year. The Dutch Spitsbergen Company, founded in 1920, bought a mine in Green Harbour from the Russians and mined coal from 1921 to 1926. The company renamed its settlement Barentsburg after the Dutch explorer Willem Barentsz. In 1932 the company sold the mine, including its settlement Barentsburg, to the Russian trust Arktikugol. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, locally lèäéjèrùbyùèn "The Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000 and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank of the Longyear Valley and on the shore of Adventfjorden, the short estuary leading into Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the island's broadest inlet. As of 2002 Longyearbyen Community Council became an official Norwegian municipality. It is the seat of the Governor of Svalbard. The town's mayor is Arild Olsen. Known as Longyear City until 1926, the town was established by and named after American John Munro Longyear, whose Arctic Coal Company started coal-mining there in 1906. Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani (SNSK) took over the mining operations in 1916, and still conducts mining. The German ''Kriegsmarine'' almost completely destroyed the town on 8 September 1943, but rebuilding took place after the Second World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NordenskiûÑld Land
NordenskiûÑld Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Van Mijenfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after Finnish-Swedish explorer and geologist Nils Adolf Erik NordenskiûÑld. The coastal region of NordenskiûÑld Land (Nordenskiû¡ldkysten) has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports breeding populations of barnacle geese and common eider The common eider (pronounced ) (''Somateria mollissima''), also called St. Cuthbert's duck or Cuddy's duck, is a large ( in body length) sea-duck that is distributed over the northern coasts of Europe, North America and eastern Siberia. It breed ...s. References Important Bird Areas of Svalbard Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danes Island
Danes Island ( no, Danskû¡ya) is an island in Norway's Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean with an area of . It lies just off the northwest coast of Spitsbergen, the largest island in the archipelago, near to Magdalenefjorden. Just to the north lies Amsterdam Island. Most of Svalbard's islands, including Danes Island, are uninhabited; only Spitsbergen, Bjû¡rnû¡ya and Hopen have settlements. History In 1631 the Danish established a permanent station in Robbe Bay ( Kobbefjorden), which was abandoned in 1658. Another station was established by the Dutch in Houcker Bay ( Virgohamna), on the north side of Danes Island in the 1630s. It was called the "Cookery of Harlingen." The remains of this station were seen by Friderich Martens in 1671.Conway, W. M. 1906. ''No Man's Land: A History of Spitsbergen from Its Discovery in 1596 to the Beginning of the Scientific Exploration of the Country''. Cambridge: At the University Press. The island is the location from which S. A. Andrû ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sû¡rkapp
Sû¡rkapp ("South Cape") is the southernmost point on Sû¡rkappû¡ya, south of Spitsbergen, the largest island in the Svalbard archipelago, Arctic Norway. It was originally named ''Point Lookout'' (1612). The cape itself is long. The point is bordered by the Greenland Sea to the west, the Norwegian Sea to the south and the Barents Sea to the east. The point is within the Sû¡rkapp Bird Sanctuary. The distance to mainland Norway at Ingû¡y is about 640 km and to Bear Island (Norway), Bear Island about 230 km. References Peninsulas of Svalbard Ramsar sites in Norway Sû¡rkappû¡ya {{Svalbard-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)