|
Clavaria Helicoides
''Clavaria'' is a genus of fungi in the family Clavariaceae. Species of ''Clavaria'' produce basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that are either cylindrical to club-shaped or branched and coral-like. They are often grouped with similar-looking species from other genera, when they are collectively known as the clavarioid fungi. All ''Clavaria'' species are terrestrial and most (if not all) are believed to be saprotrophic (decomposing dead plant material). In Europe, they are typical of old, mossy, unimproved grassland. In North America and elsewhere, they are more commonly found in woodlands. History ''Clavaria'' (the name is derived from the Latin "clava", a club) was first introduced as a genus name by Vaillant (1727), later accepted by Micheli (1729), and was one of the original genera used by Linnaeus in his ''Species Plantarum'' of 1753. It contained all species of fungi with erect, club-shaped or branched (coral-like) fruit bodies, including many that are now referred to the Asco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sébastien Vaillant
Sébastien Vaillant (May 26, 1669 – May 20, 1722) was French botanist who was born at Vigny in present-day Val d'Oise. Early years Vaillant went to school at the age of four and by the age of five, he was collecting plants and transplanting them into his father's garden. At the age of six, he was sent to a boarding school at Pontoise. He suffered with a fever for four months which he claims to have cured using lettuce seasoned with vinegar. He was sent to study with the organist of the Pontoise Cathedral. When the organist died, Vaillant succeeded him at the age of eleven. Vaillant studied medicine and surgery at the hospital in Pontoise (medicine then included studies in botany). He left Pontoise for Évreux at the age of nineteen. He was at the battle of Fleurus in 1690 as a surgeon. While still a surgeon in 1691, he was in Paris when he took as his master of botany Joseph Pitton de Tournefort (1656–1708). Tournefort used Vaillant's talents while writing (''History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
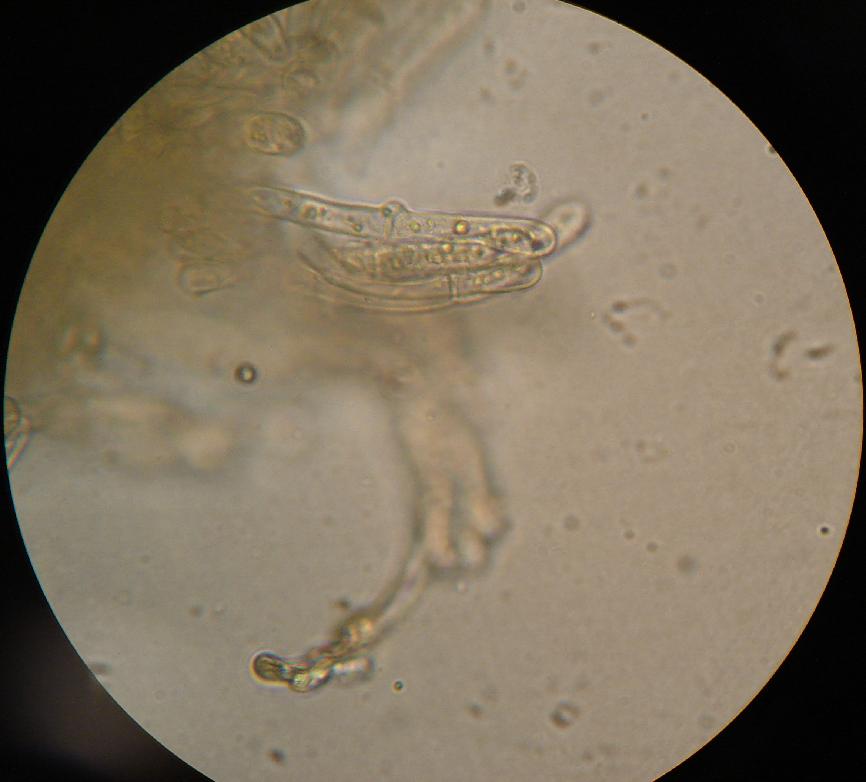
Ramariopsis
''Ramariopsis'' is a genus of coral fungi in the family Clavariaceae. The genus has a collectively widespread distribution and contains about 40 species. The name means 'having the appearance of ''Ramaria. Taxonomy ''Ramariopsis'' was originally defined as a subgenus of ''Clavaria'' by Dutch mycologist Marinus Anton Donk in 1933. Several European species similar to the type, '' Clavaria kunzei'', were included: '' Clavaria subtilis'', '' Clavaria pyxidata'', '' Clavaria angulispora'', and '' Clavaria pulchella''. In Donk's concept, defining characteristics of the group included small, branching, fruitbodies with a stipe, and an almost cartilaginous consistency to the flesh. Spores are small and hyaline (translucent), spherical to ellipsoid, and have a surface ornamentation ranging from echinulate (spiny) to verruculose (covered with small warts). E.J.H. Corner promoted the subgenus to generic status in his 1950 world monograph of clavarioid fungi. Ron Petersen emended the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavulinopsis
''Clavulinopsis'' is a genus of coral fungi in the family Clavariaceae. The genus, first described scientifically by Casper van Overeem in 1923, has a widespread distribution. The name means "having the appearance of ''Clavulina''". Species , Index Fungorum lists 67 valid species in ''Clavulinopsis'': *'' C. alcicornis'' *'' C. amoena'' *'' C. antillarum'' *'' C. appalachiensis'' *'' C. archeri'' *'' C. arctica'' *'' C. arenicola'' *'' C. aurantia'' *'' C. aurantiobrunnea'' *'' C. aurantiocinnabarina'' *'' C. boninensis'' *'' C. brevipes'' *'' C. candida'' *'' C. carneola'' *'' C. cinnamomea'' *'' C. cirrata'' *'' C. citrinoalba'' *'' C. coliformis'' *'' C. corallinorosacea'' *'' C. corniculata'' (edible) *'' C. depokensis'' *'' C. daigremontiana'' *'' C. depokensis'' *'' C. dichotoma'' *'' C. fleischeriana'' *'' C. fruticula'' *'' C. fusiformis'' *'' C. graveolens'' *'' C. griseola'' *'' C. helvola'' *'' C. hexaspora'' *'' C. hisingeri'' *'' C. hexaspora'' *'' C. laeticolor'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp Connection
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject. In library cataloging, ''monograph'' has a broader meaning—that of a nonserial publication complete in one volume (book) or a definite number of volumes. Thus it differs from a serial or periodical publication such as a magazine, academic journal, or newspaper. In this context only, books such as novels are considered monographs.__FORCETOC__ Academia The English term "monograph" is derived from modern Latin "monographia", which has its root in Greek. In the English word, "mono-" means "single" and "-graph" means "something written". Unlike a textbook, which surveys the state of knowledge in a field, the main purpose of a monograph is to present primary research and original scholarship ascertaining reliable credibility to the required recipient. This research is prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell S
Maxwell may refer to: People * Maxwell (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name ** James Clerk Maxwell, mathematician and physicist * Justice Maxwell (other) * Maxwell baronets, in the Baronetage of Nova Scotia * Maxwell (footballer, born 1979), Brazilian forward * Maxwell (footballer, born 1981), Brazilian left-back * Maxwell (footballer, born 1986), Brazilian striker * Maxwell (footballer, born 1989), Brazilian left-back * Maxwell (footballer, born 1995), Brazilian forward * Maxwell (musician) (born 1973), American R&B and neo-soul singer * Maxwell (rapper) (born 1993), German rapper, member of rap band 187 Strassenbande * Maxwell Jacob Friedman (born 1997) AEW Professional wrestler * Maxwell Silva (born 1953), Sri Lankan Sinhala Catholic cleric, Auxiliary Bishop of Colombo Places United States * Maxwell, California * Maxwell, Indiana * Maxwell, Iowa * Maxwell, Nebraska * Maxwell, New Mexico * Maxwell, Texas * Maxwell Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Conservandum
Nomen may refer to: *Nomen (Roman name), the middle part of Ancient Roman names * Nomen (Ancient Egypt), the personal name of Ancient Egyptian pharaohs *Jaume Nomen (born 1960), Catalan astronomer *Nomen, Latin for a certain part of speech *Nomen, part of the FRSAD Functional Requirements for Subject Authority Data (FRSAD), previously known as Functional Requirements for Subject Authority Records (FRSAR), is a conceptual entity-relationship model developed by the International Federation of Library Associatio ... library model See also *Nō-men, the mask used in Noh performances (see Noh#Masks) * ''Nomina'' (journal), published by the Society for Name Studies in Britain and Ireland {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homonym (biology)
In biology, a homonym is a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, that belongs to a different taxon. The rule in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature is that the first such name to be published is the senior homonym and is to be used (it is " valid"); any others are junior homonyms and must be replaced with new names. It is, however, possible that if a senior homonym is archaic, and not in "prevailing usage," it may be declared a ''nomen oblitum'' and rendered unavailable, while the junior homonym is preserved as a ''nomen protectum''. :For example: :* Cuvier proposed the genus ''Echidna'' in 1797 for the spiny anteater. :*However, Forster had already published the name ''Echidna'' in 1777 for a genus of moray eels. :*Forster's use thus has priority, with Cuvier's being a junior homonym. :*Illiger published the replacement name ''Tachyglossus'' in 1811. Similarly, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marinus Anton Donk
Marinus Anton Donk (14 August 1908 – 2 September 1972) was a Dutch mycologist. He specialized in the taxonomy and nomenclature of mushrooms. Rolf Singer wrote in his obituary that he was "one of the most outstanding figures of contemporary mycology." Early life Donk was born in Situbondo, East Java in 1908, and completed secondary school in The Hague, Netherlands. He studied biology at the University of Utrecht, starting in 1927. As a graduate student in mycology he completed the work for his 1931 "Revisie van de Nederlandse Heterobasidiomyceteae" (Revision of the Dutch Heterobasidiomycetes). He completed his studies and attained a doctorate degree in 1933 with the second part of his work, ''Revisie van de Nederlandse Heterobasidiomyceteae II''. Afterwards he returned to Java, where he worked from 1934 to 1940 as a teacher, and, starting from 1941 as a curator in the herbarium of the Buitenzorg Botanical Garden. He was interned in a Japanese prison camp from 1942 to 1945. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stackhouse (botanist)
John Stackhouse (1742 – 22 November 1819) was an English botanist, primarily interested in spermatophytes, algae and mycology. He was born in Probus, Cornwall, and built Acton Castle, above Stackhouse Cove, Cornwall, in order to further his studies about the propagation of algae from their spores. He was the author of ''Nereis Britannica; or a Botanical Description of British Marine Plants, in Latin and English, accompanied with Drawings from Nature'' (1797). Personal life The second son of William Stackhouse, D.D. (d. 1771), rector of St. Erme, Cornwall, and nephew of Thomas Stackhouse, he was born at Trehane, Probus, in Cornwall. On 20 June 1758 he matriculated at Exeter College, Oxford, and was a Fellow of the college from 1761 to 1764. On succeeding his relative, Mrs. Grace Percival, sister of Sir William Pendarves, in the Pendarves estates in 1763, he resigned his fellowship, and, after travelling abroad for two or three years, settled on his newly acquired property. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Corner_110488.jpg)
_Corner_156686.jpg)