|
Clausena Anisata
:''Should not be confused with syzygium anisatum, a tree native to eastern Australian rainforests, used as a culinary herb.'' ''Clausena anisata'' ( Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth. is a deciduous shrub or small tree, belonging to the Rutaceae or Citrus family, and widespread in the Afrotropical realm or Sub-Saharan Africa, but absent from the drier regions. It is also found in tropical and South-East Asia, growing in India and Sri Lanka and extending as far as Queensland in north-eastern Australia and some Pacific islands. It is cultivated in Malaysia and Indonesia. As with other plants useful to mankind its large range of medicinal properties has led to a global distribution and its growth wherever the climate is suitable. It grows in higher-rainfall regions in savanna, thickets, riverine forest, disturbed areas and secondary forest, up to an altitude of 3000 m. The leaves, which are foetid when bruised, give rise to the common name 'Horsewood' or the more descriptive Afrikaans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook
A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved or indented, such that it can be used to grab onto, connect, or otherwise attach itself onto another object. In a number of uses, one end of the hook is pointed, so that this end can pierce another material, which is then held by the curved or indented portion. Some kinds of hooks, particularly fish hooks, also have a barb, a backwards-pointed projection near the pointed end of the hook to ensure that once the hook is embedded in its target, it can not easily be removed. Variations * Bagging hook, a large sickle or reaping hook used for harvesting grain * Bondage hook, used in sexual bondage play * Cabin hook, a hooked bar that engages into an eye screw, used on doors * Cap hook, hat ornament of the 15th and 16th centuries * Cargo hook (helicopter), different types of hook systems for helicopters * Crochet hook, used for crocheting thread or yarn * Drapery hook Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of the '' Prose Edda'', which is a major source for what is today known as Norse mythology, and '' Heimskringla'', a history of the Norwegian kings that begins with legendary material in '' Ynglinga saga'' and moves through to early medieval Scandinavian history. For stylistic and methodological reasons, Snorri is often taken to be the author of '' Egil's saga''. He was assassinated in 1241 by men claiming to be agents of the King of Norway. Biography Early life Snorri Sturluson was born in (commonly transliterated as Hvamm or Hvammr) as a member of the wealthy and powerful Sturlungar clan of the Icelandic Commonwealth, in AD 1179. His parents were ''Sturla Þórðarson the Elder'' of ''Hvammur'' and his second wife, ''Guðný Böðvarsdó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germacrene B
Germacrenes are a class of volatile organic hydrocarbons, specifically, sesquiterpenes. Germacrenes are typically produced in a number of plant species for their antimicrobial and insecticidal properties, though they also play a role as insect pheromones. Two prominent molecules are germacrene A and germacrene D. Structures Germacrene has five isomers. Natural occurrences The essential oils of red deadnettle (''Lamium purpureum'') and hedgenettles (genus ''Stachys'') are characterized by their high contents of germacrene D, as is ''Clausena anisata :''Should not be confused with syzygium anisatum, a tree native to eastern Australian rainforests, used as a culinary herb.'' ''Clausena anisata'' ( Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth. is a deciduous shrub or small tree, belonging to the Rutaceae or Citr ...''. It is also a major component of patchouli oil. References Further reading General * Germacrene A * * * * * * Germacrene D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocimene
Ocimenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons. The ocimenes are monoterpenes found within a variety of plants and fruits. α-Ocimene and the two β-ocimenes differ in the position of the isolated double bond: it is terminal in the alpha isomer. α-Ocimene is ''cis-''3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-octatriene. β-Ocimene is ''trans-''3,7-dimethyl-1,3,6-octatriene. β-Ocimene exists in two stereoisomeric forms, ''cis'' and ''trans,'' with respect to the central double bond. The ocimenes are often found naturally as mixtures of the various forms. The mixture, as well as the pure compounds, are oils with a pleasant odor. They are used in perfumery for their sweet herbal scent, and are believed to act as plant defense and have anti-fungal properties. Like the related acyclic terpene myrcene, ocimenes are unstable in air.Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragranc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
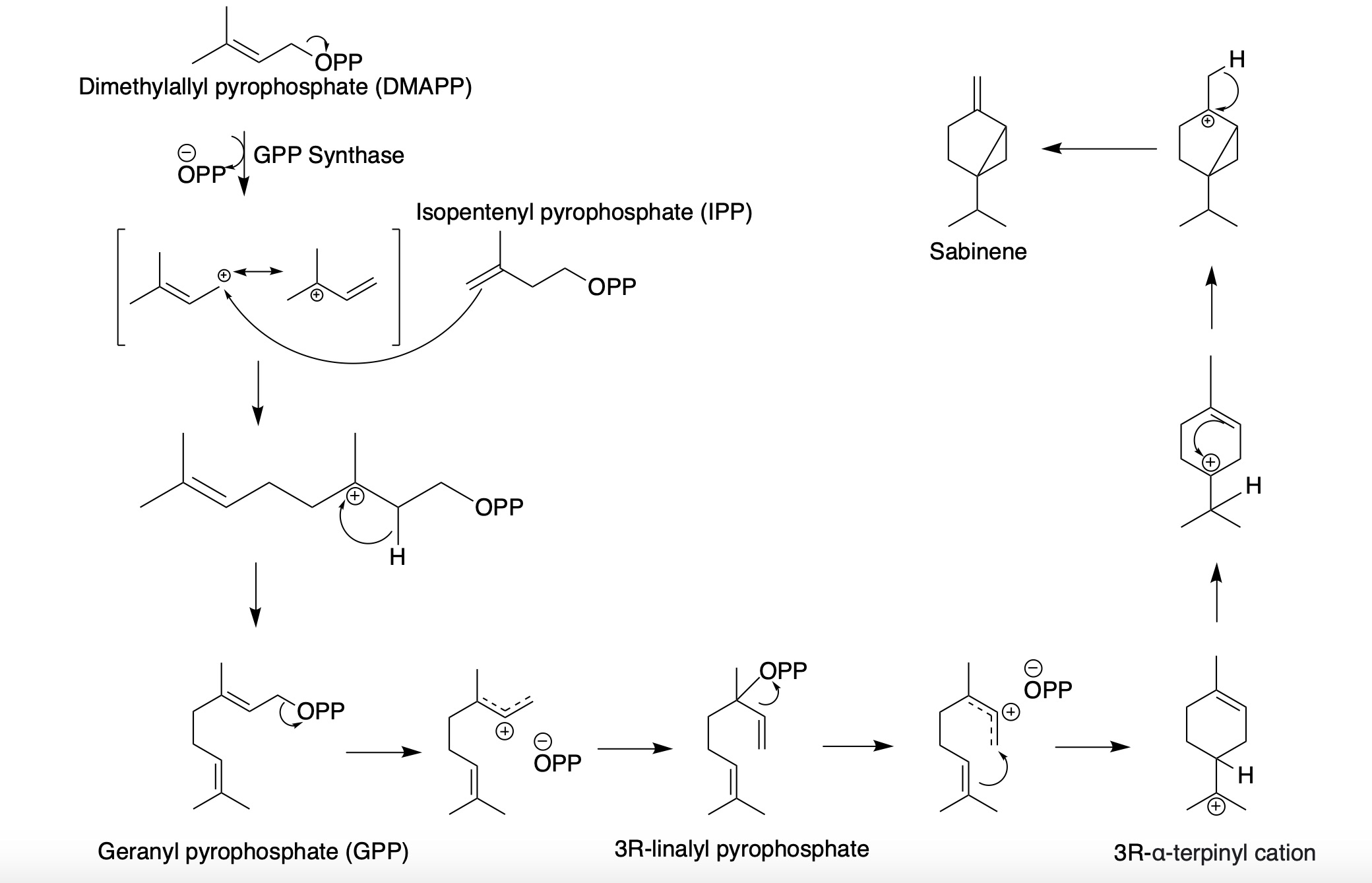
Sabinene
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including Marjoram, holm oak (''Quercus ilex'') and Norway spruce (''Picea abies''). It has a strained ring system with a cyclopentane ring fused to a cyclopropane ring. Sabinene is one of the chemical compounds that contributes to the spiciness of black pepper and is a major constituent of carrot seed oil. It also occurs in tea tree oil at a low concentration. It is also present in the essential oil obtained from nutmeg, '' Laurus nobilis'', and '' Clausena anisata''. Biosynthesis Sabinene, a bicyclic monoterpene, is present in the (+) and (-) enantiomer In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ...s. It is biosynthesized from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Chavicol
Estragole (''p''-allylanisole, methyl chavicol) is a phenylpropene, a natural organic compound. Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a methoxy group and an allyl group. It is an isomer of anethole, differing with respect to the location of the double bond. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. It is a component of various trees and plants, including turpentine (pine oil), anise, fennel, bay, tarragon, and basil. It is used in the preparation of fragrances.. The compound is named for ''estragon'', the French name of tarragon. Production Hundreds of tonnes of basil oil are produced annually by steam distillation of ''Ocimum basilicum'' (common basil). This oil is mainly estragole but also contains substantial amounts of linalool. Estragole is the primary constituent of essential oil of tarragon (comprising 60–75%). It is also present in pine oil, turpentine, fennel, anise (2%), ''Clausena anisata'' and ''Syzygium an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anethole
Anethole (also known as anise camphor) is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of phenylpropene, a type of aromatic compound that occurs widely in nature, in essential oils. It is in the class of phenylpropanoid organic compounds. It contributes a large component of the odor and flavor of anise and fennel (both in the botanical family Apiaceae), anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice ( Fabaceae), magnolia blossoms, and star anise ( Schisandraceae). Closely related to anethole is its isomer estragole, abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), that has a flavor reminiscent of anise. It is a colorless, fragrant, mildly volatile liquid. Anethole is only slightly soluble in water but exhibits high solubility in ethanol. This trait causes certain anise-flavored liqueurs to become opaque when diluted with water; the ouzo effect. Structure and production Anethole is an aromatic, unsaturated ether related to lignols. It ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estragole
Estragole (''p''-allylanisole, methyl chavicol) is a phenylpropene, a natural organic compound. Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a methoxy group and an allyl group. It is an isomer of anethole, differing with respect to the location of the double bond. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. It is a component of various trees and plants, including turpentine (pine oil), anise, fennel, bay, tarragon, and basil. It is used in the preparation of fragrances.. The compound is named for ''estragon'', the French name of tarragon. Production Hundreds of tonnes of basil oil are produced annually by steam distillation of ''Ocimum basilicum'' (common basil). This oil is mainly estragole but also contains substantial amounts of linalool. Estragole is the primary constituent of essential oil of tarragon (comprising 60–75%). It is also present in pine oil, turpentine, fennel, anise (2%), '' Clausena anisata'' and ''Syzygium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylpropanoid
The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid. Phenylpropanoids are found throughout the plant kingdom, where they serve as essential components of a number of structural polymers, provide protection from ultraviolet light, defend against herbivores and pathogens, and also mediate plant-pollinator interactions as floral pigments and scent compounds. Hydroxycinnamic acids Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemical class and considered as a lactone. Coumarin is a colorless crystalline solid with a sweet odor resembling the scent of vanilla and a bitter taste. It is found in many plants, where it may serve as a chemical defense against predators. By inhibiting synthesis of vitamin K, a related compound is used as the prescription drug warfarin – an anticoagulant – to inhibit formation of blood clots, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Etymology Coumarin is derived from ''coumarou'', the French word for the tonka bean. The word ''tonka'' for the tonka bean is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |