|
Circinus (constellation)
Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass, referring to the drafting tool used for drawing circles (it should not be confused with Pyxis, a constellation that represents a mariner's compass which points north). Its brightest star is Alpha Circini, with an apparent magnitude of 3.19. Slightly variable, it is the brightest rapidly oscillating Ap star in the night sky. AX Circini is a Cepheid variable visible with the unaided eye, and BX Circini is a faint star thought to have been formed from the merger of two white dwarfs. Two sun-like stars have planetary systems: HD 134060 has two small planets, and HD 129445 has a Jupiter-like planet. Supernova SN 185 appeared in Circinus in 185 AD and was recorded by Chinese observers. Two novae have been observed more recently, in the 20th century. The Milky Way runs through the constellation, featuring prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass (drafting)
A compass, more accurately known as a pair of compasses, is a technical drawing instrument that can be used for inscribing circles or arcs. As dividers, it can also be used as a tool to mark out distances, in particular, on maps. Compasses can be used for mathematics, drafting, navigation and other purposes. Prior to computerization, compasses and other tools for manual drafting were often packaged as a set with interchangeable parts. By the mid-twentieth century, circle templates supplemented the use of compasses. Today those facilities are more often provided by computer-aided design programs, so the physical tools serve mainly a didactic purpose in teaching geometry, technical drawing, etc. Construction and parts Compasses are usually made of metal or plastic, and consist of two "legs" connected by a hinge which can be adjusted to allow changing of the radius of the circle drawn. Typically one leg has a spike at its end for anchoring, and the other leg holds a drawing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyxis
Pyxis is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. Abbreviated from Pyxis Nautica, its name is Latin for a mariner's compass (contrasting with Circinus, which represents a draftsman's compasses). Pyxis was introduced by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. The plane of the Milky Way passes through Pyxis. A faint constellation, its three brightest stars— Alpha, Beta and Gamma Pyxidis—are in a rough line. At magnitude 3.68, Alpha is the constellation's brightest star. It is a blue-white star approximately distant and around 22,000 times as luminous as the Sun. Pyxis is located close to the stars that formed the old constellation Argo Navis, the ship of Jason and the Argonauts. Parts of Argo Navis were the Carina (the keel or hull), the Puppis (the poop deck or stern), and the Vela (the sails). These eventually became their own constellations. In the 19th century, John Herschel suggested renaming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 185
SN 185 was a transient astronomical event observed in the year AD 185, likely a supernova. The transient occurred in the direction of Alpha Centauri, between the constellations Circinus and Centaurus, centered at RA Dec , in Circinus. This "guest star" was observed by Chinese astronomers in the ''Book of Later Han'' (后汉书), and might have been recorded in Roman literature. It remained visible in the night sky for eight months. This is believed to be the first supernova for which records exist. History ''The Book of Later Han'' gives the following description: In the 2nd year of the epoch Zhongping ��平 the 10th month, on the day Guihai ��亥 ecember 7, Year 185 a 'guest star' appeared in the middle of the Southern Gate ��門 ε Centauri and Alpha Centauri">α Centauri], The size was half a bamboo mat. It displayed various colors, both pleasing and otherwise. It gradually lessened. In the 6th month of the succeeding year it disappeared. The gaseous shell RCW 86 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin language, Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 129445
HD 129445 is a G type star found in the Circinus constellation located approximately 220 light-years away from the Sun based on parallax. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.80. The star has been under the Magellan Planet Search Program observation due to its absolute visual magnitude and high metallicity. The Magellan program conducted 17 doppler velocity tests, which spans a full orbital period. The results led the program to detect a planet dubbed HD 129445 b whose readings was accurate to the Keplerian orbital model. See also * HD 152079 * HD 164604 * HD 175167 * HD 86226 * List of extrasolar planets These are lists of exoplanets. Most of these were discovered by the Kepler space telescope. There are an additional 2,054 potential exoplanets from Kepler's first mission yet to be confirmed, as well as 978 from its " Second Light" mission and ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:HD 129445 G-type main-sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 134060
HD 134060, also known by its Gould designation of 38 G. Circini, is a star in the southern constellation of Circinus. It is near the lower limit of stars visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.29. The distance to HD 134060, as determined using an annual parallax shift measurement of , is 78.4 light years. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of 43.5 km/s, having come within some 439,000 years ago. During the NStars project, Grey et al. (2006) found a stellar classification of for this star, matching a Sun-like G-type main-sequence star with an overabundance of iron in its outer atmosphere. However, an older classification of G3 IV is still used, which would suggest it is instead a more evolved subgiant star. HD 134060 has an estimated 1.07 times the mass of the Sun and 1.15 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 1.63 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes from the emission of residual thermal energy; no fusion takes place in a white dwarf. The nearest known white dwarf is at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the other stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen- fusing period of a main-sequence star of low or medium mass ends, such a star will expand to a red giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BX Circini
BX Circini is a star in the constellation Circinus. Its variability was discovered in 1995, with its apparent magnitude ranging from 12.57 to 12.62 over a period of 2 hours 33 minutes. It is currently classified as a PV Telescopii variable star, but has been put forward as the prototype of a new class of pulsating star—the BX Circini variables—along with the only other known example, V652 Herculis. This class of star is rare, possibly because this is a brief stage of stellar evolution. Its mass has been calculated to be around 40 percent that of the Sun, but the radius is a few times larger than that of the Sun. The average surface temperature is high, and has been measured at 23,390 ± 90 K using optical spectra, but 1750 K cooler if analysing it in both the visual and ultraviolet. The temperature appears to vary by 3450 K. This star has an extremely low proportion of hydrogen, which was first noticed in 1980. In fact, over 99% of its composition appears to be heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheid Variable
A Cepheid variable () is a type of star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature and producing changes in brightness with a well-defined stable period and amplitude. A strong direct relationship between a Cepheid variable's luminosity and pulsation period established Cepheids as important indicators of cosmic benchmarks for scaling galactic and extragalactic distances. This robust characteristic of classical Cepheids was discovered in 1908 by Henrietta Swan Leavitt after studying thousands of variable stars in the Magellanic Clouds. This discovery allows one to know the true luminosity of a Cepheid by simply observing its pulsation period. This in turn allows one to determine the distance to the star, by comparing its known luminosity to its observed brightness. The term ''Cepheid'' originates from Delta Cephei in the constellation Cepheus, identified by John Goodricke in 1784, the first of its type to be so identified. The mechanics of stellar pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
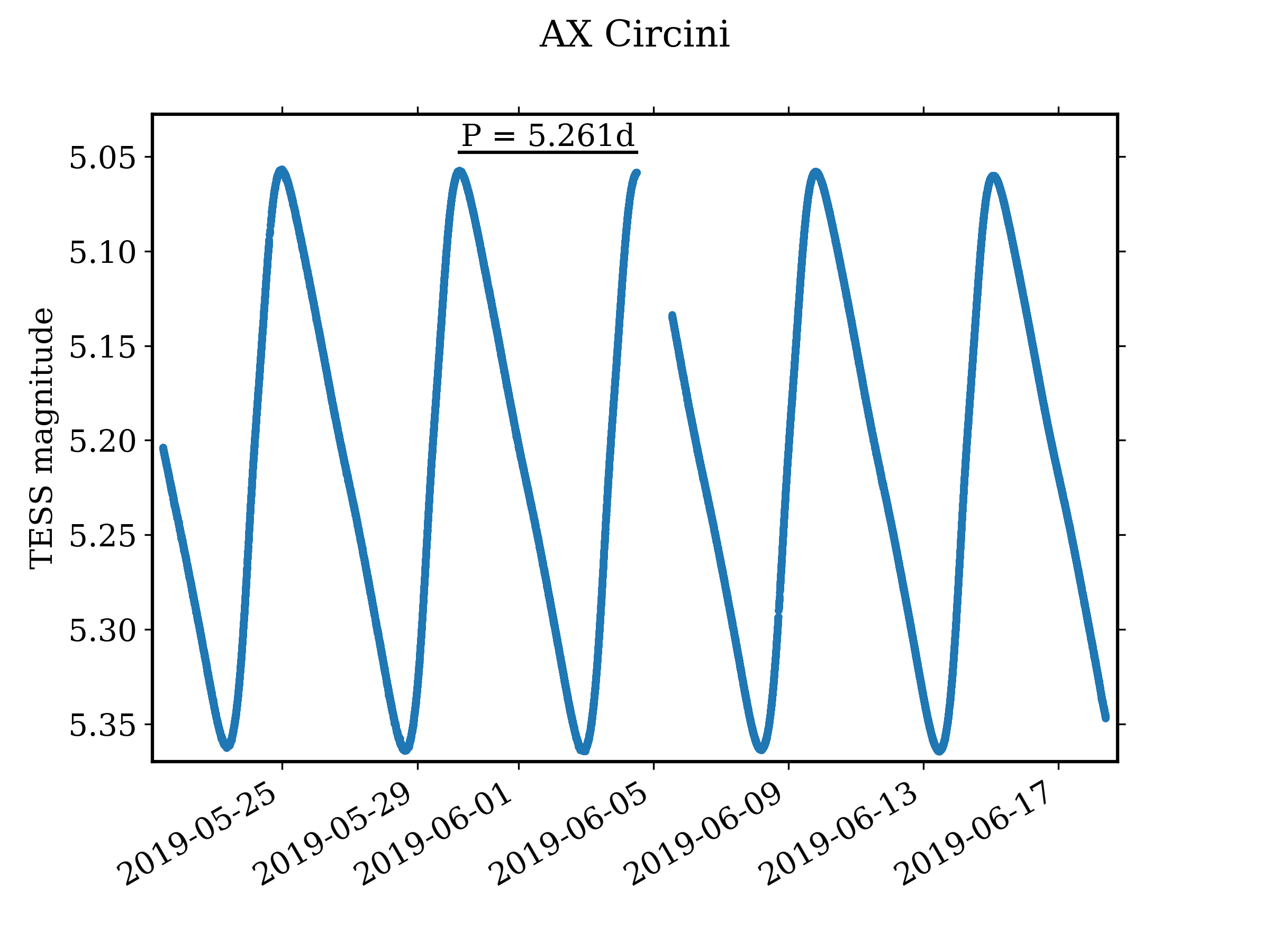
AX Circini
AX Circini is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Circinus. It has a nominal magnitude of 5.91, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located roughly 1,900 light-years from the Earth. The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −21 km/s. This is a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of and an eccentricity of 0.19. A binary companion was first suspected in 1960, as the spectrum was considered to be composite and there is an ultraviolet excess. The companion was confirmed in 1982, and it was resolved using long baseline interferometry in 2014 and 2015. The system has an ''a'' sin ''i'' value of , where ''a'' is the semimajor axis and ''i'' is the (unknown) orbital inclination. The primary, component A, is a yellow-white-hued bright giant with a stellar classification of F8 II, and it is a classical Cepheid variable. The combined apparent magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapidly Oscillating Ap Star
Rapidly oscillating Ap stars (roAp stars) are a subtype of the Ap star class that exhibit short-timescale rapid photometric or radial velocity variations. The known periods range between 5 and 23 minutes. They lie in the δ Scuti instability strip on the main sequence. Discovery The first roAp star to be discovered was HD 101065 ( Przybylski's Star). The oscillations were discovered by Donald Kurtz using the telescope at the South African Astronomical Observatory, who saw 10–20-millimagnitude variations in the light curve of the star with a period of 12.15 minutes. Classification The roAp stars are sometimes referred to as rapidly oscillating α2 Canum Venaticorum variables. Both the roAp stars and some α2 CVn variables lie on the δ Scuti instability strip and are magnetic chemically peculiar stars, but the roAp stars have very short periods less than an hour. Oscillations The roAp stars oscillate in high-overtone, low-degree, non-radial pressure modes. The usual model t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |