AX Circini on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 AX Circini is a
AX Circini is a
 AX Circini is a
AX Circini is a binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
system in the southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Circinus
Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass (drawing tool), compass, referring to the Technical drawing, drafting tool used ...
. It has a nominal magnitude of 5.91, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located roughly 1,900 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s from the Earth. The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
of −21 km/s.
This is a spectroscopic binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separa ...
with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of and an eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (graph theory) of a v ...
of 0.19. A binary companion was first suspected in 1960, as the spectrum was considered to be composite and there is an ultraviolet excess. The companion was confirmed in 1982, and it was resolved using long baseline interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
in 2014 and 2015. The system has an ''a'' sin ''i'' value of , where ''a'' is the semimajor axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longe ...
and ''i'' is the (unknown) orbital inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Earth ...
.
The primary, component A, is a yellow-white-hued bright giant
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
with a stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
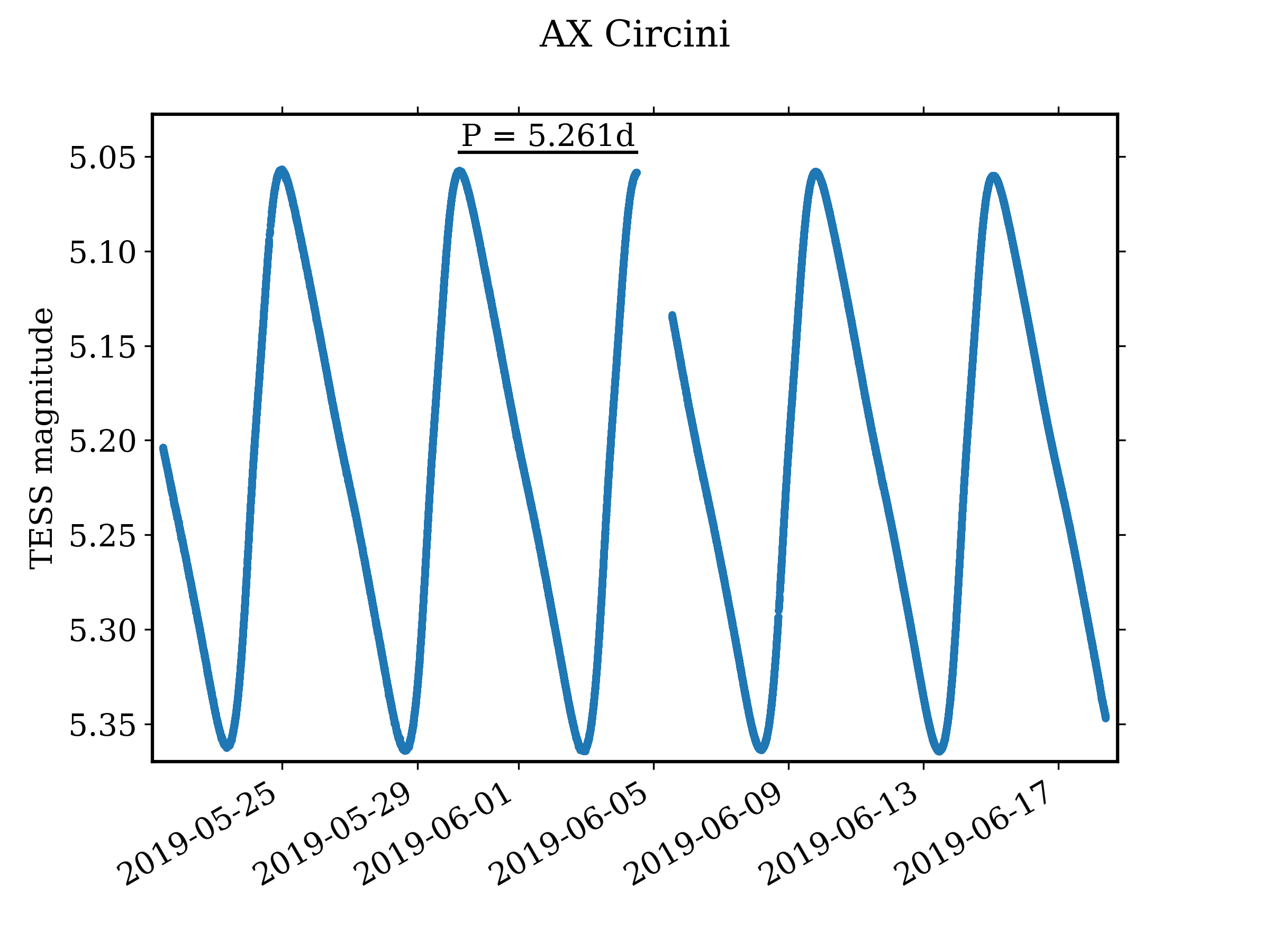
of F8 II, and it is a classical Cepheid variable
Classical Cepheids (also known as Population I Cepheids, Type I Cepheids, or Delta Cepheid variables) are a type of Cepheid variable star. They are population I variable stars that exhibit regular radial pulsations with periods of a few days to a ...
. The combined apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
of the system ranges from 5.69 to 6.19 over 5.273 days. The secondary companion, component B, is a main-sequence star
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hert ...
with a class of B6 V and an absolute magnitude of about −0.12.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:AX Circini F-type bright giants B-type main-sequence stars Classical Cepheid variables Circinus (constellation) Durchmusterung objects Circini, 26 130701/2 072773 5527 Circini, AX Spectroscopic binaries