|
Circinus
Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass (drawing tool), compass, referring to the Technical drawing, drafting tool used for drawing circles (it should not be confused with Pyxis, a constellation that represents a mariner's compass which points north). Its brightest star is Alpha Circini, with an apparent magnitude of 3.19. Slightly variable star, variable, it is the brightest rapidly oscillating Ap star in the night sky. AX Circini is a Cepheid variable visible with the unaided eye, and BX Circini is a faint star thought to have been formed from the merger of two white dwarfs. Two sun-like stars have planetary systems: HD 134060 has two small planets, and HD 129445 has a Jupiter-like planet. Supernova SN 185 appeared in Circinus in 185 AD and was recorded by Chinese observers. Two novae have been observed more recently, in the 20th century. The Milky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Circini
Alpha Circini (α Cir, α Circini) is a variable star in the faint, southern, circumpolar constellation of Circinus. At an apparent visual magnitude of 3.19, it is the brightest star in the constellation and can be readily seen with the naked eye from the southern hemisphere. Parallax measurements of this star yield an estimated distance of from the Earth. This star belongs to a class of variables known as rapidly oscillating Ap stars. It oscillates with multiple, non-radial pulsation cycles and a dominant cycle of 6.8 minutes. The spectrum shows peculiar features caused by chemical stratification of the outer atmosphere. It displays a moderate deficiency of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, while there is an overabundance of chromium (Cr). The stellar classification of A7 Vp SrCrEu indicates that this is a main sequence star with enhanced levels of strontium (Sr), chromium, and europium (Eu) in its atmosphere (compared to a typical star like the Sun). The mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 129445
HD 129445 is a G type star found in the Circinus constellation located approximately 220 light-years away from the Sun based on parallax. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.80. The star has been under the Magellan Planet Search Program observation due to its absolute visual magnitude and high metallicity. The Magellan program conducted 17 doppler velocity tests, which spans a full orbital period. The results led the program to detect a planet dubbed HD 129445 b whose readings was accurate to the Keplerian orbital model. See also * HD 152079 * HD 164604 * HD 175167 * HD 86226 * List of extrasolar planets These are lists of exoplanets. Most of these were discovered by the Kepler space telescope. There are an additional 2,054 potential exoplanets from Kepler's first mission yet to be confirmed, as well as 978 from its " Second Light" mission and ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:HD 129445 G-type main-sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangulum Australe
Triangulum Australe is a small constellation in the far Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the southern triangle", which distinguishes it from Triangulum in the northern sky and is derived from the acute, almost equilateral pattern of its three brightest stars. It was first depicted on a celestial globe as Triangulus Antarcticus by Petrus Plancius in 1589, and later with more accuracy and its current name by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. Alpha Trianguli Australis, known as Atria, is a second-magnitude orange giant and the brightest star in the constellation, as well as the 42nd-brightest star in the night sky. Completing the triangle are the two white main sequence stars Beta and Gamma Trianguli Australis. Although the constellation lies in the Milky Way and contains many stars, deep-sky objects are not prominen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 185
SN 185 was a transient astronomical event observed in the year AD 185, likely a supernova. The transient occurred in the direction of Alpha Centauri, between the constellations Circinus and Centaurus, centered at RA Dec , in Circinus. This "guest star" was observed by Chinese astronomers in the ''Book of Later Han'' (后汉书), and might have been recorded in Roman literature. It remained visible in the night sky for eight months. This is believed to be the first supernova for which records exist. History ''The Book of Later Han'' gives the following description: In the 2nd year of the epoch Zhongping ��平 the 10th month, on the day Guihai ��亥 ecember 7, Year 185 a 'guest star' appeared in the middle of the Southern Gate ��門 ε Centauri and Alpha Centauri">α Centauri], The size was half a bamboo mat. It displayed various colors, both pleasing and otherwise. It gradually lessened. In the 6th month of the succeeding year it disappeared. The gaseous shell RCW 86 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
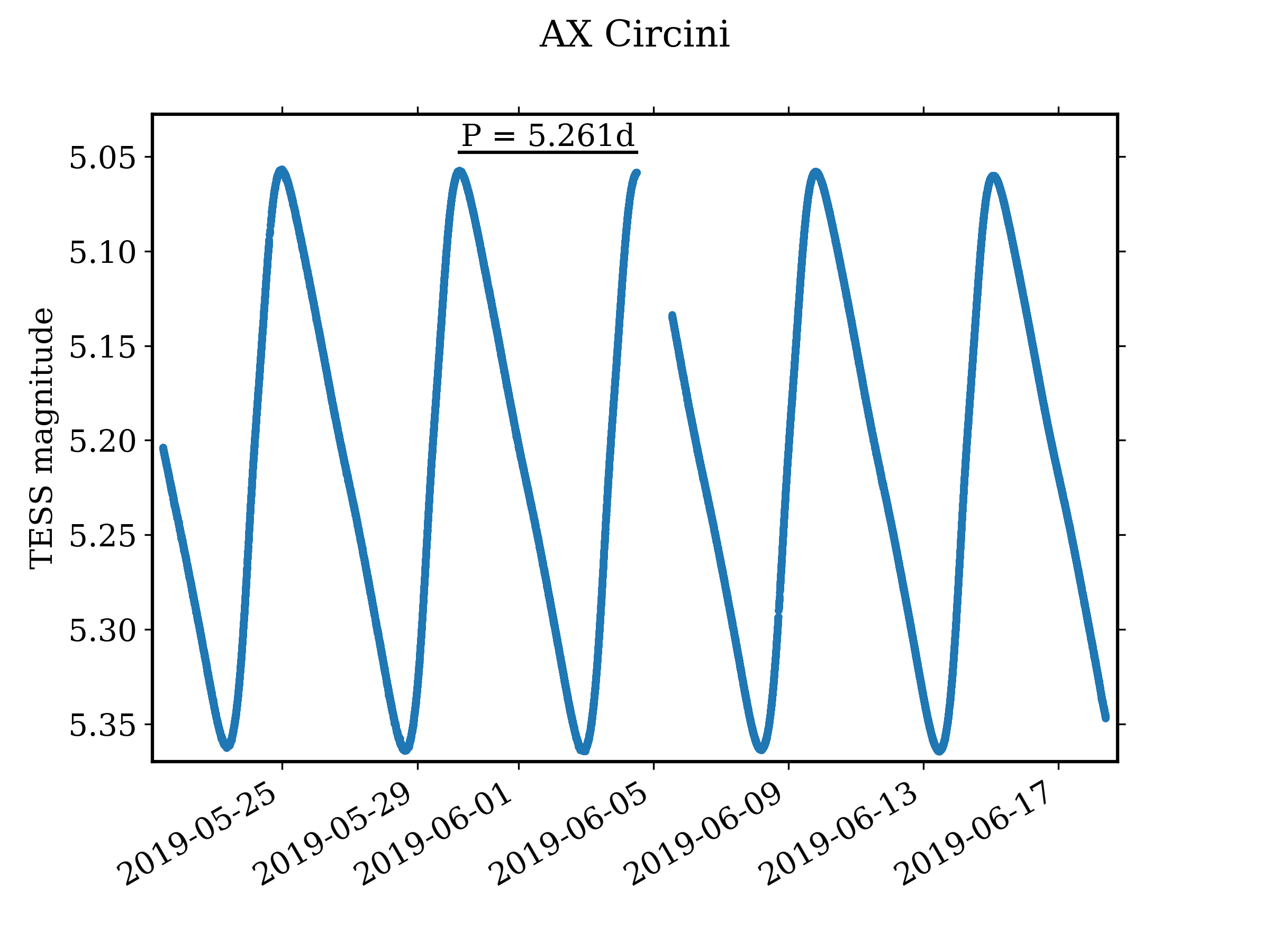
AX Circini
AX Circini is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Circinus. It has a nominal magnitude of 5.91, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located roughly 1,900 light-years from the Earth. The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −21 km/s. This is a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of and an eccentricity of 0.19. A binary companion was first suspected in 1960, as the spectrum was considered to be composite and there is an ultraviolet excess. The companion was confirmed in 1982, and it was resolved using long baseline interferometry in 2014 and 2015. The system has an ''a'' sin ''i'' value of , where ''a'' is the semimajor axis and ''i'' is the (unknown) orbital inclination. The primary, component A, is a yellow-white-hued bright giant with a stellar classification of F8 II, and it is a classical Cepheid variable. The combined apparent magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BX Circini
BX Circini is a star in the constellation Circinus. Its variability was discovered in 1995, with its apparent magnitude ranging from 12.57 to 12.62 over a period of 2 hours 33 minutes. It is currently classified as a PV Telescopii variable star, but has been put forward as the prototype of a new class of pulsating star—the BX Circini variables—along with the only other known example, V652 Herculis. This class of star is rare, possibly because this is a brief stage of stellar evolution. Its mass has been calculated to be around 40 percent that of the Sun, but the radius is a few times larger than that of the Sun. The average surface temperature is high, and has been measured at 23,390 ± 90 K using optical spectra, but 1750 K cooler if analysing it in both the visual and ultraviolet. The temperature appears to vary by 3450 K. This star has an extremely low proportion of hydrogen, which was first noticed in 1980. In fact, over 99% of its composition appears to be heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musca
Musca () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It was one of 12 constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman, and it first appeared on a celestial globe in diameter published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's ''Uranometria'' of 1603. It was also known as Apis () for 200 years. Musca remains below the horizon for most Northern Hemisphere observers. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appears to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. These include Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Zeta2 and (probably) Eta Muscae, as well as HD 100546, a blue-white Herbig Ae/Be star that is surrounded by a complex debris disk containing a large planet or brown dwarf and possible protoplanet. Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norma (constellation)
Norma is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere between Ara and Lupus, one of twelve drawn up in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and one of several depicting scientific instruments. Its name is Latin for normal, referring to a right angle, and is variously considered to represent a rule, a carpenter's square, a set square or a level. It remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Four of Norma's brighter stars—Gamma, Delta, Epsilon and Eta—make up a square in the field of faint stars. Gamma2 Normae is the brightest star with an apparent magnitude of 4.0. Mu Normae is one of the most luminous stars known, with a luminosity between a quarter million and one million times that of the Sun. Four star systems are known to harbour planets. The Milky Way passes through Norma, and the constellation contains eight open clusters visible to observers with binoculars. The constellation also hosts Abell 3627, also called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 134060
HD 134060, also known by its Gould designation of 38 G. Circini, is a star in the southern constellation of Circinus. It is near the lower limit of stars visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.29. The distance to HD 134060, as determined using an annual parallax shift measurement of , is 78.4 light years. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of 43.5 km/s, having come within some 439,000 years ago. During the NStars project, Grey et al. (2006) found a stellar classification of for this star, matching a Sun-like G-type main-sequence star with an overabundance of iron in its outer atmosphere. However, an older classification of G3 IV is still used, which would suggest it is instead a more evolved subgiant star. HD 134060 has an estimated 1.07 times the mass of the Sun and 1.15 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 1.63 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the 88 modern constellations by area, largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. In Greek mythology, Centaurus represents a centaur; a creature that is half human, half horse (another constellation named after a centaur is one from the zodiac: Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius). Notable stars include Alpha Centauri, the nearest star system to the Solar System, its neighbour in the sky Beta Centauri, and V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars yet discovered. The constellation also contains Omega Centauri, the brightest globular cluster as visible from Earth and the largest identified in the Milky Way, possibly a remnant of a dwarf galaxy. Notable features Stars Centaurus contains several very bright stars. Its alpha and beta stars are used as "pointer stars" to help observers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apus
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. First depicted on a celestial globe by Petrus Plancius in 1598, it was charted on a star atlas by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. The five brightest stars are all reddish in hue. Shading the others at apparent magnitude 3.8 is Alpha Apodis, an orange giant that has around 48 times the diameter and 928 times the luminosity of the Sun. Marginally fainter is Gamma Apodis, another ageing giant star. Delta Apodis is a double star, the two components of which are 103 Minute and second of arc, arcseconds apart and visible with the naked eye. Two star systems have been found to have exoplanet, planets. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus (constellation)
Lupus is a constellation of the mid-Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for wolf. Lupus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations but was long an asterism associated with the just westerly, larger constellation Centaurus. History and mythology In ancient times, the constellation was considered an asterism within Centaurus, and was considered to have been an arbitrary animal, killed, or about to be killed, on behalf of, or for, Centaurus. An alternative visualization, attested by Eratosthenes, saw this constellation as a wineskin held by Centaurus. It was not separated from Centaurus until Hipparchus of Bithynia named it ( meaning "beast") in the 2nd century BC. The Greek constellation is probably based on the Babylonian figure known as the Mad Dog (UR.IDIM). This was a strange hybrid creature that combined the head and torso of a man with the legs and tail of a lion (the cuneiform sign 'UR' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
