|
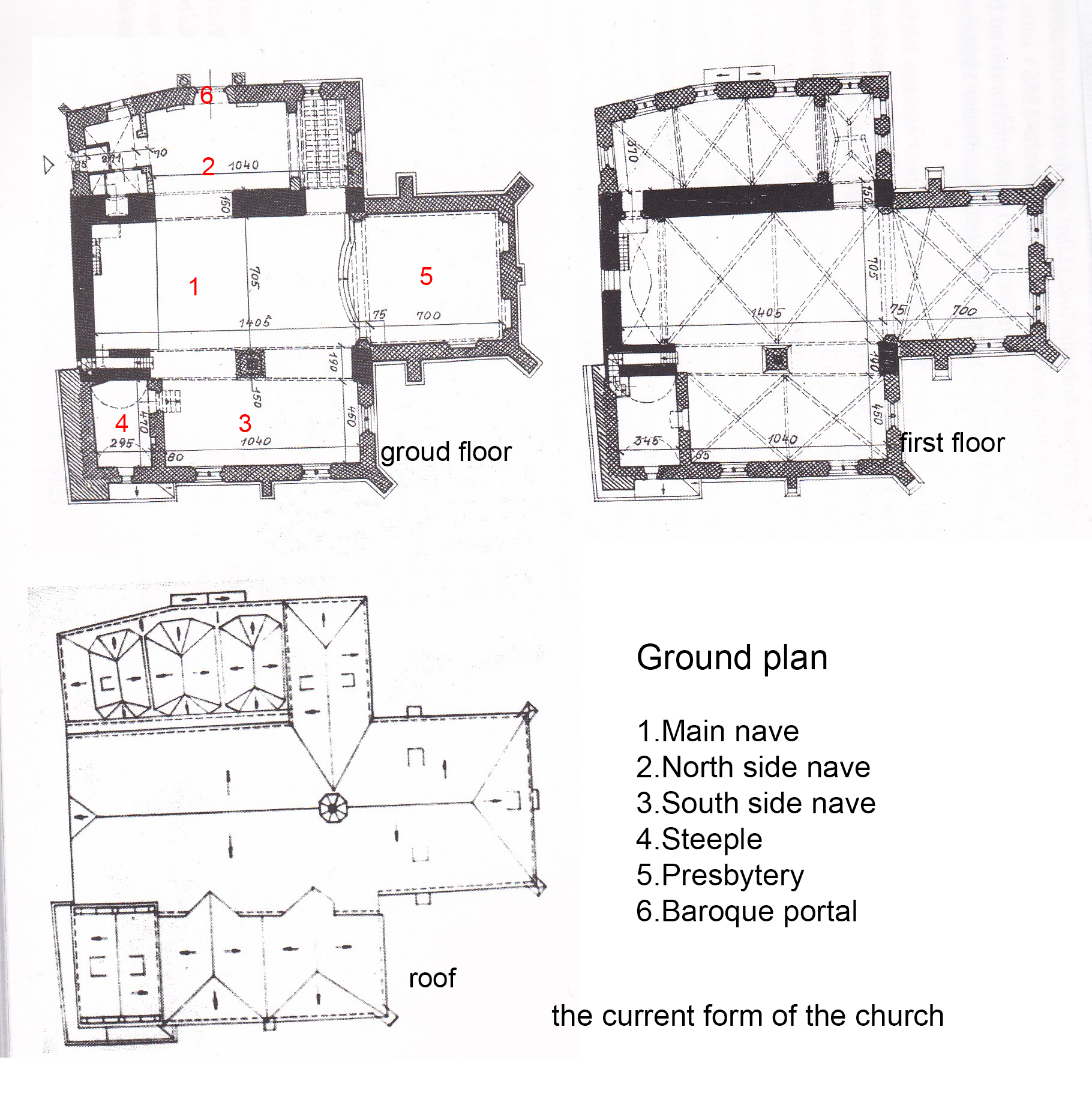
Church Of St. Martin In The Wall
The Church of St. Martin in the Wall is a Gothic church with Romanesque grounds, situated in the Old Town (Prague), Old Town of Prague, Czech Republic. It was built between 1178 and 1187 in the village of Újezd, thereafter known as Újezd u svatého Martina. The south wall of the church was built adjacent to the walls of the Old Town, hence the full name of the church "in the wall". The church belongs to the Evangelical Church of Czech Brethren. Construction Romanesque structure The settlement where the church was built was called Újezd before 1178 and Újezd u svatého Martina after 1187, so it is thought that the church was built between those years, when the settlement was the property of a duke. The settlement was a gift to the Vyšehrad Chapter by Soběslav II, Duke of Bohemia. During the construction of the Old Town walls in the 1230s, Újezd was divided into two; the larger part remained in the later New Town and the smaller part with the church became a part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate oceanic climate, with relatively warm summers and chilly winters. Prague is a political, cultural, and economic hub of central Europe, with a rich history and Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architectures. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV (r. 1346–1378). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city played major roles in the Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history as the capital of Czechoslovakia between the World Wars and the post-war Communist era. Prague is home to a number of well-known cultural attractions, many of which survived the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this later date being the most commonly held. In the 12th century it developed into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. The Romanesque style in England and Sicily is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture. Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Catholic Church, as well as various Hussite factions. At a late stage of the conflict, the Utraquists changed sides in 1432 to fight alongside Roman Catholics and opposed the Taborites and other Hussite spinoffs. These wars lasted from 1419 to approximately 1434. The unrest began after pre-Protestant Christian reformer Jan Hus was executed by the Catholic Church in 1415 for heresy. Because the King Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia had plans to be crowned the Holy Roman Emperor (requiring Papal Coronation), he suppressed the religion of the Hussites, yet it continued to spread. When King Wenceslaus IV died of natural causes a few years later, the tension stemming from the Hussites grew stronger. In Prague and various other parts of Bohemia, the Cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utraquism
Utraquism (from the Latin ''sub utraque specie'', meaning "under both kinds") or Calixtinism (from chalice; Latin: ''calix'', mug, borrowed from Greek ''kalyx'', shell, husk; Czech: kališníci) was a belief amongst Hussites, a reformist Christian movement, that communion under both kinds (both bread and wine, as opposed to the bread alone) should be administered to the laity during the celebration of the Eucharist. It was a principal dogma of the Hussites and one of the Four Articles of Prague. After the Hussite movement split into various factions early in the Hussite Wars, Hussites that emphasized the laity's right to communion under both kinds became known as Moderate Hussites, Utraquist Hussites, or simply Utraquists. The Utraquists were the largest major Hussite faction. Following the victory of allied Utraquist and Catholic forces in the Hussite Wars, Utraquists constituted a majority of the Bohemian population until the outbreak of the Thirty Years' War, nearly two centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communion Under Both Kinds
Communion under both kinds in Christianity is the reception under both "species" (i.e., both the consecrated bread and wine) of the Eucharist. Denominations of Christianity that hold to a doctrine of Communion under both kinds may believe that a Eucharist which does not include both bread and wine as elements of the religious ceremony is not valid, while others may consider the presence of both bread and wine as preferable, but not necessary, for the ceremony. In some traditions, grape juice may take the place of wine with alcohol content as the second element. Roman Catholicism Doctrine In reference to the Eucharist as a sacrifice, Communion under both kinds belongs at least to the integrity and essence, of the rite, and may not be omitted without violating the precept of Christ: "Do this in remembrance of me" (Luke 22:19). This is mentioned implicitly by the Council of Trent (Sess. XXI, c. i; XXII, c. i), and the General Instruction of the Roman Missal states that the people " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Hus
Jan Hus (; ; 1370 – 6 July 1415), sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as ''Iohannes Hus'' or ''Johannes Huss'', was a Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and the inspiration of Hussitism, a key predecessor to Protestantism, and a seminal figure in the Bohemian Reformation. Hus is considered by some to be the first Church reformer, even though some designate the theorist John Wycliffe. His teachings had a strong influence, most immediately in the approval of a reformed Bohemian religious denomination and, over a century later, on Martin Luther. Hus was a master, dean and rector at the Charles University in Prague between 1409 and 1410. Jan Hus was born in Husinec, Bohemia, to poor parents. In order to escape poverty, Hus trained for the priesthood. At an early age he traveled to Prague, where he supported himself by singing and serving in churches. His conduct was positive and, reportedly, his commitment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Of Mies
Jacob of Mies ( cs, Jakoubek ze Stříbra, la, Jacobellus de Misa; 1372 – 9 August 1429) was a Czech reformer from the Kingdom of Bohemia and colleague of Jan Hus. Life Jacob was born in 1372 in Stříbro (called ''Mies'' in German and ''Misa'' in Latin) near Pilsen in Bohemia (present-day Czech Republic). He studied at the University of Prague, receiving both bachelor's and the master's degrees in theology, and became pastor of the Church of St. Michael and an outspoken supporter of Jan Hus. In 1410 he took part in the disputations regarding John Wycliffe, defending the latter against archiepiscopal condemnation. His study of Scripture and the Fathers led him to believe that withholding of the chalice in the administration of Holy Communion to the laity was an arbitrary measure of the Catholic Church. In 1414, he propounded and defended his views in a public disputation; and when Hus, at that time in jail at Konstanz, accepted them, he began to administer the chalice to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib Vault
A rib vault or ribbed vault is an architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs. Variations were used in Roman architecture, Byzantine architecture, Islamic architecture, Romanesque architecture, and especially Gothic architecture. Thin stone panels fill the space between the ribs. This greatly reduced the weight and thus the outward thrust of the vault. The ribs transmit the load downward and outward to specific points, usually rows of columns or piers. This feature allowed architects of Gothic cathedrals to make higher and thinner walls and much larger windows. It is a type of arcuated, or arched, vault in which the severies, or panels in the bays of the vault's underside are separated from one another by ribs which conceal the groins, or the intersections of the panels. Rib vaults are, like groin vaults, formed from two or three intersecting barrel vaults; the ribs conceal the junction o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three naves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracket (architecture)
A bracket is an architectural element: a structural or decorative member. It can be made of wood, stone, plaster, metal, or other media. It projects from a wall, usually to carry weight and sometimes to "...strengthen an angle". A corbel or console are types of brackets. In mechanical engineering a bracket is any intermediate component for fixing one part to another, usually larger, part. What makes a bracket a bracket is that it is intermediate between the two and fixes the one to the other. Brackets vary widely in shape, but a prototypical bracket is the L-shaped metal piece that attaches a shelf (the smaller component) to a wall (the larger component): its vertical arm is fixed to one (usually large) element, and its horizontal arm protrudes outwards and holds another (usually small) element. This shelf bracket is effectively the same as the architectural bracket: a vertical arm mounted on the wall, and a horizontal arm projecting outwards for another element to be attached o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vault (architecture)
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed. Vault types Corbelled vaults, also called false vaults, with horizontally joined layers of stone have been documented since prehistoric times; in the 14th century BC from Mycenae. They were built regionally until modern times. The real vault construction with radially joined stones was already known to the Egyptians and Assyrians and was introduced into the buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |