|
Chromosome 13
Chromosome 13 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 13 spans about 114 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 3.5 and 4% of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 13. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 13. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases and disorders are some of those rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement.Speicher, Michael R. and Nigel P. Carter. "The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology." ''Nature'' Reviews Genetics, Vol 6. Oct 2005. The metaphase chromosomes are treated with trypsin (to partially digest the chromosome) and stained with Giemsa stain. Heterochromatic regions, which tend to be rich with adenine and thymine (AT-rich) DNA and relatively gene-poor, stain more darkly in G-banding. In contrast, less condensed chromatin (Euchromatin)—which tends to be rich with guanine and cytosine ( GC-rich) and more transcriptionally active—incorporates less Giemsa stain, and these regions appear as light bands in G-banding. The pattern of bands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensembl Genome Database Project
Ensembl genome database project is a scientific project at the European Bioinformatics Institute, which provides a centralized resource for geneticists, molecular biologists and other researchers studying the genomes of our own species and other vertebrates and model organisms. Ensembl is one of several well known genome browsers for the retrieval of genomic information. Similar databases and browsers are found at NCBI and the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC). History The human genome consists of three billion base pairs, which code for approximately 20,000–25,000 genes. However the genome alone is of little use, unless the locations and relationships of individual genes can be identified. One option is manual annotation, whereby a team of scientists tries to locate genes using experimental data from scientific journals and public databases. However this is a slow, painstaking task. The alternative, known as automated annotation, is to use the power of computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CKAP2
Cytoskeleton-associated protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CKAP2'' gene. Human CKAP2 gene, the cDNA of which is known as LB1, is a cytoskeleton-associated protein involved in mitotic progression. Its high transcriptional activity has been observed in the testes, thymus, and diffuse B-cell lymphomas. The gene codes for a protein of 683 residues, which lacks a homology to known amino acid sequences. On evidence of immunofluorescence analysis, the CKAP2 product is a cytoplasmic protein associated with cytoskeletal fibrils. The CKAP2 gene is in chromosome 13q14. Rearrangements of this region result in various tumors. Thus deletions have been detected in multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma, B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and in more than half cases of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHAMP1
Chromosome alignment-maintaining phosphoprotein 1 (CHAMP1) also known as zinc finger protein 828 (ZNF828) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHAMP1 gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References External links * * Further reading * * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCDC70
Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 70 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCDC70'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CARKD
Carbohydrate kinase domain containing protein (abbreviated as CARKD), encoded by CARKD gene, is a human protein of unknown function. The CARKD gene encodes proteins with a predicted mitochondrial propeptide (mCARKD), a signal peptide (spCARKD) or neither of them (cCARKD). Confocal microscopy analysis of transfected CHO (Chinese-hamster ovary) cells indicated that cCARKD remains in the cytosol, whereas mCARKD and spCARKD are targeted to the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum respectively. The protein is conserved throughout many species, and has predicted orthologs through eukaryotes, bacteria, and archea. __TOC__ Structure Gene Human CARKD gene has 10 exons and resides on Chromosome 13 at q34. The following genes are near CARKD on the chromosome: * COL4A2: A2 Subunit of type IV collagen * RAB20: Potential regulator of Connexin 43 trafficking. * CARS2: Mitochondrial Cystienyl-tRNA Synthetase 2 * ING1: Tumor-Suppressor Protein Protein This protein is part of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAB39L
Calcium-binding protein 39-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CAB39L'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References External links * Further reading * * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C13orf42
C13orf42 is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the gene chromosome 13 open reading frame 42 (C13orf42). RNA sequencing data shows low expression of the C13orf42 gene in a variety of tissues. The C13orf42 protein is predicted to be localized in the mitochondria, nucleus, and cytosol. Tertiary structure predictions for C13orf42 indicate multiple alpha helices. Gene Summary C13orf42 is a protein encoding gene containing 4 exons. C13orf42 is also known by aliases LINC00371 and LINC00372. RNA sequencing shows the gene's expression at low levels in various tissues. Location C13orf42 is located on the minus strand of chromosome 13 at 13q14.3 in humans. C13orf42 is located from 51.08 Mb to 51.20 Mb on chromosome 13 and spans 118 kilobases. Neighborhood The genomic neighborhood of C13orf42 consists of several pseudogenes along with ribonuclease H2 subunit B (RNASEH2B), uncharacterized LOC107984554, and family with sequence similarity 124 member A (FAM124A). Exons The C13orf42 ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer 3
Breast cancer 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA3 gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References Further reading * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are a human gene and its protein product, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double strand bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
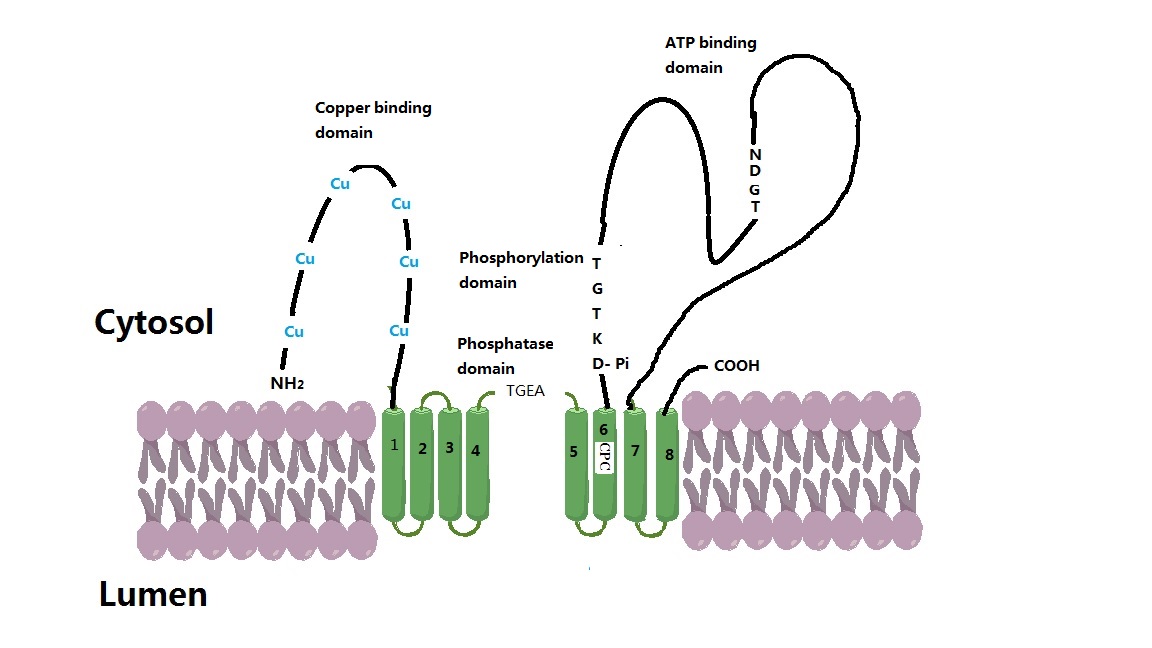
ATP7B
Wilson disease protein (WND), also known as ATP7B protein, is a copper-transporting P-type ATPase which is encoded by the ''ATP7B'' gene. The ATP7B protein is located in the trans-Golgi network of the liver and brain and balances the copper level in the body by excreting excess copper into bile and plasma. Genetic disorder of the ATP7B gene may cause Wilson's disease, a disease in which copper accumulates in tissues, leading to neurological or psychiatric issues and liver diseases. Gene Wilson disease protein is associated with ''ATP7B'' gene, approximately 80 Kb, located on human chromosome 13 and consists of 21 exons. The mRNA transcribed by ''ATP7B'' gene has a size of 7.5 Kb, and which encodes a protein of 1465 amino acids. The gene is a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family and encodes a protein with several membrane-spanning domains, an ATPase consensus sequence, a hinge domain, a phosphorylation site, and at least two putative copper-binding sites. This p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |