|
CKAP2
Cytoskeleton-associated protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CKAP2'' gene. Human CKAP2 gene, the cDNA of which is known as LB1, is a cytoskeleton-associated protein involved in mitotic progression. Its high transcriptional activity has been observed in the testes, thymus, and diffuse B-cell lymphomas. The gene codes for a protein of 683 residues, which lacks a homology to known amino acid sequences. On evidence of immunofluorescence analysis, the CKAP2 product is a cytoplasmic protein associated with cytoskeletal fibrils. The CKAP2 gene is in chromosome 13q14. Rearrangements of this region result in various tumors. Thus deletions have been detected in multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma, B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 13
Chromosome 13 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 13 spans about 114 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 3.5 and 4% of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 13. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 13. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases and disorders are some of those re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
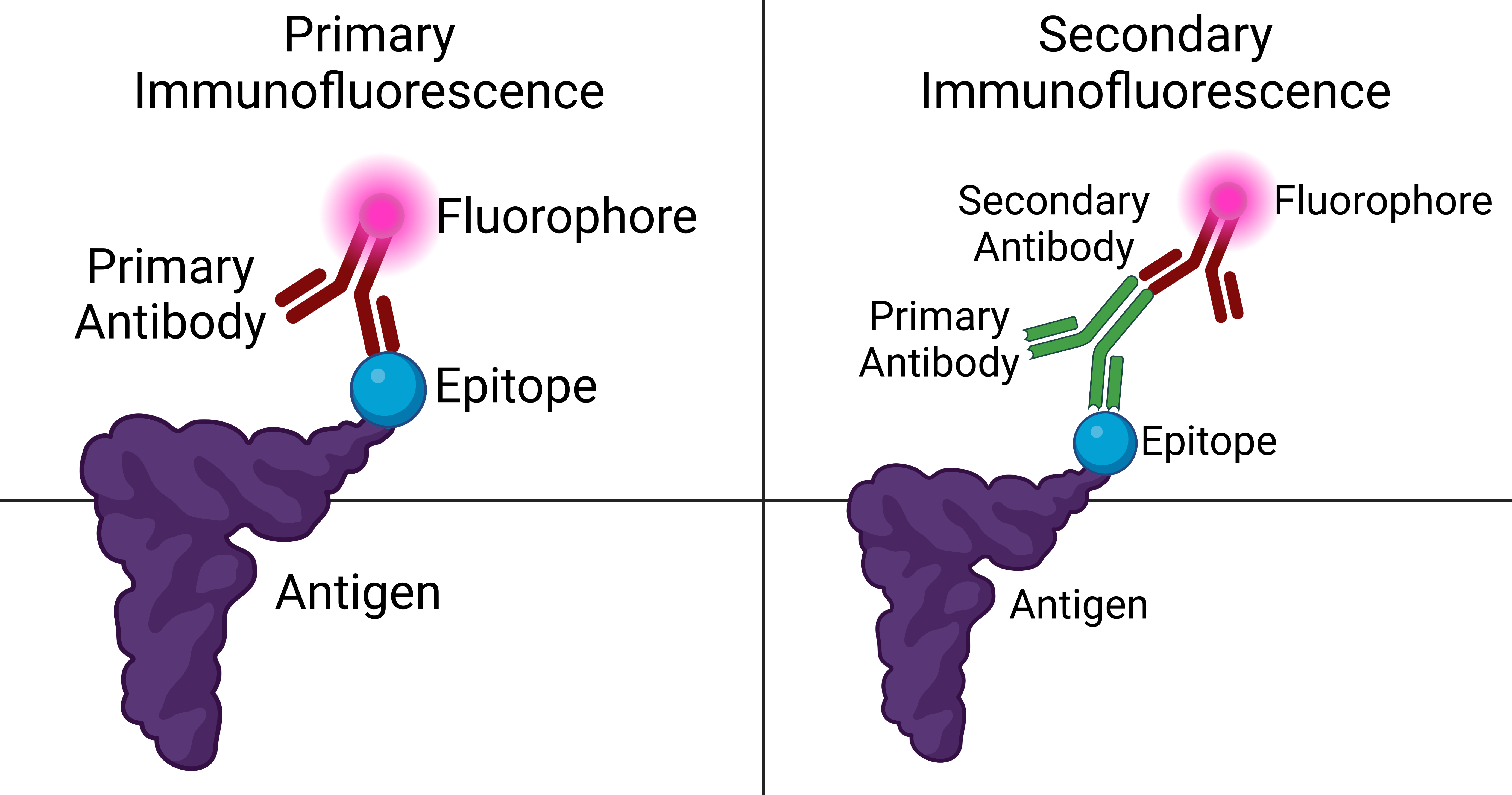
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, referred to as B-PLL, is a rare blood cancer. It is a more aggressive, but still treatable, form of leukemia. Specifically, B-PLL is a prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL) that affects prolymphocytes – immature forms of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes – in the peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleen. It is an aggressive cancer that presents poor response to treatment. Mature lymphocytes are infection-fighting immune system cells. B-lymphocytes have two responsibilities: # Production of antibodies – In response to antigens, B-lymphocytes produce and release antibodies specific to foreign substances in order to aid in their identification and elimination phagocytes # Generation of memory cells – Interactions between antibodies and antigens allow B-lymphocytes to establish cellular memories, otherwise known as immunities that allow the body to respond more rapidly and efficiently to previously encountered species Classification It is categorized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head And Neck Squamous-cell Carcinoma
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice. Some may experience a sore throat that does not go away. In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, trouble breathing may also be present. The majority of head and neck cancer is caused by the use of alcohol or tobacco, including smokeless tobacco, with increasing cases linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors include Epstein-Barr virus, betel quid, radiation exposure, certain workplace exposures. About 90% are pathologically classified as squamous cell cancers. The diagnosis is confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that surrounds the urethra just below the bladder. It is located in the hypogastric region of the abdomen. To give an idea of where it is located, the bladder is superior to the prostate gland as shown in the image The rectum is posterior in perspective to the prostate gland and the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone is inferior. Only those who have male reproductive organs are able to get prostate cancer. Most prostate cancers are slow growing. Cancerous cells may spread to other areas of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes. It may initially cause no symptoms. In later stages, symptoms include pain or difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pain in the pelvis or back. Benign prostatic hyperplasia may produce similar sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasmic
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology Modeling
Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "''target''" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the "''template''"). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure. Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure. It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night. Many subtypes of lymphomas are known. The two main categories of lymphomas are the non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (90% of cases) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (10%). The World Health Organization (WHO) includes two other categories as types of lymphoma – multiple myeloma and immunoproliferative diseases. Lymphomas and leukemias are a part of the broader group of tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma include infection with Epstein–Barr virus and a history of the disease in the family. Risk factors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_squamous_cell_carcinoma_histopathology.jpg)




