|
Chromatogram
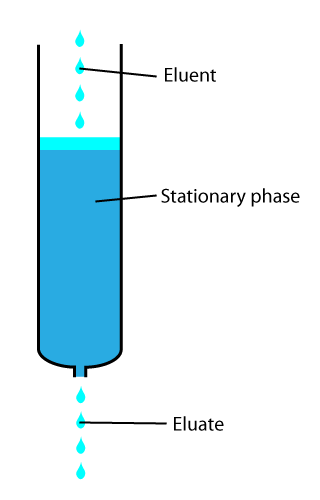
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography Of Chlorophyll - Step 7
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Tsvet
Mikhail Semyonovich Tsvet (Михаил Семёнович Цвет, also spelled Tsvett, Tswett, Tswet, Zwet, and Cvet; 14 May 1872 – 26 June 1919) was a Russian-Italian botanist who invented chromatography. His last name is Russian for "colour" and is also the root word of "flower." Biography Mikhail Tsvet was born 14 May 1872 in Asti, Italy. His mother was Italian, and his father was a Russian official. His mother died soon after his birth, and he was raised in Geneva, Switzerland. He received his BS degree from the Department of Physics and Mathematics at the University of Geneva in 1893. However, he decided to dedicate himself to botany and received his PhD degree in 1896 for his work on cell physiology. He moved to Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1896 because his father was recalled from the foreign service. There he started to work at the Biological Laboratory of the Russian Academy of Sciences. His Geneva degrees were not recognized in Russia, and he had to earn Russian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in chemistry , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , reward = 9 million SEK (2017) , year = 1901 , holder = Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten P. Meldal and Karl Barry Sharpless (2022) , most_awards = Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next=2023 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination geometry, tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kovats Retention Index
In gas chromatography, the Kovats retention index (shorter Kovats index, retention index; plural retention indices) is used to convert retention times into system-independent constants. The index is named after the Hungarian-born Swiss chemist Ervin Kováts, who outlined the concept in the 1950s while performing research into the composition of the essential oils. The retention index of a chemical compound is retention time interpolated between adjacent ''n''-alkanes. While retention times vary with the individual chromatographic system (e.g. with regards to column length, film thickness, diameter and inlet pressure), the derived retention indices are quite independent of these parameters and allow comparing values measured by different analytical laboratories under varying conditions and analysis times from seconds to hours. Tables of retention indices are used to identify peaks by comparing measured retention indices with the tabulated values. Isothermal Kovats retention index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-performance Liquid Chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material. Each component in the sample interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent material, causing different flow rates for the different components and leading to the separation of the components as they flow out of the column. HPLC has been used for manufacturing (''e.g.'', during the production process of pharmaceutical and biological products), legal (''e.g.'', detecting performance enhancement drugs in urine), research (''e.g.'', separating the components of a complex biological sample, or of similar synthetic chemicals from each other), and medical (''e.g.'', detecting vitamin D levels in blood serum) purposes. Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Electrochromatography
Capillary electrochromatography (CEC) is a chromatographic technique in which the mobile phase is driven through the chromatographic bed by electroosmosis. Capillary electrochromatography is a combination of two analytical techniques, high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Capillary electrophoresis aims to separate analytes on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio by passing a high voltage across ends of a capillary tube, which is filled with the analyte. High-performance liquid chromatography separates analytes by passing them, under high pressure, through a column filled with stationary phase. The interactions between the analytes and the stationary phase and mobile phase lead to the separation of the analytes. In capillary electrochromatography capillaries, packed with HPLC stationary phase, are subjected to a high voltage. Separation is achieved by electrophoretic migration of solutes and differential partitioning. Principle Capillary electroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eluotropic Series
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions. In a liquid chromatography experiment, for example, an analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column. The adsorbent, a solid phase (stationary phase), is a powder which is coated onto a solid support. Based on an adsorbent's composition, it can have varying affinities to "hold" onto other molecules—forming a thin film on the surface of its particles. Elution then is the process of removing analytes from the adsorbent by running a solvent, called an "eluent", past the adsorbent/analyte complex. As the solvent molecules "elute", or travel down through the chromatography column, they can either pass by the adsorbent/analyte complex or they can displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its place. After the solvent molecules displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths. Although spectrophotometry is most commonly applied to ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation, modern spectrophotometers can interrogate wide swaths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including x-ray, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and/or microwave wavelengths. Overview Spectrophotometry is a tool that hinges on the quantitative analysis of molecules depending on how much light is absorbed by colored compounds. Important features of spectrophotometers are spectral bandwidth (the range of colors it can transmit through the test sample), the percentage of sample-transmission, the logarithmic range of sample-absorption, and sometimes a percentage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
