|
Chin Hills
The Chin Hills are a range of mountains in Chin State, northwestern Burma, Burma (Myanmar), that extends northward into India's Manipur state. Geography The highest peak in the Chin Hills is Khonu Msung, or Mount Victoria, in southern Chin State, which reaches . The Chin Hills–Arakan Yoma montane forests ecoregion has diverse forests with pine, Camellia sinensis, camellia and teak. Falam (town), Falam is the largest town in the Chin Hills, lying at their southern edge. The Chin Hills are the eastern part of the Patkai, Patkai Range, which includes the Lushai Hills and runs through Nagaland in India, as well as part of Burma. The Lushai Hills are frequently discussed with the Chin Hills as the topography, people's culture and history are similar. The southern prolongation of the Chin Hills is the Arakan Mountains, Arakan Range (Arakan Yoma), stretching as well from north to south. History Historically the area of the range has been populated by the Chin people who like their ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nat Ma Taung
Nat Ma Taung ( my, နတ်မတောင်; Khaw-nu-soum or Khonuamthung in Chin), also known as Mount Victoria, is the highest mountain in the Chin State of western Burma. Geography With a height of above sea level and a prominence of , Nat Ma Taung is one of the ultra prominent peaks of Southeast Asia. Located in three townships - Kanpatlet, Mindat and Matupi, Nat Ma Taung is part of the Chin Hills range. Ecology Nat Ma Taung is in the Chin Hills–Arakan Yoma montane forests ecoregion. Surrounded at lower elevations by tropical and subtropical moist forests, Nat Ma Taung's higher elevations form a sky island, home to many temperate and alpine species typical of the Himalaya further north, and many endemic species. The White-browed nuthatch (''Sitta victoriae'') is a bird endemic to this mountain range. The peak is unique for the presence of trees, bushes and grass, which have adapted to the environment. On the way towards the top you will pass pine trees (''Pinus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patkai
The Pat-kai (Pron:pʌtˌkaɪ) or Patkai Bum ( Burmese: ''Kumon Taungdan'') are a series of mountains in the Indo-Myanmar border falling in the north-eastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Upper Burma region of Myanmar. They were created by the same tectonic processes that created the Himalayas in the Mesozoic. In Tai-Ahom language, Pat means ''to cut'' and Kai means ''chicken''. Geography The Patkai range mountains are not as rugged as the Himalayas and the peaks are much lower. Features of the range include conical peaks, steep slopes and deep valleys. Three mountain ranges come under the Patkai. The Patkai-Bum, the Garo-Khasi-Jaintia hills and the Lushai Hills. The highest point of this range is Phawngpui Tlang, which is also known as 'Blue Mountain'. The Garo-Khasi range is in the Indian state of Meghalaya. Mawsynram and Cherrapunji, on the windward side of these mountains are the world's wettest places, having the highest annual rainfall. The climat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
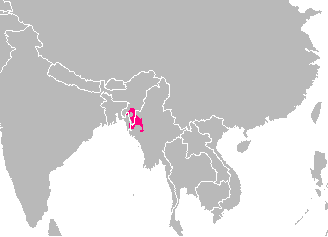
Chin Hills-Arakan Yoma Montane Forests
The chin is the forward pointed part of the anterior mandible ( mental region) below the lower lip. A fully developed human skull has a chin of between 0.7 cm and 1.1 cm. Evolution The presence of a well-developed chin is considered to be one of the morphological characteristics of ''Homo sapiens'' that differentiates them from other human ancestors such as the closely related Neanderthals. Early human ancestors have varied symphysial morphology, but none of them have a well-developed chin. The origin of the chin is traditionally associated with the anterior–posterior breadth shortening of the dental arch or tooth row; however, its general mechanical or functional advantage during feeding, developmental origin, and link with human speech, physiology, and social influence are highly debated. Functional perspectives Robinson (1913) suggests that the demand to resist masticatory stresses triggered bone thickening in the mental region of the mandible and ultimately formed a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chindwin River
, , image = Homalin aerial.jpg , image_size = , image_caption = The Chindwin at Homalin. The smaller, meandering Uyu River can be seen joining the Chindwin. , map = Irrawaddyrivermap.jpg , map_size = , map_alt = , map_caption = , source1_location = Hukawng Valley, Kachin State , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Myanmar , length = , source1_elevation = , mouth_location = Irrawaddy River , mouth_elevation = , mouth_coordinates = , discharge1_avg= The Chindwin River (also called the Ningthi River) is a river flowing entirely in Myanmar, and the largest tributary of the country's main river, the Ayeyarwady. Its official name is also spelled Chindwinn. Sources The Chindwin originates in the broad Hukawng Valley of Kachin State of Burma, roughly , where the Tanai, the Tabye, the Tawan, and the Taron (also known as Turong or Towang) rivers meet. The headwaters of the Tanai are at about on the Shwedaunggyi peak of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myittha River
Myittha River ( my, မြစ်သာမြစ်) is a river of western Burma, a tributary of the Chindwin River. Course The Myittha originates in the Chin Hills and flowing northwards drains the Kale Valley. It flows into the Chindwin, one of the main tributaries of the Irrawaddy River, on the right just below the town of Kalewa.Bird, George W. (1897) ''Wanderings in Burma'' F.J. Bright & Son, Bournemouth, Englandpage 401 See also *List of rivers of Burma This is a list of rivers in Myanmar (also known as Burma). This list is arranged by drainage basin from east to west, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name. Indian Ocean * Nāf River * Kaladan River * Lemro Riv ... References Rivers of Myanmar {{Myanmar-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsistence Agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace." Despite the self-sufficiency in subsistence farming, most subsistence farmers also participate in trade to some degree. Although their amount of trade as measured in cash is less than that of consumers in countries with modern complex markets, they use these markets mainly to obtain goods, not to generate income for food; these goods are typically not necessary for survival and may include sugar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laimi
The Kuki people are an ethnic group native to the Mizo Hills (formerly Lushai), a mountainous region in the southeastern part of Mizoram and Manipur in India. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. Some fifty tribes of Kuki peoples in India are recognised as scheduled tribes, based on the dialect spoken by that particular Kuki community as well as their region of origin. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people. History Early history The early history of the Kukis is obscure. The origin of the word "Kuki" is uncertain; it is an exonym: it was not originally as a self-designation by the tribes that are now called Kukis. According to the colonial British writer Adam Scott Reid, the earliest reference to the word Kuki can be dated to 1777 CE, when it first appeare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
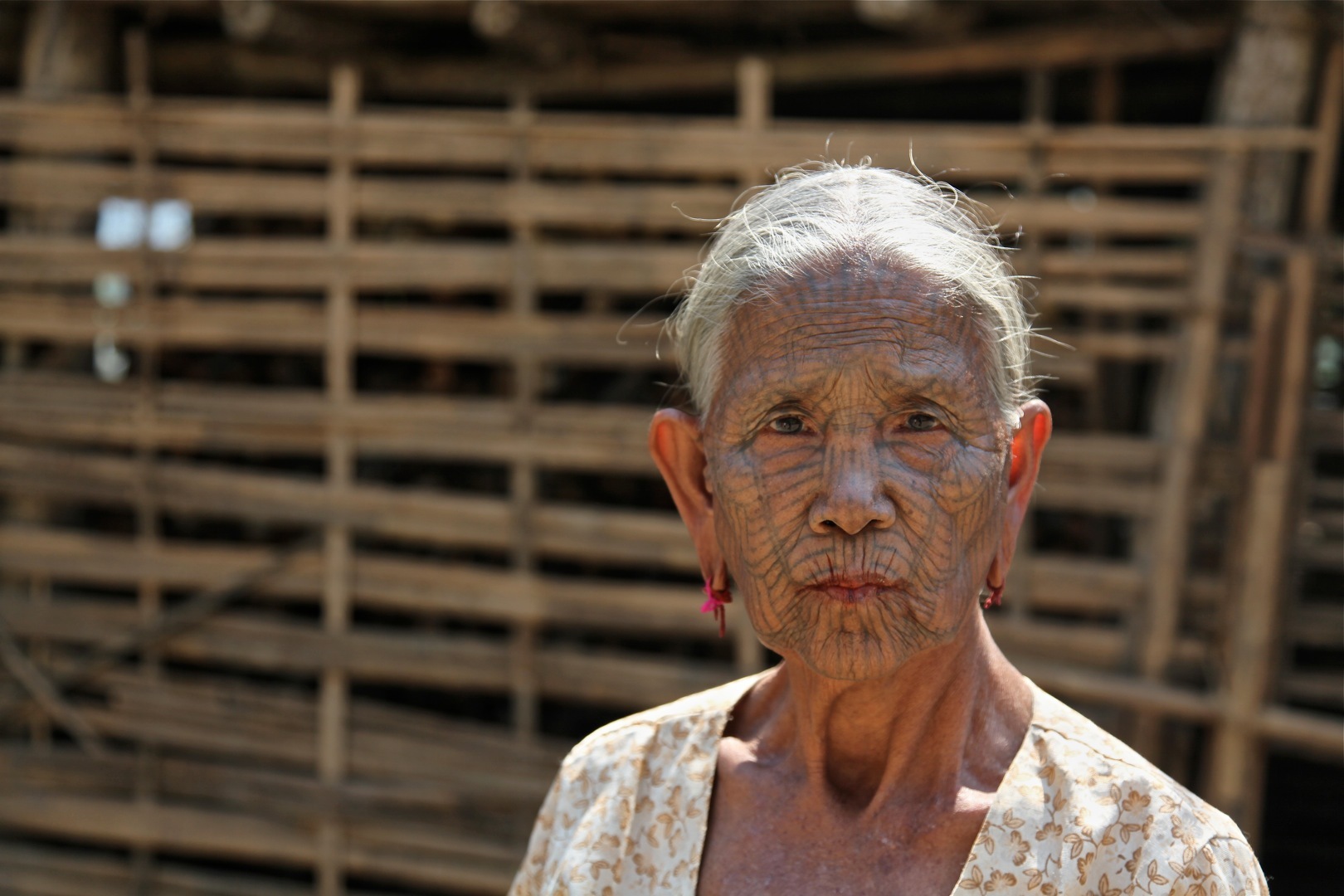
Chin People
The Chin people (, ) are a Southeast Asian people native to Chin State and its neighbouring states of Myanmar.Head, JonathanBurma's 'abused Chin need help' ''BBC News'', Jan 28, 2009, accessed Jan 28, 2009 The Chin are one of the founding groups (Chin, Kachin, Shan and Bamar) of the Union of Burma. The Chin speak a variety of related languages, share elements of cultures and traditions. According to the British state media BBC News, "The Chin people... are one of the most persecuted minority groups in Burma." These people predominantly live in the Chin State, Bago Division, Ayeyarwady Division, Magwe Division, Rakhine State and Sagaing Region of Myanmar, but are also spread throughout Burma, Bangladesh and India. In the 2014 Burmese ethnic census, the Chin ethnicity was again dismissed by the people of the Chin State. It is to be noted that the Mizo people in Mizoram, India and the Chin are both Chin-Kuki-Mizo people, who share the same history with each other. The difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arakan Mountains
The Arakan Mountains ( my, ရခိုင်ရိုးမ), also known as the Rakhine Yoma, are a mountain range in western Myanmar, between the coast of Rakhine State and the Central Myanmar Basin, in which flows the Irrawaddy River. It is the most prominent of a series of parallel ridges that arc through Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Myanmar. The Arakan Mountains run from Cape Negrais in the south in to Manipur, India in the north. They include the Naga Hills, the Chin Hills, and the Patkai range which includes the Lushai Hills. The mountain chain is submerged in the Bay of Bengal for a long stretch and emerges again in the form of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Etymology The word ''Arakan'' is derived from the Sanskrit word ''Rakshasa'' (राक्षस), a term used to refer to the inhabitants of the region. Geology and formation The Arakan Mountains and the parallel arcs to the west and east were formed by compression as the Indian Plate collided with the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital city is Kohima and its largest city is Dimapur. The state has an area of with a population of 1,980,602 as per the 2011 Census of India, making it one of the smallest states in India.Census of India 2011 Govt of India Nagaland became the 16th state of India on 1 December 1963. It is home to a rich variety of natural, cultural and environmental resources. Nagaland is a mountainous state and lies between the parallels of 95 and 94 degrees east longitude and 25.2 and 27.0 degrees latitude north. The high-profile [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lushai Hills
The Lushai (Pron: ˌlʊˈʃaɪ) Hills (or Mizo Hills) are a mountain range in Mizoram and Manipur, India. The range is part of the Patkai range system and its highest point is 2,157 m high Phawngpui, also known as 'Blue Mountain'. Flora and fauna The hills are for the most part covered with dense bamboo jungle and rank undergrowth; but in the eastern portion, owing probably to a smaller rainfall, open grass-covered slopes are found, with groves of oak and pine interspersed with rhododendrons. The Blue Mountain is the highest peak in Lushai hills. Inhabitants These hills are inhabited by the Lushais and other Mizo tribes, but the population is extremely scanty. When they invaded the district from the north. Their first attack upon British territory took place in November 1849, and after that date they proved one of the most troublesome tribes on the north-east frontier of India; but operations in 1890 resulted in the complete pacification of the northern Lushai villages, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |