|
Children Of Muhammad
The common view is that the Islamic prophet Muhammad had three sons, named Abd Allah, Ibrahim, and Qasim, and four daughters, named Fatima, Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum, and Zaynab. The children of Muhammad are said to have been born to his first wife Khadija bint Khuwaylid, except his son Ibrahim, who was born to Maria al-Qibtiyya. None of Muhammad's sons reached adulthood, but he had an adult foster son, Zayd ibn Harithah. Daughters of Muhammad all reached adulthood but only Fatima survived her father. Citing, among others, the advanced age of Khadija, some Shia sources contend that Fatima was the only biological daughter of Muhammad, as she is known to have enjoyed a close relationship with Muhammad, unlike Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum, and Zaynab. That Fatima was the only biological daughter of Muhammad appears to be the mainstream view among Shia Muslims. Sunni view In chronological order, most Sunni sources list the children of the Islamic prophet Muhammad as *Qasim (598–601) * Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qasim Ibn Muhammad
Qāsim ibn Muḥammad ( ar, قاسم بن محمد) was the eldest of the sons of Muhammad and Khadija bint Khuwaylid. He died in 601 CE (before the start of his father's prophethood in 609), after his third birthday and is buried in Jannat al-Mu'alla cemetery, Mecca. Siblings *Abdullah ibn Muhammad *Ibrahim ibn Muhammad *Zainab bint Muhammad *Ruqayya bint Muhammad *Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad *Fatimah al-Zahra Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, th ... References External links The tribe of Quraish Children of Muhammad 598 births 601 deaths Arab Muslims 6th-century Arabs People from Mecca Burials at Jannat al-Mu'alla {{Islam-bio-stub Child deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the third of the '' Rāshidun'', or "Rightly Guided Caliphs". Born into a prominent Meccan clan, Banu Umayya of the Quraysh tribe, he played a major role in early Islamic history, and is known for having ordered the compilation of the standard version of the Quran. When Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab died in office aged 60/61 years, Uthman, aged 68–71 years, succeeded him and was the oldest to rule as Caliph. Under Uthman's leadership, the Islamic empire expanded into Fars (present-day Iran) in 650, and some areas of Khorāsān (present-day Afghanistan) in 651. The conquest of Armenia had begun by the 640s. His reign also saw widespread protests and unrest that eventually led to armed revolt and his assassination. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval of the Islamic prophet Muhammad as transmitted through chains of narrators. In other words, the ḥadīth are transmitted reports attributed to what Muhammad said and did. Hadith have been called by some as "the backbone" of Islamic civilization, J.A.C. Brown, ''Misquoting Muhammad'', 2014: p.6 and for many the authority of hadith as a source for religious law and moral guidance ranks second only to that of the Quran (which Muslims hold to be the word of God revealed to Muhammad). Most Muslims believe that scriptural authority for hadith comes from the Quran, which enjoins Muslims to emulate Muhammad and obey his judgements (in verses such as , ). While the number of verses pertaining to law in the Quran is relatively few, hadith are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umamah Bint Abi Al-As
Umāma bint Abī al-ʿĀṣ ibn al-Rabīʿ ( ar, أُمَامَة بِنْت أَبِي ٱلْعَاص ابْن ٱلرَّبِيْع}), was a granddaughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Khadija, via their daughter Zaynab, and is thus also known as ''Umāma bint Zaynab'' (). Muhammad was her maternal grandfather, and thus she is a member of his Ahl al-Bayt. She is also numbered among the Companions of the Prophet. Biography She was the daughter of Abu al-As ibn al-Rabi', who married Muhammad's eldest daughter Zaynab. She had one sibling, Ali. Her maternal aunts were Muhammad's daughters Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum and Fatima. When Umama was a small child, Muhammad used to carry her on his shoulder while he prayed. He used to put her down to prostrate and then pick her up again as he rose. Muhammad once promised to give an onyx necklace to "her whom I love best." His wives expected him to give it to Aisha, but he presented it to Umama. On a different occasion, he gave her a gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Ibn Abi Al-As
ʿAlī ibn Abī al-ʿĀṣ or ʿAlī ibn Zaynab bint Muḥammad was a sahaba, companion and a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his eldest daughter. Ali was born to Abu al-As ibn al-Rabi' and Zaynab bint Muhammad, and his sister was Umamah bint Zainab, Umamah bint Zaynab. Ali ibn Zaynab is reported to have died in infancy in 630 Common Era, CE (9 Hijri calendar, AH). Family tree * * indicates that the marriage order is disputed * Note that direct lineage is marked in bold. External links Holy prophet's life Companions of the Prophet 630s deaths Family of Muhammad Year of birth unknown Burials at Jannat al-Baqī {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Allah Ibn Uthman
Abd Allah ibn Uthman ( ar, عبد الله ابن عثمان, translit=ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿUthmān; ), was the son of the third caliph Uthman () and Ruqayya bint Muhammad. Born in Abyssinia, Abd Allah was the first grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Biography Mus'ab al-Zubayri narrated that when Uthman Migration to Abyssinia, migrated to Abyssinia, he was accompanied by his wife Ruqayya bint Muhammad Ruqayya bint Muhammad ( ar, رقية بنت محمد, translit=Ruqayya bint Muḥammad; –March 624) was the second eldest daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Khadija bint Khuwaylid, Khadija. She married the third caliph Uthman and the .... A child named Abd Allah was born in the land of Abyssinia in 2 BH. Abd Allah died after a rooster bit his eye in November 625 (Jumada al-Thani 4 AH) at the age of six. Muhammad led his funeral prayers.Kitab Tabaqat Al-Kubra by Ibn Sa'd Volume 2, Part 3, Pg.131 References Bibliography * {{Cite book , last=Madelung , fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companions Of The Prophet
The Companions of the Prophet ( ar, اَلصَّحَابَةُ; ''aṣ-ṣaḥāba'' meaning "the companions", from the verb meaning "accompany", "keep company with", "associate with") were the disciples and followers of Muhammad who saw or met him during his lifetime, while being a Muslim and were physically in his presence. "Al-ṣaḥāba" is definite plural; the indefinite singular is masculine ('), feminine ('). Later Islamic scholars accepted their testimony of the words and deeds of Muhammad, the occasions on which the Quran was revealed and other various important matters of Islamic history and practice. The testimony of the companions, as it was passed down through trusted chains of narrators (''isnad''s), was the basis of the developing Islamic tradition. From the traditions (''hadith'') of the life of Muhammad and his companions are drawn the Muslim way of life ('' sunnah''), the code of conduct ('' sharia'') it requires, and the jurisprudence (''fiqh'') by whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-As Ibn Al-Rabi'
Abū al-ʿĀṣ ibn al-Rabīʿ ( ar, أبو العاص بن الربيع, died in February, AD 634), was a son-in-law and Companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. His original name was said to have been Hushaym or Yasser. Family He was the son of Hala bint Khuwaylid.Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir'' vol. 8. Translated by Bewley, A. (1995). ''The Women of Madina'', p. 21. London: Ta-Ha Publishers. His legal father was Al-Rabi ibn Abd al-Uzza of the Abdshams clan of the Quraysh tribe.Ibn Hajar, ''Al-Isaba'' vol. 7 #10176. He became a successful merchant and was considered an important person in Mecca.Muhammad ibn Ishaq. ''Sirat Rasul Allah''. Translated by Guillaume, A. (1955). ''The Life of Muhammad'', p. 313. Oxford: Oxford University Press. His aunt Khadija regarded him as her son, and he frequently visited her home. In due course Khadija asked her husband Muhammad to find him a wife. Muhammad gave Abu al-As their eldest daughter, Zaynab, apparently with so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharif
Sharīf ( ar, شريف, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef or sherif, feminine sharīfa (), plural ashrāf (), shurafāʾ (), or (in the Maghreb) shurfāʾ, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, from the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad ( ). It may be used in three senses: #In the broadest sense, it refers to any descendant of Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim (the Banu Hashim or Hashimites, already in Muhammad's day an established clan within the Meccan tribe of the Quraysh), including all descendants of Muhammad's paternal uncles Abu Talib (the Talibids) and al-Abbas (the Abbasids).. #More often, it refers to a descendant of Ali, a son of Abu Talib and a paternal cousin of Muhammad (the Alids), especially but not exclusively through Ali's marriage with Muhammad's daughter Fatima (the Fatimids). In this sense, the most common one, the term effectively refers to all descendants of the prophet. #In its narrowest sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyid
''Sayyid'' (, ; ar, سيد ; ; meaning 'sir', 'Lord', 'Master'; Arabic plural: ; feminine: ; ) is a surname of people descending from the Prophets in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandsons, Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali, sons of Muhammad's daughter Fatimah, Fatima and his cousin and son-in-law Ali (Ali ibn Abi Talib). While in the Islamic golden age, early islamic period the title Al-Sayyid was applied on all the members of the of Banu Hashim, banu hashim, the tribe of Muhammad. But later on the title was made specific to those of Hasanids, Hasani and Hussaini descent, Primarily by the List of Fatimid caliphs, Fatimid Caliphs. Female ''sayyids'' are given the titles ''sayyida'', ''syeda'', ''alawiyah'' . In some regions of the Islamic world, such as in Iraq, the descendants of Muhammad are given the title ''Emir, amīr'' or ''mīr'', meaning "aristocrats", "commander", or "ruler". In Shia Islam the son of a non Sayyid father and a Sayyida mother claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
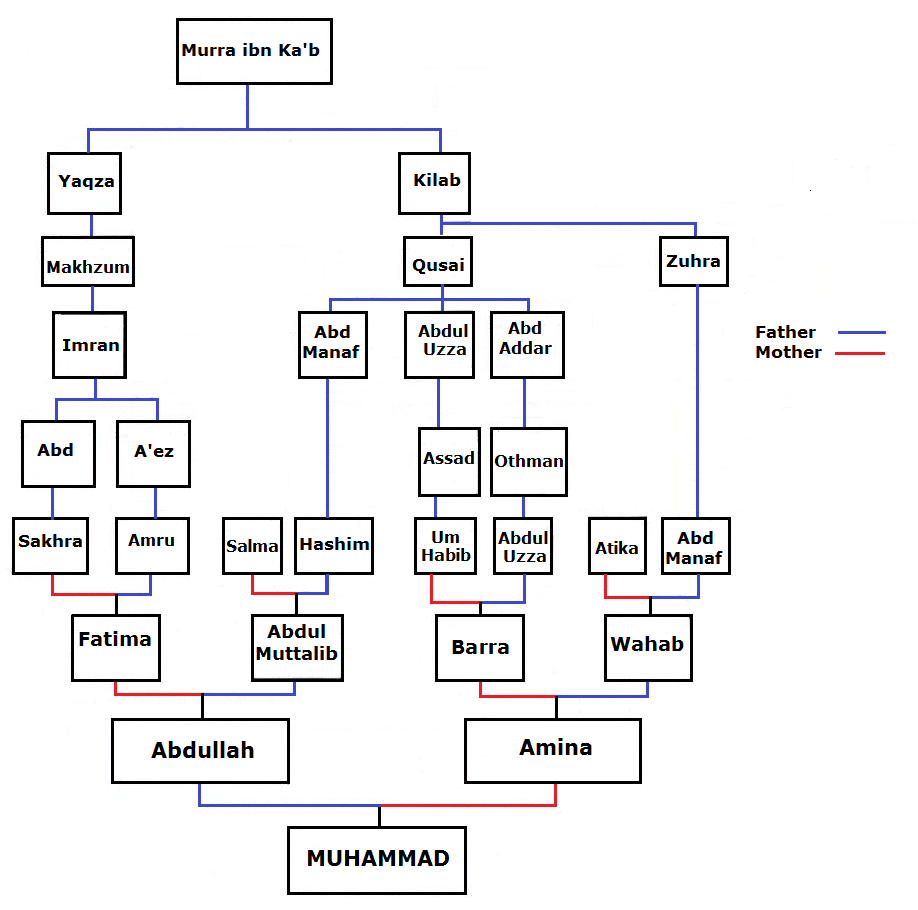
Family Tree Of Muhammad
This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad known as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Qurayshs tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label ‘arabicised’ is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |