|
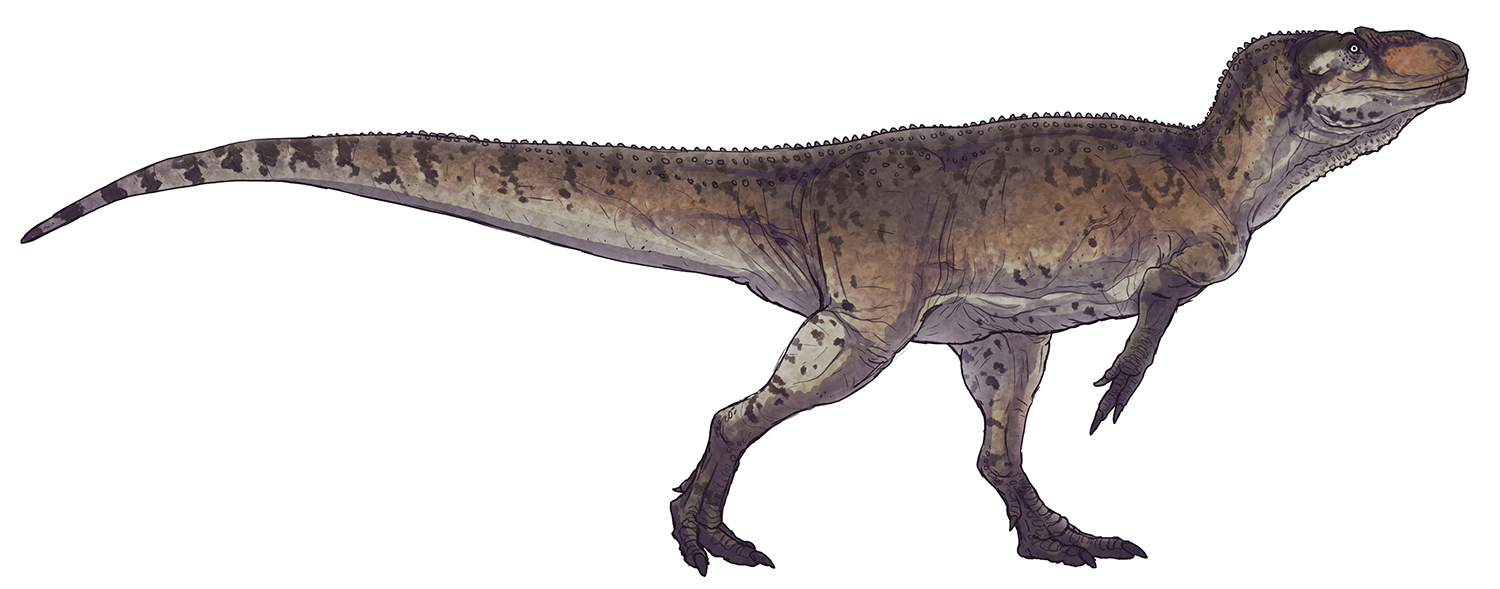
Chilantaisaurus
''Chilantaisaurus'' (" lizard") is a genus of large theropod dinosaur, possibly a neovenatorid or a primitive coelurosaur, from the Late Cretaceous Ulansuhai Formation of China (Turonian age, about 92 million years ago). The type species, ''C. tashuikouensis'', was described by Hu in 1964. Description ''Chilantaisaurus'' was a large theropod, estimated as weighing between and . In 2010, Brusatte et al. estimated it to weigh , based on femur length measurements. However, considering that greater femoral circumference indicates the greater capacity to withstand greater locomotor loads (not greater body mass), the 2020 study moderated the body mass of the holotype at . It is estimated to be around to long. Classification Hu considered ''Chilantaisaurus'' to be a carnosaur related to ''Allosaurus'', though some subsequent studies suggested that it may be a spinosauroid, possibly a primitive member of the spinosaurid family (Sereno, 1998; Chure, 2000; Rauhut, 2001) because it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilantaisaurus Skeletal
''Chilantaisaurus'' (" lizard") is a genus of large theropod dinosaur, possibly a neovenatorid or a primitive coelurosaur, from the Late Cretaceous Ulansuhai Formation of China (Turonian age, about 92 million years ago). The type species, ''C. tashuikouensis'', was described by Hu in 1964. Description ''Chilantaisaurus'' was a large theropod, estimated as weighing between and . In 2010, Brusatte et al. estimated it to weigh , based on femur length measurements. However, considering that greater femoral circumference indicates the greater capacity to withstand greater locomotor loads (not greater body mass), the 2020 study moderated the body mass of the holotype at . It is estimated to be around to long. Classification Hu considered ''Chilantaisaurus'' to be a carnosaur related to ''Allosaurus'', though some subsequent studies suggested that it may be a spinosauroid, possibly a primitive member of the spinosaurid family (Sereno, 1998; Chure, 2000; Rauhut, 2001) because i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilantaisaurus
''Chilantaisaurus'' (" lizard") is a genus of large theropod dinosaur, possibly a neovenatorid or a primitive coelurosaur, from the Late Cretaceous Ulansuhai Formation of China (Turonian age, about 92 million years ago). The type species, ''C. tashuikouensis'', was described by Hu in 1964. Description ''Chilantaisaurus'' was a large theropod, estimated as weighing between and . In 2010, Brusatte et al. estimated it to weigh , based on femur length measurements. However, considering that greater femoral circumference indicates the greater capacity to withstand greater locomotor loads (not greater body mass), the 2020 study moderated the body mass of the holotype at . It is estimated to be around to long. Classification Hu considered ''Chilantaisaurus'' to be a carnosaur related to ''Allosaurus'', though some subsequent studies suggested that it may be a spinosauroid, possibly a primitive member of the spinosaurid family (Sereno, 1998; Chure, 2000; Rauhut, 2001) because it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulansuhai Formation
The Ulansuhai Formation () is a geological formation in Inner Mongolia, north China. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Cretaceous, Asia)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 563-570. . The Ulansuhai Formation has traditionally been considered to date to the Aptian-Albian stages of the Lower Cretaceous, due to similarities between the Ulansuhai fauna and known Aptian formations. However, radiometric dating done on underlying formations has shown this to be incorrect. Due to the age of underlying rocks, the Ulansuhai Formation cannot be older than the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 92 Ma.Kobayashi, Y., and Lu, J.-C. (2003). "A new ornithomimid dinosaurian with gregarious habits from the Late Cretaceous of China." ''Acta Palaeontol. Pol.'', 48: 235–259.Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therizinosaur
Therizinosaurs (once called segnosaurs) were large herbivorous Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs whose fossils have been found across the Early Cretaceous, Early to Late Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Various features of the forelimbs, skull and pelvis unite these finds as both theropods and maniraptorans, close relatives to birds. The name of the representative genus, ''Therizinosaurus'', is derived from the Ancient Greek , Greek (, 'to reap' or 'scythe')Translated paper and (, 'lizard'). The older representative, ''Segnosaurus'', is derived from the Latin ('slow') and the Greek . History of research [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neovenatorid
Neovenatoridae is a proposed clade of carcharodontosaurian dinosaurs uniting some primitive members of the group such as ''Neovenator'' with the Megaraptora, a group of theropods with controversial affinities. Other studies recover megaraptorans as basal coelurosaurs unrelated to carcharodontosaurs. Other theropods with uncertain affinities such as ''Gualicho'', ''Chilantaisaurus'' and ''Deltadromeus'' are also sometimes included. Classification Phylogenetic studies conducted by Benson, Carrano and Brusatte (2010) and Carrano, Benson and Sampson (2012) recovered the group Megaraptora as members of the Neovenatoridae. This would make neovenatorids the latest-surviving allosauroids; at least one megaraptoran, ''Orkoraptor'', lived near the end of the Mesozoic era, dating to the early Maastrichtian stage of the latest Cretaceous period, about 70 million years ago. On the other hand, Novas ''et al.'' (2012), while confirming that ''Neovenator'' was closely related to carcharodontosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neovenatoridae
Neovenatoridae is a proposed clade of carcharodontosaurian dinosaurs uniting some primitive members of the group such as ''Neovenator'' with the Megaraptora, a group of theropods with controversial affinities. Other studies recover megaraptorans as basal coelurosaurs unrelated to carcharodontosaurs. Other theropods with uncertain affinities such as ''Gualicho'', ''Chilantaisaurus'' and ''Deltadromeus'' are also sometimes included. Classification Phylogenetic studies conducted by Benson, Carrano and Brusatte (2010) and Carrano, Benson and Sampson (2012) recovered the group Megaraptora as members of the Neovenatoridae. This would make neovenatorids the latest-surviving allosauroids; at least one megaraptoran, ''Orkoraptor'', lived near the end of the Mesozoic era, dating to the early Maastrichtian stage of the latest Cretaceous period, about 70 million years ago. On the other hand, Novas ''et al.'' (2012), while confirming that ''Neovenator'' was closely related to carcharodontosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turginskaya Svita
The Turginskaya Svita is an Early Cretaceous period geologic formation located in Russia. Dinosaur remains were recovered from it as early as 1915, including partial theropod remains. Weishampel, David B.; ''et al''. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Cretaceous, Asia)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): ''The Dinosauria'', 2nd, ''Berkeley: University of California Press''. Pp. 563-570. . Paleofauna * Theropoda (previously informally known as '' Allosaurus? sibiricus'', '' Antrodemus? sibiricus'' and currently known as '' Chilantaisaurus? sibiricus'') See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with ... ** List of stratigraphic units with few dinosaur genera References Mesozoic Erathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaochilong
''Shaochilong'' (meaning "shark toothed dragon") is an extinct genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid-Cretaceous (Late Cenomanian to the end of the Turonian stage) Ulansuhai Formation of China (about 92 million years ago). The type species, ''S. maortuensis'', was originally named ''Chilantaisaurus maortuensis'', but was re-described and reclassified in 2009. It was one of the last known carcharodontosaurids to walk the earth. Alongside ''Ulughbegsaurus'' from Uzbekistan and ''Mapusaurus'' from Argentina, they were the only members of the family to live until the end of the Turonian epoch. History The material referred to ''Shaochilong'', IVPP V.2885.1-7, consisted of skull fragments (a braincase, partial skull roof, quadrates, and a right maxilla), axis and six caudal vertebrae. A fragmentary left maxilla was also referred to the species, although it has apparently gone missing as of 2009. Although these are believed to belong to a single individual, a lectotype was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosaurus
''Allosaurus'' () is a genus of large carnosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived 155 to 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic epoch (Kimmeridgian to late Tithonian). The name "''Allosaurus''" means "different lizard" alluding to its unique (at the time of its discovery) concave vertebrae. It is derived from the Greek (') ("different, other") and (') ("lizard / generic reptile"). The first fossil remains that could definitively be ascribed to this genus were described in 1877 by paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh. As one of the first well-known theropod dinosaurs, it has long attracted attention outside of paleontological circles. ''Allosaurus'' was a large bipedal predator. Its skull was light, robust and equipped with dozens of sharp, serrated teeth. It averaged in length for ''A. fragilis'', with the largest specimens estimated as being long. Relative to the large and powerful hindlimbs, its three-fingered forelimbs were small, and the body was balanced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs. Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyrannosaurs, ornithomimosaurs, and maniraptorans; Maniraptora includes birds, the only known dinosaur group alive today. Most feathered dinosaurs discovered so far have been coelurosaurs. Philip J. Currie had considered it likely and probable that all coelurosaurs were feathered. However, several skin impressions found for some members of this group show pebbly, scaly skin, indicating that feathers did not completely replace scales in all taxa. In the past, Coelurosauria was used to refer to all small theropods, but this classification has since been abolished. Anatomy Bodyplan The studying of anatomical traits in coelurosaurs indicates that the last common ancestor had evolved the ability to eat and digest plant matter, adapting to an omniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurosaur
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs. Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyrannosaurs, ornithomimosaurs, and maniraptorans; Maniraptora includes birds, the only known dinosaur group alive today. Most feathered dinosaurs discovered so far have been coelurosaurs. Philip J. Currie had considered it likely and probable that all coelurosaurs were feathered. However, several skin impressions found for some members of this group show pebbly, scaly skin, indicating that feathers did not completely replace scales in all taxa. In the past, Coelurosauria was used to refer to all small theropods, but this classification has since been abolished. Anatomy Bodyplan The studying of anatomical traits in coelurosaurs indicates that the last common ancestor had evolved the ability to eat and digest plant matter, adapting to an omnivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avetheropoda
Avetheropoda, or "bird theropods", is a clade that includes carnosaurians and coelurosaurs to the exclusion of other dinosaurs. Definition Avetheropoda was named by Gregory S. Paul in 1988, and was first defined as a clade by Currie and Padian in 1997, to include ''Allosaurus'', modern birds, and other animals descended from their most recent ancestor. In 1999, Paul Sereno named another group, Neotetanurae, for the clade containing Allosauroidea and Coelurosauria, and excluding other tetanurans such as megalosauroids, but this definition was published slightly later. A monophyletic Avetheropoda is recovered in many papers, however recent findings suggest a monophyletic Carnosauria model with allosauroids and megalosauroids being each other’s closest relatives instead of Allosaurs and Coelurosaurs. Classification The cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.jpg)