|
Chikuzen Dialect
The Chikuzen dialect (Japanese: ńŁæÕēŹµ¢╣Ķ©Ć ''chikuzen hogen'') is a Japanese dialect spoken in western Fukuoka Prefecture in an area corresponding to the former Chikuzen Province. It is classified as a Hichiku dialect of the wider Kyushu dialect of Japanese, although the eastern part of the accepted dialect area has more similarities with the Buzen dialect, and the Asakura District in the south bears a stronger resemblance to the Chikugo dialect. The Chikuzen dialect is considered the wider dialect to which the Hakata dialect, the Fukuoka dialect and the Munakata dialect belong. Phonology The perfective aspect, commonly -''yoru'' (-ŃéłŃéŗ) in West Japanese and Kyushu dialects, is often said as -''yo''- (-ŃéłŃüå) in the Chikuzen dialect. For example, ''ikiyoru'' (ĶĪīŃüŹŃéłŃéŗ, ''I am here'') becomes ''ikiyou'' (ĶĪīŃüŹŃéłŃüå). Similarly, the progressive aspect, -''toru'' (-Ńü©Ńéŗ), becomes ''-tou'' (-Ńü©Ńüå). E.g. ''ittoru'' (ĶĪīŃüŻŃü©Ńéŗ, ''I am going'') becomes ''ittoo'' (Ķ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hichiku Dialect
The Hichiku dialect is a group of the Japanese dialects spoken in western Kyushu. The name ''Hichiku'' (ĶéźńŁæ) is constructed by extracting a representative kanji from ''Hizen'' (ĶéźÕēŹ), '' Higo'' (ĶéźÕŠī), '' Chikuzen'' (ńŁæÕēŹ) and '' Chikugo'' (ńŁæÕŠī), the names of old provinces. The Hichiku dialect includes: * Chikuzen dialect (western Fukuoka Prefecture, formerly known as Chikuzen Province, includes the Hakata dialect of Hakata district in Fukuoka) * Chikugo dialect (southern Fukuoka Prefecture, formerly known as Chikugo Province) ** ┼īmuta dialect ( ┼īmuta) ** Yanagawa dialect (Yanagawa) * Saga dialect (Saga Prefecture) ** Karatsu dialect (northern Saga Prefecture centered Karatsu) ** Tashiro dialect (easternmost Saga Prefecture centered Tashiro) * Nagasaki dialect (Nagasaki Prefecture) ** Sasebo dialect (northern Nagasaki Prefecture centered Sasebo) ** Hirado dialect (Hirado Island, west of Nagasaki Prefecture) * Kumamoto dialect (Kumamoto Prefecture) * Hita dialect ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukuoka
is the sixth-largest city in Japan, the second-largest port city after Yokohama, and the capital city of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The city is built along the shores of Hakata Bay, and has been a center of international commerce since ancient times. The area has long been considered the gateway to the country, as it is the nearest point among Japan's main islands to the Asian mainland. Although humans occupied the area since the Jomon period, some of the earliest settlers of the Yayoi period arrived in the Fukuoka area. The city rose to prominence during the Yamato period. Because of the cross-cultural exposure, and the relatively great distance from the social and political centers of Kyoto, Osaka, and later, Edo (Tokyo), Fukuoka gained a distinctive local culture and dialect that has persisted to the present. Fukuoka is the most populous city on Kyūshū island, followed by Kitakyushu. It is the largest city and metropolitan area west of Keihanshin. The city was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Aspect
The continuous and progressive aspects (abbreviated and ) are grammatical aspects that express incomplete action ("to do") or state ("to be") in progress at a specific time: they are non-habitual, imperfective aspects. In the grammars of many languages the two terms are used interchangeably. This is also the case with English: a construction such as ''"He is washing"'' may be described either as ''present continuous'' or as ''present progressive''. However, there are certain languages for which two different aspects are distinguished. In Chinese, for example, ''progressive'' aspect denotes a current action, as in "he is getting dressed", while ''continuous'' aspect denotes a current state, as in "he is wearing fine clothes". As with other grammatical categories, the precise semantics of the aspects vary from language to language, and from grammarian to grammarian. For example, some grammars of Turkish count the -iyor form as a present tense; some as a progressive tense; and som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
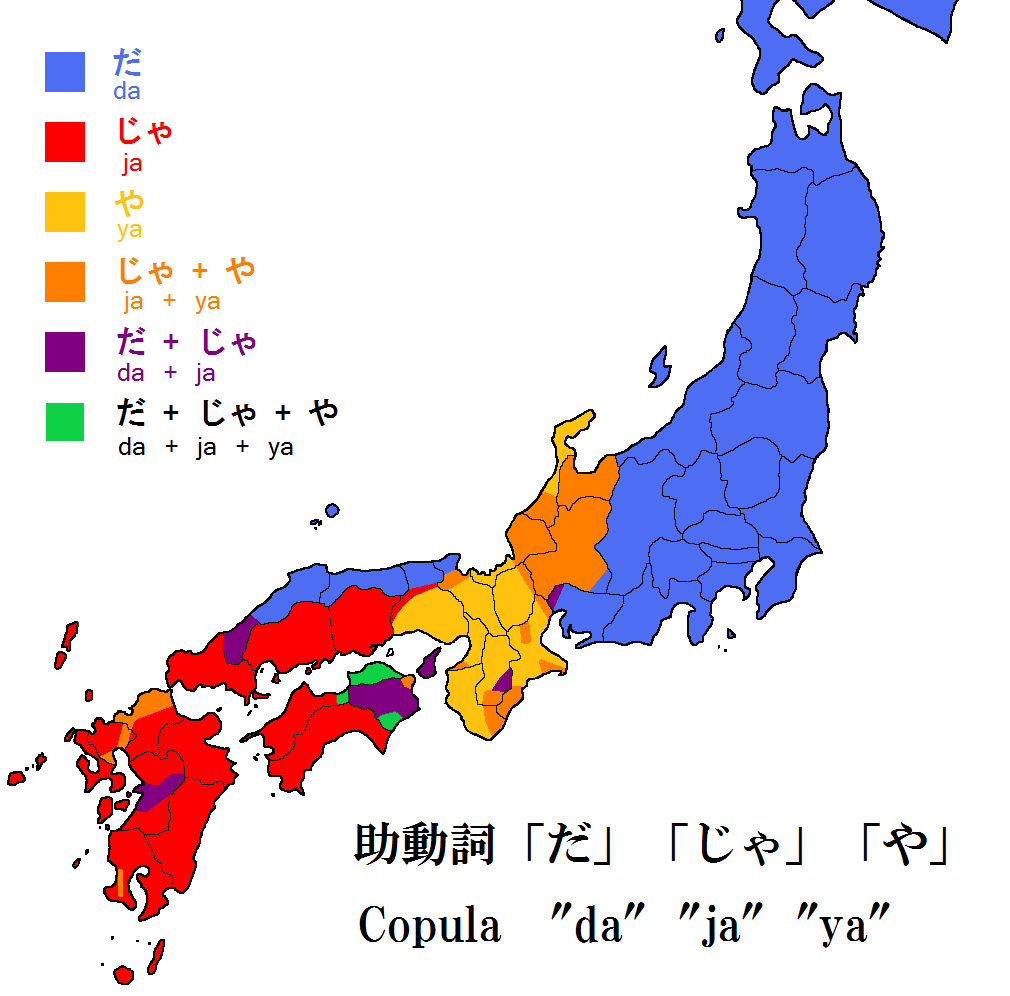
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being co-operative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula, although some (like Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while others have none. In the case of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Adjectives
This article deals with Japanese equivalents of English adjectives. Types of adjective In Japanese, nouns and verbs can modify nouns, with nouns taking the ŃĆ£Ńü« particles when functioning attributively (in the genitive case), and verbs in the attributive form ( ķĆŻõĮōÕĮó ). These are considered separate classes of words, however. Most of the words that can be considered to be adjectives in Japanese fall into one of two categories ŌĆō variants of verbs, and nouns: *adjectival verb (Japanese: ÕĮóÕ«╣Ķ®×, ', literally ÕĮóÕ«╣ "description" or "appearance" + Ķ®× "word"), or ''i''-adjectives :These can be considered specialized verbs, in that they inflect for various aspects such as past tense or negation, and they can be used predicatively to end a sentence, without the need for any other "to be" verb. For example, ' (µÜæŃüä) "hot": ::µÜæŃü䵌ź () ("a hot day") ::õ╗ŖµŚźŃü»µÜæŃüäŃĆé(.) ("Today is hot.") * adjectival noun ( ÕĮóÕ«╣ÕŗĢĶ®×, ', literally ÕĮóÕ«╣ "description" or "app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperative Mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request. The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. To form the imperative mood, use the base form of the verb. They are sometimes called ''directives'', as they include a feature that encodes directive force, and another feature that encodes modality of unrealized interpretation. An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (''you''), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive). Imperative mood can be denoted by the glossing abbreviation . It is one of the irrealis moods. Formation Imperative mood is often expressed using special conjugated verb forms. Like other finite ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Godan And Ichidan Verbs
The Japanese language has two main types of verbs which are referred to as and . Verb groups Categories are important when conjugating Japanese verbs, since conjugation patterns vary according to the verb's category. For example, and belong to different verb categories (godan and ichidan, respectively) and therefore follow different conjugation patterns. Most Japanese verbs are allocated into two categories: # # Statistically, there are far more godan verbs than ichidan verbs. Sometimes categorization is expanded to include a third category of irregular verbsŌĆöwhich most notably include the verbs and . Classical Japanese had more verb groups, such as and , which are archaic in Modern Japanese. Terminology Within the terms and , the numbers and correspond with the number of rows that a verb stem (or inflectional suffix) can span in the goj┼½on kana table. This is best visualized by comparing various verb conjugations to an extracted column of the goj┼½on table: I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichidan
The Japanese language has two main types of verbs which are referred to as and . Verb groups Categories are important when conjugating Japanese verbs, since conjugation patterns vary according to the verb's category. For example, and belong to different verb categories (godan and ichidan, respectively) and therefore follow different conjugation patterns. Most Japanese verbs are allocated into two categories: # # Statistically, there are far more godan verbs than ichidan verbs. Sometimes categorization is expanded to include a third category of irregular verbsŌĆöwhich most notably include the verbs and . Classical Japanese had more verb groups, such as and , which are archaic in Modern Japanese. Terminology Within the terms and , the numbers and correspond with the number of rows that a verb stem (or inflectional suffix) can span in the goj┼½on kana table. This is best visualized by comparing various verb conjugations to an extracted column of the goj┼½on table: In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Verb Conjugation
Japanese verbs, like the verbs of many other languages, can be phonetically modified to change their purpose, nuance or meaning ŌĆō a process known as conjugation. In Japanese, the beginning of a word (the ''stem'') is preserved during conjugation, whilst the ending of the word is altered in some way to change the meaning (this is the ''inflectional suffix''). Japanese verb conjugations are independent of person, number and gender (they do not depend on whether the subject is ''I'', ''you'', ''he'', ''she'', ''we'', etc.); the conjugated forms can express meanings such as negation, present and past tense, volition, passive voice, causation, imperative and conditional mood, and ability. There are also special forms for conjunction with other verbs, and for combination with particles for additional meanings. Japanese verbs have agglutinating properties: some of the conjugated forms are themselves conjugable verbs (or ''i''-adjectives), which can result in several suffixes being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buzen Province
was an old province of Japan in northern Ky┼½sh┼½ in the area of Fukuoka Prefecture and ┼īita Prefecture. It was sometimes called , with Bungo Province. Buzen bordered on Bungo and Chikuzen Provinces. History The ruins of the ancient capital of the province were found near Toyotsu, Fukuoka. The castle town of Kokura was also in Buzen, and a seat of many feudal rulers. During the Meiji period, the provinces of Japan were converted into prefectures. Maps of Japan and Buzen Province were reformed in the 1870s. After the abolition of the clan system in 1871 Buzen Province became Kokura Prefecture for four years until it was absorbed by Fukuoka Prefecture in 1876. At the same time, the province continued to exist for some purposes. For example, Buzen is explicitly recognized in the 1894 treaties with the United States and the United Kingdom. Shrines and temples '' Usa jinj┼½'' was the chief Shinto shrine (''ichinomiya'') of Buzen. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
┼īita Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Ky┼½sh┼½. ┼īita Prefecture has a population of 1,136,245 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 6,340 km2 (2,448 sq mi). ┼īita Prefecture borders Fukuoka Prefecture to the northwest, Kumamoto Prefecture to the southwest, and Miyazaki Prefecture to the south. ┼īita is capital and largest city of ┼īita Prefecture, with other major cities including Beppu, Nakatsu, and Saiki. ┼īita Prefecture is located in the northeast of Ky┼½sh┼½ on the Bungo Channel, connecting the Pacific Ocean and Seto Inland Sea, across from Ehime Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. ┼īita Prefecture is famous for its hot springs and is a popular tourist destination in Japan for its '' onsens'' and '' ryokans'', particularly in and around the city of Beppu. History Around the 6th century Kyushu consisted of four regions: Tsukushi Province, Hi Province, Kumaso Province and Toyo Province. Toyo Province was later divided into two regions, upper and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikugo Province
is the name of a former province of Japan in the area that is today the southern part of Fukuoka Prefecture on Kyūshū. It was sometimes called or , with Chikuzen Province. Chikugo was bordered by Hizen, Chikuzen, Bungo, and Higo Provinces. History The ancient capital of the province was located near the modern city of Kurume, Fukuoka. During the Edo period the province was divided into two fiefs: the Tachibana clan held the southern fief at Yanagawa, and the Arima clan held the northern fief at Kurume. During_the_Meiji_era.html" ;"title="DF 6-7 of 80/nowiki>">DF ... in Sengoku period. --> During the Meiji era">DF 6-7 of 80/nowiki>">DF ... in Sengoku period. --> During the Meiji era, the provinces of Japan were converted into prefectures. Maps of Japan and Chikugo Province were reformed in the 1870s. Timeline * 1359 (''Enbun 4''): Battle of Chikugo River (''Chikugogawa''), Ashikaga gain a military victory. * 1361 (''Enbun 6'') : Imperial forces led by Kikuch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |