|
Chief Garry
Spokane Garry (sometimes spelled Spokan Garry, Spokane: Slough-Keetcha) ( 1811 – 1892) was a Native American leader of the Middle Spokane tribe. He also acted as a liaison between white settlers and American Indian tribes in the area which is now eastern Washington state. Early life and education Slough-Keetcha was born at the junction of the Spokane and the Little Spokane Rivers in or around 1811. He was the son of the tribal chief of the Middle Spokanes, whose name is given by various sources as Illum-Spokanee, Illim-Spokanee"The Treaty Trail, Context for Treatymaking: Biography of Spokan Garry". Washington State Historical Society. and Ileeum Spokanee. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spokane (tribe)
The Spokan or Spokane people are a Native American Plateau tribe who inhabit the eastern portion of present-day Washington state and parts of northern Idaho in the United States of America. The current Spokane Indian Reservation is located in northeastern Washington state, centered at Wellpinit (Sčecuwe). The reservation is located almost entirely in Stevens County, but also includes two small parcels of land (totaling about ) in Lincoln County, including part of the Spokane River. In total, the reservation is about . The city of Spokane, Washington (Sʎˈetkʷ) is named after the tribe. It developed along the Spokane River, within the historic ancestral land of the tribe, but not within the reservation (see map). The Spokane language (Npoqínišcn) belongs to the Interior Salishan language family, being a dialect of Montana Salish. Therefore they are close kin both by language and culture to the neighboring Bitterroot Salish (Flathead) (Tˈatˈʔayaqn) and Pend d'Ore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the portion of the Oregon Territory north of the lower Columbia River and north of the 46th parallel east of the Columbia. At its largest extent, it also included the entirety of modern Idaho and parts of Montana and Wyoming, before attaining its final boundaries in 1863. History Agitation in favor of self-government developed in the regions of the Oregon Territory north of the Columbia River in 1851–1852. A group of prominent settlers from the Cowlitz and Puget Sound regions met on November 25, 1852, at the " Monticello Convention" in present-day Longview, to draft a petition to the United States Congress calling for a separate territory north of the Columbia River. After gaining approval from the Oregon territorial government, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1811 Births
Events January–March * January 8 – An unsuccessful slave revolt is led by Charles Deslondes, in St. Charles and St. James Parishes, Louisiana. * January 17 – Mexican War of Independence – Battle of Calderón Bridge: A heavily outnumbered Spanish force of 6,000 troops defeats nearly 100,000 Mexican revolutionaries. * January 22 – The Casas Revolt begins in San Antonio, Spanish Texas. * February 5 – British Regency: George, Prince of Wales becomes prince regent, because of the perceived insanity of his father, King George III of the United Kingdom. * February 19 – Peninsular War – Battle of the Gebora: An outnumbered French force under Édouard Mortier routs and nearly destroys the Spanish, near Badajoz, Spain. * March 1 – Citadel Massacre in Cairo: Egyptian ruler Muhammad Ali kills the last Mamluk leaders. * March 5 – Peninsular War – Battle of Barrosa: A French attack fails, on a larger Anglo-Portugue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoreline, Washington
Shoreline is a city in King County, Washington, United States. It is located between the city limits of Seattle and the Snohomish County border, approximately north of Downtown Seattle. As of the 2020 census, the population of Shoreline was 58,608, making it the 22nd largest city in the state. Based on per capita income, one of the more reliable measures of affluence, Shoreline ranks 91st of 522 areas in the state of Washington to be ranked. History Shoreline began in 1890 with the platting of the neighborhood of Richmond Beach, on Puget Sound, in anticipation of the arrival of the Great Northern Railway the next year. Over the next two decades, Shoreline was connected to Seattle via the Seattle- Everett Interurban streetcar line (1906) and North Trunk Road (now Aurora Avenue N., State Route 99) (1913), helping to increase its population. The name "Shoreline" was applied to this stretch of unincorporated King County in 1944 when it was given to the school district, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudley C
Dudley is a large market town and administrative centre in the county of West Midlands, England, southeast of Wolverhampton and northwest of Birmingham. Historically an exclave of Worcestershire, the town is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley; in 2011 it had a population of 79,379. The Metropolitan Borough, which includes the towns of Stourbridge and Halesowen, had a population of 312,900. In 2014 the borough council named Dudley as the capital of the Black Country. Originally a market town, Dudley was one of the birthplaces of the Industrial Revolution and grew into an industrial centre in the 19th century with its iron, coal, and limestone industries before their decline and the relocation of its commercial centre to the nearby Merry Hill Shopping Centre in the 1980s. Tourist attractions include Dudley Zoo and Castle, the 12th century priory ruins, and the Black Country Living Museum. History Early history Dudley has a history dating back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestead Act
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of the total area of the United States, was given away free to 1.6 million homesteaders; most of the homesteads were west of the Mississippi River. An extension of the homestead principle in law, the Homestead Acts were an expression of the Free Soil policy of Northerners who wanted individual farmers to own and operate their own farms, as opposed to Southern slave-owners who wanted to buy up large tracts of land and use slave labor, thereby shutting out free white farmers. The first of the acts, the Homestead Act of 1862, opened up millions of acres. Any adult who had never taken up arms against the Federal government of the United States could apply. Women and immigrants who had applied for citizenship were eligible. Several additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Canadian
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French colonists who settled in Canada beginning in the 17th century or to French-speaking or Francophone Canadians of any ethnic origin. During the 17th century, French settlers originating mainly from the west and north of France settled Canada. It is from them that the French Canadian ethnicity was born. During the 17th to 18th centuries, French Canadians expanded across North America and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. As a result people of French Canadian descent can be found across North America. Between 1840 and 1930, many French Canadians immigrated to New England, an event known as the Grande Hémorragie. Etymology French Canadians get their name from '' Canada'', the most developed and densely populated region of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colville Indian Reservation
The Colville Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the northwest United States, in north central Washington, inhabited and managed by the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation, which is federally recognized. Established in 1872, the reservation currently consists of , located primarily in the southeastern section of Okanogan County and the southern half of Ferry County. It also includes other pieces of trust land in eastern Washington, including in Chelan County, just to the northwest of the city of Chelan. The reservation's name is adapted from that of Fort Colville, which was named by British colonists for Andrew Colville, a London governor of the Hudson's Bay Company. The Confederated Tribes have 8,700 descendants from twelve aboriginal tribes. The tribes are known in English as: the Colville, Nespelem, Sanpoil, Lakes (after the Arrow Lakes of British Columbia, or Sinixt), Palus, Wenatchi, Chelan, Entiat, Methow, southern Okanaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
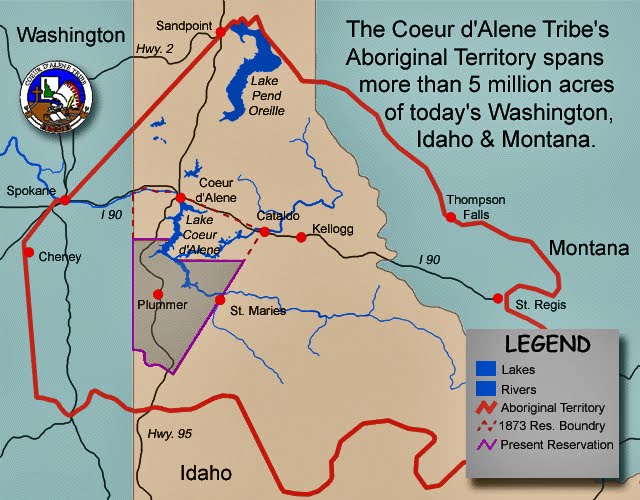
Coeur D'Alene Tribe
The Coeur d'Alene (also ''Skitswish''; natively ''Schi̲tsu'umsh'') are a Native American nation and one of five federally recognized tribes in the state of Idaho. The Coeur d'Alene have sovereign control of their Coeur d'Alene Reservation, which includes a significant portion of Lake Coeur d'Alene and its submerged lands. In '' Idaho v. United States'' (2001), the United States Supreme Court ruled against the state's claim of the submerged lands of the lower third of Lake Coeur d'Alene and related waters of the St. Joe River. It said that the Coeur d'Alene were the traditional owners and that the Executive Branch and Congress had clearly included this area in their reservation, with compensation for ceded territory. This area was designated in 1983 by the Environmental Protection Agency as Bunker Hill Mine and Smelting Complex, the nation's second-largest Superfund site for cleanup. Concerned at the slow pace of progress, in 1991 the tribe filed suit against mining compani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakima River
The Yakima River is a tributary of the Columbia River in south central and eastern Washington state, named for the indigenous Yakama people. Lewis and Clark mention in their journals that the Chin-nâm pam (or the Lower Snake River Chamnapam Nation) called the river ''Tâpe têtt'' (also rendered ''Tapteete''), possibly from the French ''tape-tête'', meaning "head hit". The length of the river from headwaters to mouth is , with an average drop of . It is the longest river entirely in Washington state. Course The river rises in the Cascade Range at an elevation of at Keechelus Dam on Keechelus Lake near Snoqualmie Pass, near Easton. The river flows through that town, skirts Ellensburg, passes the city of Yakima, and continues southeast to Richland, where it flows into the Columbia River creating the Yakima River Delta at an elevation of . About 9 million years ago, the Yakima River flowed south from near Vantage to the Tri-Cities, and then turned west straight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakima War
The Yakima War (1855–1858), also referred to as the Yakima Native American War of 1855 or the Plateau War, was a conflict between the United States and the Yakama, a Sahaptian-speaking people of the Northwest Plateau, then part of Washington Territory, and the tribal allies of each. It primarily took place in the southern interior of present-day Washington. Isolated battles in western Washington and the northern Inland Empire were sometimes separately referred to as the Puget Sound War and the Palouse War, respectively. Background Treaties between the United States and several Indian tribes in the Washington Territory resulted in reluctant tribal recognition of U.S. sovereignty over a vast amount of land in the Washington Territory. The tribes, in return for this recognition, were to receive half of the fish in the territory in perpetuity, awards of money and provisions, and reserved lands where white settlement would be prohibited. While governor Isaac Stevens had guaran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakama
The Yakama are a Native American tribe with nearly 10,851 members, based primarily in eastern Washington state. Yakama people today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribe, the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. Their Yakama Indian Reservation, along the Yakima River, covers an area of approximately 1.2 million acres (5,260 km²). Today the nation is governed by the Yakama Tribal Council, which consists of representatives of 14 tribes. Many Yakama people engage in ceremonial, subsistence, and commercial fishing for salmon, steelhead, and sturgeon in the Columbia River and its tributaries, including within land ceded by the tribe to the United States. Their right to fish in their former territory is protected by treaties and was re-affirmed in late 20th-century court cases such as ''United States v. Washington'' (known as the Boldt Decision, 1974) and ''United States v. Oregon'' (''Sohappy v. Smith'', 1969), though more than a century of U.S. indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |